Abstract
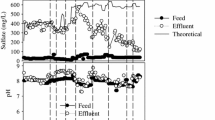
The biological degradation of nitrate and sulfate was investigated using a mixed microbial culture and lactate as the carbon source, with or without limited-oxygen fed. It was found that sulfate reduction was slightly inhibited by nitrate, since after nitrate depletion the sulfate reduction rate increased from 0.37 mg SO4 2−/mg VSS d to 0.71 mg SO4 2−/mg VSS d, and the maximum rate of sulfate reduction in the presence of nitrate corresponded to 56 % of the non-inhibited sulfate reduction rate determined after nitrate depleted. However, simultaneous but not sequential reduction of both oxy-anions was observed in this study, unlike some literature reports in which sulfate reduction starts only after depletion of nitrate, and this case might be due to the fact that lactate was always kept above the limiting conditions. At limited oxygen, the inhibited effect on sulfate reduction by nitrate was relieved, and the sulfate reduction rate seemed relatively higher than that obtained without limited-oxygen fed, whereas kept almost constant (0.86–0.89 mg SO4 2−/mg VSS d) cross the six ROS states. In contrast, nitrate reduction rates decreased substantially with the increase in the initial limited-oxygen fed, showing an inhibited effect on nitrate reduction by oxygen. Kinetic parameters determined for the mixed microbial culture showed that the maximum specific sulfate utilization rate obtained (0.098 ± 0.022 mg SO4 2−/(mg VSS h)) was similar to the reported typical value (0.1 mg SO4 2−/(mg VSS h)), also indicating a moderate inhibited effect by nitrate.





Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association & Water Pollution Control Federation (APHA, AWWA & WPCF) (1995) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. In: Eaton AD, Clesceri LS, Greenberg AE (Eds.), Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. Port City, Baltimore
An SJ, Stone H, Nemati M (2011) Biological removal of nitrate by an oil reservoir culture capable of autotrophic and heterotrophic activities: kinetic evaluation and modeling of the heterotrophic process. J Hazard Mater 190:686–693
Bell LC, Richardson DJ, Ferguson SJ (1990) Periplasmic and membrane-bound respiratory nitrate reductases in Thiosphaera pantotropha. FEMS Lett 265:85–87
Celis-Garcia LB, Gonzalez-Blanco G, Meraz M (2008) Removal of sulfur inorganic compounds by a biofilm of sulfate reducing and sulfide oxidizing bacteria in a down-flow fluidized bed reactor. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 83:260–268
Chen YR, Hashimoto AG (1980) Substrate utilization kinetic model for biological treatment processes. Biotechnol Bioeng 22:2081–2095
Chen C, Ren NQ, Wang AJ, Yu ZG, Lee DJ (2008) Microbial community of granules in expanded granular sludge bed reactor for simultaneous biological removal of sulfate, nitrate and lactate. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 79:1071–1077
Dannenberg S, Kroder M, Dilling W, Cypionka H (1992) Oxidation of H2, organic compounds and inorganic sulfur compounds coupled to reduction of O2 or nitrate by sulfate-reducing bacteria. Arch Microbiol 158:93–99
European Community (EC) (1980) Council directive of 15 July 1980 relating to the quality of water intended for human consumption. Off J Eur Commun 23(L229):11
Gal H, Ronen Z, Weisbrod N, Dahan O, Ronit N (2008) Perchlorate biodegradation in contaminated soils and the deep unsaturated zone. Soil Biol Biochem 40:1751–1757
Garica de Lomas J, Corzo A, Gonzalez JM, Andrades JA, Iglesias E, Montero MJ (2006) Nitrate promotes biological oxidation of sulfide in wastewaters: experiment at plant-scale. Biotechnol Bioeng 93:801–811
Garcia de Lomas J, Corzo A, Portillo MC, Gonzalez JM, Andrades JA, Saiz-Jimenez C, Garcia-Robledo E (2007) Nitrate stimulation of indigenous nitrate-reducing, sulfide-oxidizing bacterial community in wastewater anaerobic biofilms. Water Res 41:3121–3131
Gevertz D, Telang AJ, Voordouw G, Jenneman GE (2000) Isolation and characterization of strains of CVO and FWKO B. Two novel nitrate-reducing, sulfide-oxidizing bacteria isolated from oilfield brine. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:2491–2501
Greene EA, Hubert C, Nemati M, Jenneman GE, Voordouw G (2003) Nitrite reductase activity of sulfate-reducing bacteria prevents their inhibition by nitrate-reducing, sulfide-oxidizing bacteria. Environ Microbiol 5:607–617
Hooijmans CM, Geraats SGM, van Neil EWJ, Robertson LA, Heijnen JJ, Luyben K (1990) Determination of growth and coupled nitrification/denitrification by immobilized Thiosphaera pantotropha using measurement and modeling of oxygen profiles. Biotechnol Bioeng 36:931–939
Hubert C, Voordouw G (2007) Oil field souring control by nitrate-reducing Sulphurospirillum spp. that outcompete sulfate-reducing bacteria for organic electron donors. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:2644–2652
Ingvorsen K, Zehnder AJB, Jorgensen BB (1984) Kinetics of sulfate uptake by Desulfobacter postgatei. Appl Environ Microbiol 47:403–408
Johnston SL, Voordouw G (2012) Sulfate-reducing bacteria lower sulfur-mediated pitting corrosion under conditions of oxygen ingress. Environ Sci Technol 46:9183–9190
Kaster KM, Grigoriyan A, Jenneman G, Voordouw G (2007) Effect of nitrate and nitrite on sulfide production by two thermophilic, sulfate-reducing enrichments from an oil field in the North Sea. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 75:195–203
Kelly DP, Wood AP (2000) Confirmation of Thiobacillus denitrificans as a species of genus Thiobacillus, in the β-subclass of the Proteobacteria, with strain NCIMB 9548 as the type strain. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 50:547–550
Klok JBM, van den Bosch PLF, Buisman CJN, Stams AJM, Keesman KJ, Janssen AJH (2012) Pathways of sulfide oxidation by haloalkaliphilic bacteria in limited-oxygen gas lift bioreactors. Environ Sci Technol 46:7581–7586
Knowles R (1982) Denitrification. Microbiol Rev 46:43–70
Kornaros M, Lyberatos G (1998) Kinetic modeling of Pseudomonas denitrificans growth and denitrification under aerobic, anoxic and transient operating conditions. Water Res 32:1912–1922
Matlab (2006) The Mathworks, Inc., Natick, MA, USA
Moosa S, Nemati M, Harrison STL (2002) A kinetic study on anaerobic reduction of sulfate, Part I: effect of sulfate concentration. Chem Eng Sci 57:2773–2780
Ni BJ, Ruscalleda M, Pellicer-Nacher C, Smets BF (2011) Modeling nitrous oxide production during biological nitrogen removal via nitrification and denitrification: extensions to the general ASM models. Environ Sci Technol 45:7768–7776
Oh J, Silverstein J (1999) Oxygen inhibition of activated sludge denitrification. Water Res 33:1925–1937
Okabe S, Ito T, Sugita K, Satoh H (2005) Succession of internal sulfur cycles and sulfur-oxidizing bacterial communities in microaerophilic wastewater biofilms. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:2520–2529
Patureau D, Davison J, Bernet N, Moletta R (1994) Denitrification under various aeration conditions in Comamonas sp., strain SGLY 2. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 14:71–78
Payne WJ (1973) Reduction of nitrogenous oxides by microorganisms. Bacteriol Rev 37:409–452
Plosz BG, Jobbagy A, Grady CPL Jr (2003) Factors influencing deterioration of denitrification by oxygen entering an anoxic reactor through the surface. Water Res 37:853–863
Reyes-Avila J, Razo-Flores E, Gomez J (2004) Simultaneous biological removal of nitrogen, carbon and sulfur by denitrification. Water Res 38:3313–3321
Ricardo AR, Garvalho G, Velizarou S, Crespo JG, Reis MAM (2012) Kinetics of nitrate and perchlorate removal and biofilms stratification in an ion exchange membrane bioreactor. Water Res 46:4556–4568
Rittmann BE, McCarty PL (2001) Environmental biotechnology: principles and application. McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc, New York
Robertson LA, Kuenen JG (1984) Aerobic denitrification: a controversy revived. Arch Microbiol 139:351–354
Robertson LA, van Niel EWJ, Torremans RAM, Kuenen JG (1988) Simultaneous nitrification and denitrification in aerobic chemostat culture of Thiosphaera pantotropha. Appl Environ Microbiol 54:2812–2818
Stouthamer AH (1988) Dissimilatory reduction of oxidized nitrogen compounds. In: Zehnder AJB (ed) Biology of anaerobic microorganisms. John Wiley & Sons, New York
Tang Y, Ziv-El M, Zhou C, Shin JH, Ahn CH, Meyer K, Candelaria D, Friese D, Overstreet R, Scott R, Rittmann BE (2010) Bioreduction of nitrate in groundwater using a pilot-scale hydrogen-based membrane biofilm reactor. Front Environ Sci Eng China 4:280–285
Thauer RK, Jungermann K, Decker K (1977) Energy conservation in chemotrophic anaerobic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev 41:100–180
Tiedje JM (1988) Ecology of denitrification and dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium. In: Zehnder AJB (ed) Biology of anaerobic microorganisms. John Wiley & Sons, New York
US Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) (2010) National primary drinking water regulations; announcement of the results of EPA’s review of existing drinking water standards and request for public comment and/or information on related issues. Fed Regist 75(59):15500–15572
US Environmental Protection Agency. Sulfate in drinking water. http://water.epa.gov/drink/contaminats/unregulated/sulfate.cfm. Accessed 7 Jun 2012
Valencia AO, Ziv-El M, Zhao HP, Feng L, Rittmann BE, Krajmalnik-Brown R (2012) Interactions between nitrate-reducing and sulfate-reducing bacteria coexisting in a hydrogen-fed biofilm. Environ Sci Technol 46:11289–11298
van den Ende FP, Meier J, van Gemerden H (1997) Syntrophic growth of sulfate-reducing bacteria and colorless sulfur bacteria during oxygen limitation. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 23:65–80
Vasiliadou IA, Pavlou S, Vayenas DV (2006) A kinetic study of hydrogenotrophic denitrification. Process Biochem 41:1401–1408
Visser A (1995) The anaerobic treatment of sulfate containing wastewater. Ph.D. thesis. Wageningen Argricultural University, Wageningen, The Netherlands
von Schulthess R, Gujer W (1996) Release of nitrous oxide (N2O) from denitrifying activated sludge: verification and application of a mathematical model. Water Res 30:521–530
Wu Q, Knowles R, Niven DF (1994) O2 regulation of denitrification in Flexibacter Canadensis. Can J Microbiol 40:916–921
Xu XJ, Chen C, Wang AJ, Fang N, Yuan Y, Ren NQ, Lee DJ (2012) Enhanced elementary sulfur recovery in integrated sulfate-reducing, sulfur-producing reactor under micro-aerobic condition. Bioresour Technol 116:517–521
Xu XJ, Chen C, Lee DJ, Wang AJ, Guo WQ, Zhou X, Guo HL, Yuan Y, Ren NQ, Chang JS (2013) Sulfate-reduction, sulfide-oxidation and elemental sulfur bioreduction process: modeling and experimental validation. Bioresour Technol 147:202–211
Zhang LH, De Schryver P, De Gusseme B, De Muynck W, Boon N, Verstrate W (2008) Chemical and biological technologies for hydrogen sulfide emission control in sewer systems: a review. Water Res 42:1–12
Zhao HP, Valencia AO, Tang YN, Kim BO, Ilhan ZE, Krajmalnik-Brown R, Rittmann BE (2013) Using a two-stage hydrogen-based membrane biofilms reactor (MBfR) to achieve complete perchlorate reduction in the present of nitrate and sulfate. Environ Sci Technol 47:1565–1572
Ziv-El M, Rittmann BE (2009) Water-quality assessment after treatment in a membrane biofilms reactor. J Am Water Works Assoc 101(12):77–83
Zumft WG (1992) The denitrifying prokaryotes. In: Balows AB, Truper HG, Dworkin M, Harder W, Schleifer KH (eds) The prokaryotes. Springer-Verlag, New York, pp 554–582
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National High-tech R&D Program of China (863 Program, Grant No. 2011AA060904), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51176037 and 51308147), Project 51121062 (National Creative Research Groups), the State Key Laboratory of Urban Water Resource and Environment (2012DX06), and the Academician Workstation Construction in Guangdong Province (2012B090500018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Xj., Chen, C., Wang, Aj. et al. Kinetics of nitrate and sulfate removal using a mixed microbial culture with or without limited-oxygen fed. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98, 6115–6124 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5642-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5642-6