Abstract
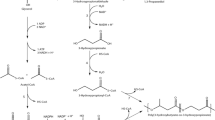
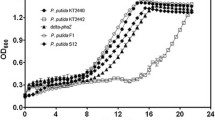
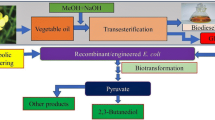
Ralstonia eutropha H16 is a well-studied bacterium with respect to biosynthesis of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs), which has attracted attentions as biodegradable bio-based plastics. However, this strain shows quite poor growth on glycerol of which bulk supply has been increasing as a major by-product of biodiesel industries. This study examined enhancement of glycerol assimilation ability of R. eutropha H16 by introduction of the genes of aquaglyceroporin (glpF) and glycerol kinase (glpK) from Escherichia coli. Although introduction of glpFK Ec into the strain H16 using a multi-copy vector was not successful, a recombinant strain possessing glpFK Ec within the chromosome showed much faster growth on glycerol than H16. Further analyses clarified that weak expression of glpK Ec alone allowed to establish efficient glycerol assimilation pathway, indicating that the poor growth of H16 on glycerol was caused by insufficient kination activity to glycerol, as well as this strain had a potential ability for uptake of extracellular glycerol. The engineered strains expressing glpFK Ec or glpK Ec produced large amounts of poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate] [P(3HB)] from glycerol with much higher productivity than H16. Unlike other glycerol-utilizable wild strains of R. eutropha, the H16-derived engineered strains accumulated P(3HB) with no significant decrease in molecular weights on glycerol, and the polydispersity index of the glycerol-based P(3HB) synthesized by the strains expressing glpFK Ec was lower than those by the parent strains. The present study demonstrated possibility of R. eutropha H16-based platform for production of useful compounds from inexpensive glycerol.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Austin D, Larson TJ (1991) Nucleotide sequence of the glpD gene encoding aerobic sn-glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogenase of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol 173:101–107
Brigham CJ, Speth DR, Rha C, Sinskey AJ (2012) Whole-genome microarray and gene deletion studies reveal regulation of the polyhydroxyalkanoate production cycle by the stringent response in Ralstonia eutropha H16. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:8033–8044
Budde CF, Riedel SL, Willis LB, Rha C, Sinskey AJ (2011) Production of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) from plant oil by engineered Ralstonia eutropha strains. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:2847–2854
Cavalheiro JMBT, de Almeida MCMD, Grandfils C, da Fonseca MMR (2009) Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) production by Cupriavidus necator using waste glycerol. Process Biochem 44:509–515
Cavalheiro JM, Raposo RS, de Almeida MC, Cesario MT, Sevrin C, Grandfils C, da Fonseca MM (2012) Effect of cultivation parameters on the production of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate) and poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-4-hydroxybutyrate-3-hydroxyvalerate) by Cupriavidus necator using waste glycerol. Bioresour Technol 111:391–397
Dobson R, Gray V, Rumbold K (2012) Microbial utilization of crude glycerol for the production of value-added products. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 39:217–226
Durnin G, Clomburg J, Yeates Z, Alvarez PJ, Zygourakis K, Campbell P, Gonzalez R (2009) Understanding and harnessing the microaerobic metabolism of glycerol in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Bioeng 103:148–161
Freedberg WB, Kistler WS, Lin EC (1971) Lethal synthesis of methylglyoxal by Escherichia coli during unregulated glycerol metabolism. J Bacteriol 108:137–144
Fukui T, Chou K, Harada K, Orita I, Nakayama Y, Bamba T, Nakamura S, Fukusaki E (2014) Metabolite profiles of polyhydroxyalkanoate-producing Ralstonia eutropha H16. Metabolomics 10:190–202
Garcia IL, Lopez JA, Dorado MP, Kopsahelis N, Alexandri M, Papanikolaou S, Villar MA, Koutinas AA (2013) Evaluation of by-products from the biodiesel industry as fermentation feedstock for poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) production by Cupriavidus necator. Bioresour Technol 130:16–22
Hiroe A, Hyakutake M, Thomson NM, Sivaniah E, Tsuge T (2013) Endogenous ethanol affects biopolyester molecular weight in recombinant Escherichia coli. ACS Chem Biol 8:2568–2576
Insomphun C, Mifune J, Orita I, Numata K, Nakamura S, Fukui T (2013) Modification of β-oxidation pathway in Ralstonia eutropha for production of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) from soybean oil. J Biosci Bioeng 117:184–190
Kaddor C, Steinbuchel A (2011) Implications of various phosphoenolpyruvate-carbohydrate phosphotransferase system mutations on glycerol utilization and poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) accumulation in Ralstonia eutropha H16. AMB Express 1:16
Kato M, Bao HJ, Kang CK, Fukui T, Doi Y (1996) Production of a novel copolyester of 3-hydroxybutyric acid and medium chain length 3-hydroxyalkanaic acids by Pseudomonas sp. 61-3 from sugars. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 45:363–370
Kawashima Y, Cheng W, Mifune J, Orita I, Nakamura S, Fukui T (2012) Characterization and functional analyses of R-specific enoyl coenzyme A hydratases in polyhydroxyalkanoate-producing Ralstonia eutropha. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:493–502
Keshavarz T, Roy I (2010) Polyhydroxyalkanoates: bioplastics with a green agenda. Curr Opin Microbiol 13:321–326
Loo CY, Lee WH, Tsuge T, Doi Y, Sudesh K (2005) Biosynthesis and characterization of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) from palm oil products in a Wautersia eutropha mutant. Biotechnol Lett 27:1405–1410
Lu J, Brigham CJ, Gai CS, Sinskey AJ (2012) Studies on the production of branched-chain alcohols in engineered Ralstonia eutropha. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 96:283–297
Lu J, Brigham CJ, Rha C, Sinskey AJ (2013) Characterization of an extracellular lipase and its chaperone from Ralstonia eutropha H16. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:2443–2454
Madden LA, Anderson AJ, Shah DT, Asrar J (1999) Chain termination in polyhydroxyalkanoate synthesis: involvement of exogenous hydroxy-compounds as chain transfer agents. Int J Biol Macromol 25:43–53
Meiswinkel TM, Rittmann D, Lindner SN, Wendisch VF (2013) Crude glycerol-based production of amino acids and putrescine by Corynebacterium glutamicum. Bioresour Technol 145:254–258
Mifune J, Nakamura S, Fukui T (2008) Targeted engineering of Cupriavidus necator chromosome for biosynthesis of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) from vegetable oil. Can J Chem 86:621–627
Mifune J, Nakamura S, Fukui T (2010) Engineering of pha operon on Cupriavidus necator chromosome for efficient biosynthesis of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) from vegetable oil. Polym Degrad Stab 95:1305–1312
Mothes G, Schnorpfeil C, Ackermann JU (2007) Production of PHB from crude glycerol. Eng Life Sci 7:475–479
Mukoyama M (2007) Method of imparting glycerol-assimilation ability to bacterium. International Patent Publication WO2007/013695
Nikodinovic-Runic J, Guzik M, Kenny ST, Babu R, Werker A, O’Connor KE (2013) Carbon-rich wastes as feedstocks for biodegradable polymer (polyhydroxyalkanoate) production using bacteria. Adv Appl Microbiol 84:139–200
Orita I, Iwazawa R, Nakamura S, Fukui T (2011) Identification of mutation points in Cupriavidus necator NCIMB 11599 and genetic reconstitution of glucose-utilization ability in wild strain H16 for polyhydroxyalkanoate production. J Biosci Bioeng 113:63–69
Pan P, Inoue Y (2009) Polymorphism and isomorphism in biodegradable polyesters. Prog Polym Sci 34:605–640
Peplinski K, Ehrenreich A, Doring C, Bomeke M, Reinecke F, Hutmacher C, Steinbuchel A (2010) Genome-wide transcriptome analyses of the 'Knallgas' bacterium Ralstonia eutropha H16 with regard to polyhydroxyalkanoate metabolism. Microbiology 156:2136–2152
Pohlmann A, Fricke WF, Reinecke F, Kusian B, Liesegang H, Cramm R, Eitinger T, Ewering C, Potter M, Schwartz E, Strittmatter A, Voss I, Gottschalk G, Steinbuchel A, Friedrich B, Bowien B (2006) Genome sequence of the bioplastic-producing "Knallgas" bacterium Ralstonia eutropha H16. Nat Biotechnol 24:1257–1262
Raberg M, Peplinski K, Heiss S, Ehrenreich A, Voigt B, Doring C, Bomeke M, Hecker M, Steinbuchel A (2011) Proteomic and transcriptomic elucidation of the mutant Ralstonia eutropha G+1 with regard to glucose utilization. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:2058–2070
Raberg M, Kaddor C, Kusian B, Stahlhut G, Budinova R, Kolev N, Bowien B, Steinbuchel A (2012) Impact of each individual component of the mutated PTSNag on glucose uptake and phosphorylation in Ralstonia eutropha G+1. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 95:735–744
Riedel SL, Bader J, Brigham CJ, Budde CF, Yusof ZA, Rha C, Sinskey AJ (2011) Production of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) by Ralstonia eutropha in high cell density palm oil fermentations. Biotechnol Bioeng 109:74–83
Rittmann D, Lindner SN, Wendisch VF (2008) Engineering of a glycerol utilization pathway for amino acid production by Corynebacterium glutamicum. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:6216–6222
Schafer A, Tauch A, Jager W, Kalinowski J, Thierbach G, Puhler A (1994) Small mobilizable multi-purpose cloning vectors derived from the Escherichia coli plasmids pK18 and pK19: selection of defined deletions in the chromosome of Corynebacterium glutamicum. Gene 145:69–73
Shimizu R, Chou K, Orita I, Suzuki Y, Nakamura S, Fukui T (2013) Detection of phase-dependent transcriptomic changes and Rubisco-mediated CO2 fixation into poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) under heterotrophic condition in Ralstonia eutropha H16 based on RNA-seq and gene deletion analyses. BMC Microbiol 13:169
Sichwart S, Hetzler S, Broker D, Steinbuchel A (2011) Extension of the substrate utilization range of Ralstonia eutropha strain H16 by metabolic engineering to include mannose and glucose. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:1325–1334
Simon R, Priefer U, Pühler A (1983) A broad host range mobilization system for in vivo genetic engineering. Transposon mutagenesis in Gram negative bacteria. Bio/Technology 1:784–791
Spoljaric IV, Lopar M, Koller M, Muhr A, Salerno A, Reiterer A, Horvat P (2013a) In silico optimization and low structured kinetic model of poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate] synthesis by Cupriavidus necator DSM 545 by fed-batch cultivation on glycerol. J Biotechnol 168:625–635
Spoljaric IV, Lopar M, Koller M, Muhr A, Salerno A, Reiterer A, Malli K, Angerer H, Strohmeier K, Schober S, Mittelbach M, Horvat P (2013b) Mathematical modeling of poly[(R)-3-hydroxyalkanoate] synthesis by Cupriavidus necator DSM 545 on substrates stemming from biodiesel production. Bioresour Technol 133:482–494
Taguchi S, Iwata T, Abe H, Doi Y (2012) Poly(hydroxyalkanoate)s. In: Matyjaszewski K, Möller M (eds) Polymer science: a comprehensive reference. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 157–182
Taidi B, Anderson AJ, Dawes EA, Byrom D (1994) Effect of carbon source and concentration on the molecular mass of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) produced by Methylobacterium extorquens and Alcaligenes eutrophus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 40:786–790
Tanadchangsaeng N, Yu J (2012) Microbial synthesis of polyhydroxybutyrate from glycerol: gluconeogenesis, molecular weight and material properties of biopolyester. Biotechnol Bioeng 109:2808–2818
Tomizawa S, Saito Y, Hyakutake M, Nakamura Y, Abe H, Tsuge T (2010) Chain transfer reaction catalyzed by various polyhydroxyalkanoate synthases with poly(ethylene glycol) as an exogenous chain transfer agent. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 87:1427–1435
Tomizawa S, Sato S, Lan JC, Nakamura Y, Abe H, Tsuge T (2013) In vitro evidence of chain transfer to tetraethylene glycols in enzymatic polymerization of polyhydroxyalkanoate. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:4821–4829
Tsuge T, Watanabe S, Shimada D, Abe H, Doi Y, Taguchi S (2007) Combination of N149S and D171G mutations in Aeromonas caviae polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase and impact on polyhydroxyalkanoate biosynthesis. FEMS Microbiol Lett 277:217–222
Verlinden RA, Hill DJ, Kenward MA, Williams CD, Radecka I (2007) Bacterial synthesis of biodegradable polyhydroxyalkanoates. J Appl Microbiol 102:1437–1449
Wang Y, Schulten K, Tajkhorshid E (2005) What makes an aquaporin a glycerol channel? A comparative study of AqpZ and GlpF. Structure 13:1107–1118
Weissenborn DL, Wittekindt N, Larson TJ (1992) Structure and regulation of the glpFK operon encoding glycerol diffusion facilitator and glycerol kinase of Escherichia coli K-12. J Biol Chem 267:6122–6131
Yang F, Hanna MA, Sun R (2012) Value-added uses for crude glycerol—a byproduct of biodiesel production. Biotechnol Biofuels 5:13
Zhu MM, Skraly FA, Cameron DC (2001) Accumulation of methylglyoxal in anaerobically grown Escherichia coli and its detoxification by expression of the Pseudomonas putida glyoxalase I gene. Metab Eng 3:218–225
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Assoc. Prof. Takeharu Tsuge and Dr. Ayaka Hiroe (Department of Innovative and Engineered Materials, Tokyo Institute of Technology, Japan) for GPC analysis. This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI grant number 25292058.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Table S1
(PDF 110 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fukui, T., Mukoyama, M., Orita, I. et al. Enhancement of glycerol utilization ability of Ralstonia eutropha H16 for production of polyhydroxyalkanoates. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98, 7559–7568 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5831-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5831-3