Abstract
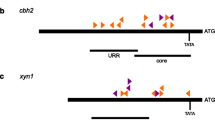
Nucleosome positioning within the promoter and coding regions of the cellobiohydrolase-encoding cbh1 gene of Trichoderma reesei was investigated. T. reesei is a filamentous fungus that is able to degrade dead plant biomass by secreting enzymes such as cellulases, a feature which is exploited in industrial applications. In the presence of different carbon sources, regulation of one of these cellulase-encoding genes, cbh1, is mediated by various transcription factors including CRE1. Deletion or mutation of cre1 caused an increase in cbh1 transcript levels under repressing conditions. CRE1 was shown to bind to several consensus recognition sequences in the cbh1 promoter region in vitro. Under repressing conditions (glucose), the cbh1 promoter and coding regions are occupied by several positioned nucleosomes. Transcription of cbh1 in the presence of the inducer sophorose resulted in a loss of nucleosomes from the coding region and in the re-positioning of the promoter nucleosomes which prevents CRE1 from binding to its recognition sites within the promoter region. Strains expressing a non-functional CRE1 (in strains with mutated CRE1 or cre1-deletion) exhibited a loss of positioned nucleosomes within the cbh1 coding region under repressing conditions only. This indicates that CRE1 is important for correct nucleosome positioning within the cbh1 coding region under repressing conditions.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aro N, Saloheimo A, Ilmén M, Penttilä M (2001) ACEII, a novel transcriptional activator involved in regulation of cellulase and xylanase genes of Trichoderma reesei. J Biol Chem 276:24309–24314. doi:10.1074/jbc.M003624200
Aro N, Ilmén M, Saloheimo A, Penttilä M (2003) ACE1 of Trichoderma reesei is a repressor of cellulase and xylanase expression. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:56–65. doi:10.1128/AEM.69.1.56-65.2003
Arya G, Maitra A, Grigoryev SA (2010) A structural perspective on the where, how, why and what of nucleosome positioning. J Biomol Struct Dyn 27:803–819. doi:10.1080/07391102.2010.10508585
Brosch G, Loidl P, Graessle S (2008) Histone modifications and chromatin dynamics: a focus on filamentous fungi. FEMS Microbiol Rev 32:409–439. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6976.2007.00100.x
Bustin SA (2000) Absolute quantification of mRNA using real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction assays. J Mol Endocrinol 25:169–193
Clark DJ (2010) Nucleosome positioning, nucleosome spacing and the nucleosome code. J Biomol Struct Dyn 27:781–791. doi:10.1080/073911010010524945
Cockerill PN (2011) Structure and function of active chromatin and DNase I hypersensitive sites. FEBS J 278:2182–2210. doi:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2011.08128.x
Cziferszky A, Mach RL, Kubicek CP (2002) Phosphorylation positively regulates DNA binding of the carbon catabolite repressor CRE1 of Hypocrea jecorina (Trichoderma reesei). J Biol Chem 277:14688–14694. doi:10.1074/jbc.M200744200
Furukawa T, Shida Y, Kitagami N, Mori K, Kato M, Kobayashi T, Okada H, Ogasawara W, Morikawa Y (2009) Identification of specific binding sites for XYR1, a transcriptional activator of cellulolytic and xylanolytic genes in Trichoderma reesei. Fungal Genet Biol 46:564–574. doi:10.1016/j.fgb.2009.04.001
García I, Gonzalez R, Gómez D, Scazzocchio C (2004) Chromatin rearrangements in the prnD–prnB bidirectional promoter: dependence on transcription factors. Eukaryot Cell 3:144–156. doi:10.1128/EC.3.1.144-156.2004
Gonzalez R, Scazzocchio C (1997) A rapid method for chromatin structure analysis in the filamentous fungus Aspergillus nidulans. Nucl Acids Res 25:3955–3956. doi:10.1093/nar/25.19.3955
Häkkinen M, Arvas M, Oja M, Aro N, Penttilä M, Saloheimo M, Pakula TM (2012) Re-annotation of the CAZy genes of Trichoderma reesei and transcription in the presence of lignocellulosic substrates. Microb Cell Fact 11:134–160. doi:10.1186/1475-2859-11-134
Ilmén M, Thrane C, Penttilä M (1996) The glucose repressor gene cre1 of Trichoderma: isolation and expression of a full length and a truncated mutant form. Mol Gen Genet 251:451–460. doi:10.1007/BF02172374
Ilmén M, Thrane C, Penttilä M (1998) The glucose repressor gene cre1 of Trichoderma: isolation and expression of a full length and a truncated mutant form. Mol Gen Genet 257(Corrigendum):386
Knob A, Terrasan CRF, Carmona EC (2010) β-Xylosidases from filamentous fungi: an overview. World J Microb Biotechnol 26:389–407. doi:10.1007/s11274-009-0190-4
Kubicek CP, Mikus M, Schuster A, Schmoll M, Seiboth B (2009) Metabolic engineering strategies for the improvement of cellulase production by Hypocrea jecorina. Biotechnol Biofuels 2:6834–6848. doi:10.1186/1754-6834-2-19
Le Crom S, Schackwitz W, Pennacchio L, Magnuson JK, Culley DE, Collett JR, Martin J, Druzhinina IS, Mathis H, Monot F, Seiboth B, Cherry B, Rey M, Berka R, Kubicek CP, Baker SE, Margeot A (2009) Tracking the roots of cellulase hyperproduction by the fungus Trichoderma reesei using massively parallel DNA sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:16151–16156. doi:10.1073/pnas.0905848106
Ling M, Qin Y, Li N, Liang Z (2009) Binding of two transcriptional factors, XYR1 and ACE1 in the promoter region of cellulase cbh1 gene. Biotechnol Lett 31:227–231. doi:10.1007/s10529-008-9857-4
Liu T, Wang T, Li X, Liu X (2008) Improved heterologous gene expression in Trichoderma reesei by cellobiohydrolase I gene (cbh1) promoter optimisation. Acta Biochem Biophys Sin 40:158–165. doi:10.1111/j.1745-7270.2008.00388.x
Mach RL, Zeilinger Z (2003) Regulation of gene expression in industrial fungi: Trichoderma. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 60:515–522. doi:10.1007/s00253-002-1162-x
Mach RL, Seiboth B, Myasnikov A, Gonzalez R, Strauss J, Harkki AM, Kubicek CP (1995) The bgl1 gene of Trichoderma reesei QM9414 encodes an extracellular, cellulose-inducible β-glucosidase involved in cellulase induction by sophorose. Mol Microbiol 16:687–697. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.1995.tb02430.x
Mach-Aigner AR, Pucher ME, Steiger MG, Bauer GE, Preis SJ, Mach RL (2008) Transcriptional regulation of xyr1, encoding the main regulator of the xylanolytic and cellulolytic enzyme system in Hypocrea jecorina. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:6554–6562. doi:10.1128/AEM.01143-08
Mandels M, Reese ET (1957) Induction of cellulase in Trichoderma viride as influenced by carbon sources and metals. J Bacteriol 73:269–278
Mandels M, Weber J, Parizek R (1971) Enhanced cellulase production by a mutant of Trichoderma viride. Appl Microbiol 21:152–154
Martinez D, Berka RM, Henrissat B, Saloheimo M, Arvas M, Baker SE, Chapman J, Chertkov O, Coutinho PM, Cullen D, Danchin EGJ, Grigoriev IV, Harris P, Jackson M, Kubicek C, Han CS, Ho I, Larrondo LF, Lopez de Leon A, Magnuson JK, Merino S, Misra M, Nelson B, Putnam N, Robbertse B, Salamov AA, Schmoll M, Terry A, Thayer N, Westerholm-Parvinen A, Schoch CL, Yao J, Barbote R, Nelson MA, Detter C, Bruce D, Kuske CR, Xie G, Richardson P, Rokhsar DS, Lucas SM, Rubin EM, Dunn-Coleman N, Ward M, Brettin TS (2008) Genome sequencing and analysis of the biomass-degrading fungus Trichoderma reesei (syn. Hypocrea jecorina). Nature Biotechnol 26:553–560. doi:10.1038/nbt1403
Mathieu M, Nikolaev I, Scazzocchio C, Felenbok B (2005) Patterns of nucleosomal organisation in the alc regulon of Aspergillus nidulans: roles of the AlcR transcriptional activator and the CreA global repressor. Mol Microbiol 56:535–548. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.2005.04559.x
Montenecourt BS, Eveleigh DE (1979) Selective isolation of high yielding cellulase mutants of Trichoderma reesei. Adv Chem Ser 181:289–301. doi:10.1021/ba-1979-0181.ch014
Nakari-Setälä T, Paloheimo M, Kallio J, Vehmaanperä J, Penttilä M, Saloheimo M (2009) Genetic modification of carbon catabolite repression in Trichoderma reesei for improved protein production. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:4853–4860. doi:10.1128/AEM.00282-09
Porciuncula JO, Furukawa T, Mori K, Shida Y, Hirakawa H, Tashiro K, Kuhara S, Nakagawa S, Morikawa Y, Ogasawara W (2013) Single nucleotide polymorphism analysis of a Trichoderma reesei hyper-cellulolytic mutant developed in Japan. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 77:534–543. doi:10.1271/bbb.129794
Portnoy T, Margeot A, Linke R, Atanasova L, Fekete E, Sandor E, Hartl L, Karaffa L, Druzhinina IS, Seiboth B, Le Crom S, Kubicek CP (2011) The CRE1 carbon catabolite repressor of the fungus Trichoderma reesei: a master regulator of carbon assimilation. BMC Genomics 12:269–281. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-12-269
Rahman Z, Shida Y, Furukawa T, Suzuki Y, Okada H, Ogasawara W, Morikawa Y (2009) Evaluation and characterisation of Trichoderma reesei cellulase and xylanase promoters. Appl Microbiol Biot 82:899–908. doi:10.1007/s00253-008-1841-3
Scazzocchio C, Ramón A (2008) Chromatin in the genus Aspergillus. In: Goldman GH, Osmani SA (eds) The aspergilli: genomics, medical aspects, biotechnology and research methods, vol 26. CRC, Boca Raton, pp 321–341
Schuster A, Schmoll M (2010) Biology and biotechnology of Trichoderma. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 87:787–799. doi:10.1007/s00253-010-2632-1
Sekinger EA, Moqtaderi Z, Struhl K (2005) Intrinsic histone–DNA interactions and low nucleosome density are important for preferential accessibility of promoter regions in yeast. Mol Cell 18:735–748. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2005.05.003
Stricker AR, Grosstessner-Hain K, Würleiter E, Mach RL (2006) XYR1 (Xylanase Regulator 1) regulates both the hydrolytic enzyme system and D-xylose metabolism in Hypocrea jecorina. Eukaryot Cell 5:2128–2137. doi:10.1128/EC.00211-06
Stricker AR, Mach RL, de Graaff HL (2008) Regulation of transcription of cellulases- and hemicellulases-encoding genes in Aspergillus niger and Hypocrea jecorina (Trichoderma reesei). Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 78:211–220. doi:10.1007/s00253-007-1322-0
Takashima S, Jikura H, Nakamura A, Masaki H, Uozumi T (1996) Analysis of CRE1 binding sites in the Trichoderma reesei cbh1 upstream region. FEMS Microbiol Lett 145:361–366. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6968.1996.tb08601.x
Zeilinger S, Schmoll M, Pail M, Mach RL, Kubicek CP (2003) Nucleosome transactions on the Hypocrea jecorina (Trichoderma reesei) cellulase promoter cbh2 associated with cellulase induction. Mol Genet Gen 270:46–55. doi:10.1007/s00438-003-0895-2
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from a BBSRC CASE studentship with associated support from Roal Oy (Finland), the BBSRC Sustainable Bioenergy Centre (BB/G01616X/1) and the Foundation for Biotechnical and Industrial Fermentation Research (Finland).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 290 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ries, L., Belshaw, N.J., Ilmén, M. et al. The role of CRE1 in nucleosome positioning within the cbh1 promoter and coding regions of Trichoderma reesei . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98, 749–762 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-5354-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-5354-3