Abstract
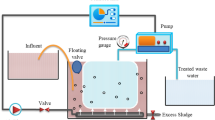
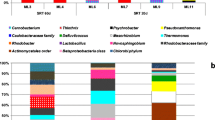
Anaerobic–oxic membrane bioreactor (AOMBR) has been proposed as a highly effective method in municipal and industrial wastewater treatment. In this study, according to the sewage treatment system in a campus, long-term experiments were conducted to assess the impacts of the sludge retention time (SRT) on sludge characteristics and membrane fouling, and the sludge parameters include biomass concentration, particle size distribution, extracellular polymeric substances (EPS), soluble microbial products (SMPs), and specific resistance to filtration (SRF). Our results clearly demonstrated that SRT was one of the most important factors influencing sludge characteristics, and different sludge characteristics resulted in different membrane fouling degrees. A better treatment and filtration performances were observed at the SRT of 30 days compared to two SRTs of 10 and 90 days. Among these parameters, SMP had the most significant correlation with the membrane fouling rate (dTMP/dt), and it had a negative impact on membrane filtration performance. The impact of SRT on membrane fouling process was discussed further by filtration models. At 10 days SRT, the complete-standard blocking model curve had a comparatively higher goodness-of-fit with the fouling process, and at 30 and 90 days SRT, the cake-standard blocking model curve had a relatively higher goodness-of-fit with respective fouling process.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed Z, Cho J, Lim BR, Song KG, Ahn KH (2007) Effects of sludge retention time on membrane fouling and microbial community structure in a membrane bioreactor. J Membr Sci 287:211–218
Bolton G, Lacasse D, Kuriyel R (2006) Combined models of membrane fouling: development and application to microfiltration and ultrafiltration of biological fluids. J Membr Sci 277:75–84
Bouhabila EH, Aim RB, Buisson H (2001) Fouling characterisation in membrane bioreactors. Sep Purif Technol 22:123–132
Buntner D, Spanjers H, van Lier JB (2014) The influence of hydrolysis induced biopolymers from recycled aerobic sludge on specific methanogenic activity and sludge filterability in an anaerobic membrane bioreactor. Water Res 51:284–292
Bura R, Cheung M, Liao B, Finlayson J, Lee BC, Droppo IG, Leppard GG, Liss SN (1998) Composition of extracellular polymeric substances in the activated sludge floc matrix. Water Sci Technol 37:325–333
Chang IS, Kim SN (2005) Wastewater treatment using membrane filtration—effect of biosolids concentration on cake resistance. Process Biochem 40:1307–1314
Cho BD, Fane AG (2002) Fouling transients in nominally subcritical flux operation of a membrane bioreactor. J Membr Sci 209:391–403
Cho JW, Song KG, Lee SH, Ahn KH (2005a) Sequencing anoxic/anaerobic membrane bioreactor (SAM) pilot plant for advanced wastewater treatment. Desalination 178:219–225
Cho JW, Song KG, Yun H, Ahn KH, Kim JY, Chung TH (2005b) Quantitative analysis of biological effect on membrane fouling in submerged membrane bioreactor. Water Sci Technol 51:9–18
Delrue F, Stricker AE, Mietton-Peuchot M, Racault Y (2011) Relationships between mixed liquor properties, operating conditions and fouling on two full-scale MBR plants. Desalination 272:9–19
Dereli RK, Ersahin ME, Ozgun H, Ozturk I, Jeison D, van der Zee F, van Lier JB (2012) Potentials of anaerobic membrane bioreactors to overcome treatment limitations induced by industrial wastewaters. Bioresour Technol 122:160–170
Dereli RK, Grelot A, Heffernan B, van der Zee FP, van Lier JB (2014) Implications of changes in solids retention time on long term evolution of sludge filterability in anaerobic membrane bioreactors treating high strength industrial wastewater. Water Res 59:11–22
Dubois M, Gilles KA, Hamilton JK, Rebers PA, Smith F (1956) Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal Chem 28:350–356
Ersahin ME, Ozgun H, Tao Y, van Lier JB (2014) Applicability of dynamic membrane technology in anaerobic membrane bioreactors. Water Res 48:420–429
Frølund B, Griebe T, Nielsen PH (1995) Enzymatic activity in the activated-sludge floc matrix. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 43:755–761
Geng Z, Hall ER (2007) A comparative study of fouling-related properties of sludge from conventional and membrane enhanced biological phosphorus removal processes. Water Res 41:4329–4338
Han SS, Bae TH, Jang GG, Tak TM (2005) Influence of sludge retention time on membrane fouling and bioactivities in membrane bioreactor system. Process Biochem 40:2393–2400
Hua XF, Wu ZJ, Zhang HX, Lu DN, Wang M, Liu YM, Liu Z (2010) Degradation of hexadecane by Enterobacter cloacae strain TU that secretes an exopolysaccharide as a bioemulsifier. Chemosphere 80:951–956
Huang Z, Ong SL, Ng HY (2011) Submerged anaerobic membrane bioreactor for low-strength wastewater treatment: effect of HRT and SRT on treatment performance and membrane fouling. Water Res 45:705–713
Le-Clech P, Chen V, Fane TAG (2006) Fouling in membrane bioreactors used in wastewater treatment. J Membr Sci 284:17–53
Lee JM, Ahn WY, Lee CH (2001) Comparison of the filtration characteristics between attached and suspended growth microorganisms in submerged membrane bioreactor. Water Res 35:2435–2445
Lee W, Kang S, Shin H (2003) Sludge characteristics and their contribution to microfiltration in submerged membrane bioreactors. J Membr Sci 216:217–227
Liang S, Liu C, Song L (2007) Soluble microbial products in membrane bioreactor operation: behaviors, characteristics, and fouling potential. Water Res 41:95–101
Lubbecke S, Vogelpohl A, Dewjanin W (1995) Wastewater treatment in a biological high-performance system with high biomass concentration. Water Res 29:793–802
Masse A, Sperandio M, Cabassud C (2006) Comparison of sludge characteristics and performance of a submerged membrane bioreactor and an activated sludge process at high solids retention time. Water Res 40:2405–2415
Meng FG, Chae SR, Drews A, Kraume M, Shin HS, Yang FL (2009) Recent advances in membrane bioreactors (MBRs): Membrane fouling and membrane material. Water Res 43:1489–1512
Ng HY, Tan TW, Ong SL (2006) Membrane fouling of submerged membrane bioreactors: impact of mean cell residence time and the contributing factors. Environ Sci Technol 40:2706–2713
Pollice A, Giordano C, Laera G, Saturno D, Mininni G (2007) Physical characteristics of the sludge in a complete retention membrane bioreactor. Water Res 41:1832–1840
Pollice A, Laera G, Saturno D, Giordano C (2008) Effects of sludge retention time on the performance of a membrane bioreactor treating municipal sewage. J Membr Sci 317:65–70
Rosenberger S, Kraume M (2003) Filterability of activated sludge in membrane bioreactors. Desalination 151:195–200
Rosenberger S, Evenblij H, Poele ST, Wintgens T, Laabs C (2005) The importance of liquid phase analyses to understand fouling in membrane assisted activated sludge processes—six case studies of different European research groups. J Membr Sci 263:113–126
Wang XH, Qian JJ, Li XF, Chen K, Ren YP, Hua ZZ (2012) Influences of sludge retention time on the performance of submerged membrane bioreactor with the addition of iron ion. Desalination 296:24–29
Yamato N, Kimura K, Miyoshi T, Watanabe Y (2006) Difference in membrane fouling in membrane bioreactors (MBRs) caused by membrane polymer materials. J Membr Sci 280:911–919
Zhang JS (2007) Membrane fouling mechanism and sustainable operation principle of MBR. Ph.D. dissertation, Dalian University of Technology, pp 122–124
Zhang J, Chua HC, Zhou J, Fane AG (2006) Factors affecting the membrane performance in submerged membrane bioreactors. J Membr Sci 284:54–66
Acknowledgments
This work was kindly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 51378330).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 268 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Yue, X., Liu, Z. et al. Impacts of sludge retention time on sludge characteristics and membrane fouling in a submerged anaerobic–oxic membrane bioreactor. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99, 4893–4903 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6383-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6383-x