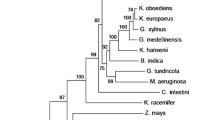
Abstract
Phosphoketolases (PKs) are large thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP)-dependent enzymes playing key roles in a number of essential pathways of carbohydrate metabolism. The putative PK genes of Lactococcus lactis (Ll) and Leuconostoc mesenteroides (Lm) were cloned in a prokaryotic vector, and the encoded proteins were expressed and purified yielding high purity proteins termed PK-Ll and PK-Lm, respectively. Similarly, the PK gene of Pseudomonas aeruginosa was expressed, and the corresponding protein (PK-Pa) was purified to homogeneity. The amino acid sequences predicted on the basis of genes’ nucleotide sequences were confirmed by mass spectrometry and display low relative similarities. Circular dichroism (CD) spectra of these proteins predict higher α-helix than β-strand contents. In addition, it is predicted that PK-Ll contains tightly packed domains. Enzymatic analysis showed that all three recombinant proteins, despite their dissimilar amino acid sequences, are active PKs and accept both xylulose 5-phosphate (X5P) and fructose 6-phosphate (F6P) as substrates. However, they display substantially higher preference for X5P than for F6P. Kinetic measurements indicated that PK-Pa has the lowest K m values for X5P and F6P suggesting the highest capacity for substrate binding. PK-Ll has the largest k cat values for both substrates. Nevertheless, in terms of substrate specificity constant, PK-Pa has been found to be the most active PK against X5P. Structural models for all three analysed PKs predict similar folds in spite of amino acid sequence dissimilarities and contribute to understanding the enzymatic peculiarities of PK-Pa compared to PK-Ll and PK-Lm.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrade MA, Chacon P, Merelo JJ, Moran F (1993) Evaluation of secondary structure of proteins from UV circular dichroism using an unsupervised learning neural network. Protein Eng 6:383–390
Bagos PG, Tsirigos KD, Liakopoulos TD, Hamodrakas SJ (2008) Prediction of lipoprotein signal peptides in Gram-positive bacteria with a Hidden Markov Model. J Proteome Res 7(12):5082–5093. doi:10.1021/pr800162c
Bolotin A, Wincker P, Mauger S, Jaillon O, Malarme K, Weissenbach J, Ehrlich SD, Sorokin A (2001) The complete genome sequence of the lactic acid bacterium Lactococcus lactis ssp. lactis IL1403. Genome Res 11(5):731–753. doi:10.1101/gr.169701
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Chinen A, Kozlov YI, Hara Y, Izui H, Yasueda H (2007) Innovative metabolic pathway design for efficient l-glutamate production by suppressing CO2 emission. J Biosci Bioeng 103(3):262–269. doi:10.1263/jbb.103.262
Compton LA, Johnson WC Jr (1986) Analysis of protein circular dichroism spectra for secondary structure using a simple matrix multiplication. Anal Biochem 155:155–167
Dereeper A, Guignon V, Blanc G, Audic S, Buffet S, Chevenet F, Dufayard JF, Guindon S, Lefort V, Lescot M, Claverie JM, Gascuel O (2008) Phylogeny.fr: robust phylogenetic analysis for the non-specialist. Nucleic Acids Res 36(Web Server issue):W465–W469. doi:10.1093/nar/gkn180
Duggleby RG (2006) Domain relationships in thiamine diphosphate-dependent enzymes. Acc Chem Res 39(8):550–557. doi:10.1021/ar068022z
Emsley P, Lohkamp B, Scott WG, Cowtan K (2010) Features and development of Coot. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 66(Pt 4):486–501. doi:10.1107/S0907444910007493
Erlandson KA, Park JH, El Wissam K, Kao HH, Basaran P, Brydges S, Batt CA (2000) Dissolution of xylose metabolism in Lactococcus lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol 66(9):3974–3980
Fleige C, Kroll J, Steinbuchel A (2011) Establishment of an alternative phosphoketolase-dependent pathway for fructose catabolism in Ralstonia eutropha H16. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 91(3):769–776. doi:10.1007/s00253-011-3284-5
Fushinobu S (2010) Unique sugar metabolic pathways of Bifidobacteria. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 74(12):2374–2384
Gille C, Frommel C (2001) STRAP: editor for STRuctural Alignments of Proteins. Bioinformatics 17(4):377–378
Goldberg ML, Racker E (1962) Formation and isolation of a glycolaldehyde-phosphoketolase intermediate. J Biol Chem 237:3841–3842
Gouet P, Robert X, Courcelle E (2003) ESPript/ENDscript: extracting and rendering sequence and 3D information from atomic structures of proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 31(13):3320–3323
Greenfield NJ (1999) Applications of circular dichroism in protein and peptide analysis. Trends Anal Chem 18:236–244
Heath EC, Hurwitz J, Horecker BL, Ginsburg A (1958) Pentose fermentation by Lactobacillus plantarum. I. The cleavage of xylulose 5-phosphate by phosphoketolase. J Biol Chem 231(2):1009–1029
Hofvendahl K, Hahn-Hagerdal B (2000) Factors affecting the fermentative lactic acid production from renewable resources(1). Enzym Microb Technol 26(2–4):87–107
Horecker BL, Smyrniotis PZ, Klenow H (1953) The formation of sedoheptulose phosphate. J Biol Chem 205(2):661–682
Imperi F, Ciccosanti F, Perdomo AB, Tiburzi F, Mancone C, Alonzi T, Ascenzi P, Piacentini M, Visca P, Fimia GM (2009) Analysis of the periplasmic proteome of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a metabolically versatile opportunistic pathogen. Proteomics 9(7):1901–1915. doi:10.1002/pmic.200800618
Jeong DW, Lee JM, Lee HJ (2007) Cloning and characterization of a gene encoding phosphoketolase in a Lactobacillus paraplantarum isolated from Kimchi. J Microbiol Biotechnol 17(5):822–829
Kelly SM, Price NC (2000) The use of circular dichroism in the investigation of protein structure and function. Curr Protein Pept Sci 1:349–384
Lee JM, Jeong DW, Koo OK, Kim MJ, Lee JH, Chang HC, Kim JH, Lee HJ (2005) Cloning and characterization of the gene encoding phosphoketolase in Leuconostoc mesenteroides isolated from kimchi. Biotechnol Lett 27(12):853–858. doi:10.1007/s10529-005-6718-2
Lees JG, Miles AJ, Wien F, Wallace BA (2006) A reference database for circular dichroism spectroscopy covering fold and secondary structure space. Bioinformatics 22:1955–1962
Makarova K, Slesarev A, Wolf Y, Sorokin A, Mirkin B, Koonin E, Pavlov A, Pavlova N, Karamychev V, Polouchine N, Shakhova V, Grigoriev I, Lou Y, Rohksar D, Lucas S, Huang K, Goodstein DM, Hawkins T, Plengvidhya V, Welker D, Hughes J, Goh Y, Benson A, Baldwin K, Lee JH, Diaz-Muniz I, Dosti B, Smeianov V, Wechter W, Barabote R, Lorca G, Altermann E, Barrangou R, Ganesan B, Xie Y, Rawsthorne H, Tamir D, Parker C, Breidt F, Broadbent J, Hutkins R, O’Sullivan D, Steele J, Unlu G, Saier M, Klaenhammer T, Richardson P, Kozyavkin S, Weimer B, Mills D (2006) Comparative genomics of the lactic acid bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103(42):15611–15616. doi:10.1073/pnas.0607117103
Mao D, Wachter E, Wallace BA (1982) Folding of the mitochondrial proton adenosine triphosphatase proteolipid channel in phospholipid vesicles. Biochemistry 21:4960–4968
Meile L, Rohr LM, Geissmann TA, Herensperger M, Teuber M (2001) Characterization of the d-xylulose 5-phosphate/d-fructose 6-phosphate phosphoketolase gene (xfp) from Bifidobacterium lactis. J Bacteriol 183(9):2929–2936. doi:10.1128/JB.183.9.2929-2936.2001
Nagy CI, Lupan I, Ferencz BK, Popescu O (2007) Cloning and expression of the gene encoding phosphoketolase in Pseudomonas aeruginosa 15442. Ann West Univ Timisoara Ser Chem 16(3):73–80
Noda-Garcia L, Camacho-Zarco AR, Medina-Ruiz S, Gaytan P, Carrillo-Tripp M, Fulop V, Barona-Gomez F (2013) Evolution of substrate specificity in a recipient’s enzyme following horizontal gene transfer. Mol Biol Evol 30(9):2024–2034. doi:10.1093/molbev/mst115
Orban JI, Patterson JA (2000) Modification of the phosphoketolase assay for rapid identification of Bifidobacteria. J Microbiol Methods 40(3):221–224
Panagiotou G, Andersen MR, Grotkjaer T, Regueira TB, Hofmann G, Nielsen J, Olsson L (2008) Systems analysis unfolds the relationship between the phosphoketolase pathway and growth in Aspergillus nidulans. PLoS One 3(12):e3847. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0003847
Petrareanu G, Balasu MC, Zander U, Scheidig AJ, Szedlacsek SE (2010) Preliminary X-ray crystallographic analysis of the D-xylulose 5-phosphate phosphoketolase from Lactococcus lactis. Acta Crystallogr F 66(7):805–807
Posthuma CC, Bader R, Engelmann R, Postma PW, Hengstenberg W, Pouwels PH (2002) Expression of the xylulose 5-phosphate phosphoketolase gene, xpkA, from Lactobacillus pentosus MD363 is induced by sugars that are fermented via the phosphoketolase pathway and is repressed by glucose mediated by CcpA and the mannose phosphoenolpyruvate phosphotransferase system. Appl Environ Microbiol 68(2):831–837
Provencher SW, Glockner J (1981) Estimation of globular protein secondary structure from circular dichroism. Biochemistry 20:33–37
Racker E (1962) Fructose 6-phosphate phosphoketolase from Acetobacter xylinum. Methods Enzymol 5:276–280
Rohr LM, Teuber M, Meile L (2002) Phosphoketolase, a neglected enzyme of microbial carbohydrate metabolism. Chimia 56:270–273
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4(4):406–425
Sanchez B, Zuniga M, Gonzalez-Candelas F, de los Reyes-Gavilan CG, Margolles A (2010) Bacterial and eukaryotic phosphoketolases: phylogeny, distribution and evolution. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 18(1):37–51. doi:10.1159/000274310
Schorken U, Sprenger GA (1998) Thiamin-dependent enzymes as catalysts in chemoenzymatic syntheses. Biochim Biophys Acta 1385(2):229–243
Shevchenko A, Tomas H, Havlis J, Olsen JV, Mann M (2006) In-gel digestion for mass spectrometric characterization of proteins and proteomes. Nat Protoc 1(6):2856–2860. doi:10.1038/nprot.2006.468
Sreerama N, Woody RW (2000) Estimation of protein secondary structure from CD spectra: comparison of CONTIN, SELCON and CDSSTR methods with an expanded reference set. Anal Biochem 282:252–260
Suzuki R, Katayama T, Kim BJ, Wakagi T, Shoun H, Ashida H, Yamamoto K, Fushinobu S (2010) Crystal structures of phosphoketolase: thiamine diphosphate-dependent dehydration mechanism. J Biol Chem 285(44):34279–34287. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.156281
Takahashi K, Tagami U, Shimba N, Kashiwagi T, Ishikawa K, Suzuki E (2010) Crystal structure of Bifidobacterium longum phosphoketolase; key enzyme for glucose metabolism in Bifidobacterium. FEBS Lett 584(18):3855–3861. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2010.07.043
Tanaka K, Komiyama A, Sonomoto K, Ishizaki A, Hall SJ, Stanbury PF (2002) Two different pathways for D-xylose metabolism and the effect of xylose concentration on the yield coefficient of L-lactate in mixed-acid fermentation by the lactic acid bacterium Lactococcus lactis IO-1. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 60(1–2):160–167. doi:10.1007/s00253-002-1078-5
Termine E, Michel GP (2009) Transcriptome and secretome analyses of the adaptive response of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to suboptimal growth temperature. Int Microbiol 12(1):7–12
Veiga-da-Cunha M, Santos H, Van Schaftingen E (1993) Pathway and regulation of erythritol formation in Leuconostoc oenos. J Bacteriol 175(13):3941–3948
Werner G, Fleige C, Geringer U, van Schaik W, Klare I, Witte W (2011) IS element IS16 as a molecular screening tool to identify hospital-associated strains of Enterococcus faecium. BMC Infect Dis 11:80. doi:10.1186/1471-2334-11-80
Whitmore L, Wallace BA (2004) DICHROWEB: an online server for protein secondary structure analyses from circular dichroism spectroscopic data. Nucleic Acids Res 32:W668–W673
Whitmore L, Wallace BA (2009) Advances in biomedical spectroscopy—modern techniques for circular dichroism and synchrotron radiation circular dichroism spectroscopy, vol 1. IOS Press, Amsterdam
Widmann M, Radloff R, Pleiss J (2010) The Thiamine diphosphate dependent Enzyme Engineering Database: a tool for the systematic analysis of sequence and structure relations. BMC Biochem 11:9. doi:10.1186/1471-2091-11-9
Yevenes A, Frey PA (2008) Cloning, expression, purification, cofactor requirements, and steady state kinetics of phosphoketolase-2 from Lactobacillus plantarum. Bioorg Chem 36(3):121–127. doi:10.1016/j.bioorg.2008.03.002
Yuan J, Zhu L, Liu X, Li T, Zhang Y, Ying T, Wang B, Wang J, Dong H, Feng E, Li Q, Wang J, Wang H, Wei K, Zhang X, Huang C, Huang P, Huang L, Zeng M, Wang H (2006) A proteome reference map and proteomic analysis of Bifidobacterium longum NCC2705. Mol Cell Proteomics 5(6):1105–1118. doi:10.1074/mcp.M500410-MCP200
Zamfir M, Vancanneyt M, Makras L, Vaningelgem F, Lefebvre K, Pot B, Swings J, De Vuyst L (2006) Biodiversity of lactic acid bacteria in Romanian dairy products. Syst Appl Microbiol 29(6):487–495. doi:10.1016/j.syapm.2005.10.002
Zhang Y (2008) I-TASSER server for protein 3D structure prediction. BMC Bioinforma 9:40. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-9-40
Zhang J, Liu YJ (2013) Computational studies on the catalytic mechanism of phosphoketolase. Comput Theor Chem 1025:1–7. doi:10.1016/j.comptc.2013.09.026
Zhao J, Xu L, Wang Y, Zhao X, Wang J, Garza E, Manow R, Zhou S (2013) Homofermentative production of optically pure L-lactic acid from xylose by genetically engineered Escherichia coli B. Microb Cell Factories 12:57. doi:10.1186/1475-2859-12-57
Acknowledgement
We are deeply indebted to Octavian Bârzu for the initial research idea of the research project behind this manuscript. We are grateful to Alexei Sorokin (Institut National de la Recherche Agronomique, Jouy en Josas, France) for the L. lactis genomic fragment containing the PK-Ll gene, to Medana Zamfir for the L. mesenteroides strain (Institute of Biology of the Romanian Academy, Bucharest, Romania) and to Octavian Popescu (University Babes-Bolyai, Cluj Napoca, Romania) for the pET28b-PK vector containing the PK-Pa gene. We thank Mihaela Mentel for her kind help during manuscript editing. G.P., M.B., A.V and S.S. work was supported by grants from BIOTECH, CNMP, CNCSIS, European Social Fund, Alexander von Humboldt Foundation, Romanian National Authority for Scientific Research CNCS–UEFISCDI, projects 02-2-PED-427, CEEX 1/2005, PN-II-ID-PCE-210/2007, POSDRU/89/1.5/S/60746, PN-II-PT-PCCA- 79/2012 and by the Romanian Academy project no. 5 of the Institute of Biochemistry of the Romanian Academy. C.V.A.M. acknowledges support from Romanian National Authority for Scientific Research CNCS–UEFISCDI, project code PN-II-ID-PCE-2011-3-0342 no. 181/2011 for mass spectrometry work. Circular dichroism determinations were supported by a grant of the Romanian National Authority for Scientific Research, CNCS–UEFISCDI, project PN-II-RU-TE-2011-3-0281.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Georgiana Petrareanu and Mihaela C. Balasu contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 50 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Petrareanu, G., Balasu, M.C., Vacaru, A.M. et al. Phosphoketolases from Lactococcus lactis, Leuconostoc mesenteroides and Pseudomonas aeruginosa: dissimilar sequences, similar substrates but distinct enzymatic characteristics. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98, 7855–7867 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5723-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5723-6