Abstract
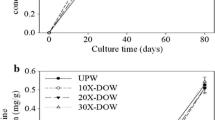
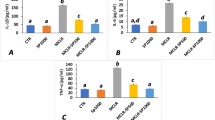
Antrodia camphorata is a unique fungus in Taiwan; the submerged fermentation product is used as the functional food for liver protection. Deep ocean water (DOW) containing rich metals and trace elements is proven to stimulate the production of functional metabolites and health function of functional fungus product in our previous study. Therefore, A. camphorata-fermented product cultured in DOW (DOW-AC) or reverse osmosis water (ROW-AC) as culture water was daily fed thioacetamide (TAA)-induced fibrosis rat for 8 weeks in order to investigate whether DOW promoted the effect of A. camphorata-fermented product on the prevention against TAA-induced liver damage and fibrosis. In the results, feeding one dose of DOW-AC prevented from TAA-induced weight loss and had more effect on inhibiting lipid peroxidation, reactive oxygen species, iNOS, and TNF-α expression than one dose of ROW-AC. Furthermore, DOW-AC also had more potent effect on protection against TAA-induced liver damage and fibrosis according to the results of H&E stain and collagen stain. However, higher liver protection of DOW-AC should be due to the fact that DOW not only increased the production of A. camphorata-fermented functional metabolites including triterpenoids, polysaccharides, flavonoids, and polyphenols but also contributed to protection against TAA-induced damage and fibrosis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abediankenari S, Ghasemi M, Nasehi MM, Abedi S, Hosseini V (2011) Determination of trace elements in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Acta Med Iran 49:667–669
Ao ZH, Xu ZH, Lu ZM, Xu HY, Zhang XM, Dou WF (2009) Niuchangchih (Antrodia camphorata) and its potential in treating liver diseases. J Ethnopharmacol 121:194–212
Bak JP, Kim YM, Son J, Kim CJ, Kim EH (2012) Application of concentrated deep sea water inhibits the development of atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions in NC/Nga mice. BMC Complement Alternat Med 12:108
Bataller R, Brenner DA (2005) Liver fibrosis. J Clin Invest 115:209–218
Beloborodova EV, Beloborodova EI, Akbasheva OE, Serebrov V, Chernogoriuk GE, Rachkovskii MI, Purlik IL, Ostanko VL, Chvyrina DV (2010) The parameters of collagen proteolytic and metabolic systems in chronic liver diseases of viral and toxic etiologies. Ter Arkh 82:29–34
Bihaqi SW, Singh AP, Tiwari M (2012) Supplementation of Convolvulus pluricaulis attenuates scopolamine-induced increased tau and amyloid precursor protein (AbetaPP) expression in rat brain. Indian J Pharmacol 44:593–598
Boyd E (1935) The growth of the surface area of human body. University of Minnesota Press
Chen YJ, Cheng PC, Lin CN, Liao HF, Chen YY, Chen CC, Lee KM (2008) Polysaccharides from Antrodia camphorata mycelia extracts possess immunomodulatory activity and inhibits infection of Schistosoma mansoni. Int Immunopharmacol 8:458–467
Chen IS, Chang YY, Hsu CL, Lin HW, Chang MH, Chen JW, Chen SS, Chen YC (2013) Alleviative effects of deep-seawater drinking water on hepatic lipid accumulation and oxidation induced by a high-fat diet. J Chin Med Assoc 76:95–101
Cliffe S, Fawer MS, Maier G, Takata K, Ritter G (1994) Enzyme assays for the phenolic content of natural juices. J Agric Food Chem 42:1824–1828
Cui T, Li JZ, Kayahara H, Ma L, Wu LX, Nakamura K (2006) Quantification of the polyphenols and triterpene acids in Chinese hawthorn fruit by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Agric Food Chem 54:4574–4581
Dubois M, Gilles K, Hamilton JK, Rebers PA, Smith F (1951) A colorimetric method for the determination of sugars. Nature 168:167
Dyroff MC, Neal RA (1983) Studies of the mechanism of metabolism of thioacetamide S-oxide by rat liver microsomes. Mol Pharmacol 23:219–227
Fujita D (2001) Deep ocean water. Shokuhin Eiseigaku Zasshi 42:J340–J342
Gebhardt R (2002) Oxidative stress, plant-derived antioxidants and liver fibrosis. Planta Med 68:289–296
Han HF, Nakamura N, Zuo F, Hirakawa A, Yokozawa T, Hattori M (2006) Protective effects of a neutral polysaccharide isolated from the mycelium of Antrodia cinnamomea on Propionibacterium acnes and lipopolysaccharide induced hepatic injury in mice. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 54:496–500
Hataguchi Y, Tai H, Nakajima H, Kimata H (2005) Drinking deep-sea water restores mineral imbalance in atopic eczema/dermatitis syndrome. Eur J Clin Nutr 59:1093–1096
Hsieh YC, Rao YK, Whang-Peng J, Huang CY, Shyue SK, Hsu SL, Tzeng YM (2011) Antcin B and its ester derivative from Antrodia camphorata induce apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells involves enhancing oxidative stress coincident with activation of intrinsic and extrinsic apoptotic pathway. J Agric Food Chem 59:10943–10954
Hunter AL, Holscher MA, Neal RA (1977) Thioacetamide-induced hepatic necrosis. I. Involvement of the mixed-function oxidase enzyme system. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 200:439–448
Hwang HS, Kim HA, Lee SH, Yun JW (2009) Anti-obesity and antidiabetic effects of deep sea water on ob/ob mice. Mar Biotechnol (NY) 11:531–539
Jaeschke H (2011) Reactive oxygen and mechanisms of inflammatory liver injury: present concepts. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 26(Suppl 1):173–179
Katsuda S, Yasukawa T, Nakagawa K, Miyake M, Yamasaki M, Katahira K, Mohri M, Shimizu T, Hazama A (2008) Deep-sea water improves cardiovascular hemodynamics in Kurosawa and Kusanagi-hypercholesterolemic (KHC) rabbits. Biol Pharm Bull 31:38–44
Kimata H, Tai H, Nakagawa K, Yokoyama Y, Nakajima H, Ikegami Y (2002) Improvement of skin symptoms and mineral imbalance by drinking deep sea water in patients with atopic eczema/dermatitis syndrome (AEDS). Acta Med (Hradec Kralove) 45:83–84
Kuo MC, Chang CY, Cheng TL, Wu MJ (2008) Immunomodulatory effect of Antrodia camphorata mycelia and culture filtrate. J Ethnopharmacol 120:196–203
Kuwayama H, Nagasaki A (2008) Desalted deep sea water increases transformation and homologous recombination efficiencies in Dictyostelium discoideum. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 14:157–162
Kwak KG, Wang JH, Shin JW, Lee DS, Son CG (2011) A traditional formula, Chunggan extract, attenuates thioacetamide-induced hepatofibrosis via GSH system in rats. Hum Exp Toxicol 30:1322–1332
Lee IH, Huang RL, Chen CT, Chen HC, Hsu WC, Lu MK (2002) Antrodia camphorata polysaccharides exhibit anti-hepatitis B virus effects. FEMS Microbiol Lett 209:63–67
Lee CL, Hung HK, Wang JJ, Pan TM (2007a) Red mold dioscorea has greater hypolipidemic and antiatherosclerotic effect than traditional red mold rice and unfermented dioscorea in hamsters. J Agric Food Chem 55:7162–7169
Lee CL, Kuo TF, Wang JJ, Pan TM (2007b) Red mold rice ameliorates impairment of memory and learning ability in intracerebroventricular amyloid beta-infused rat by repressing amyloid beta accumulation. J Neurosci Res 85:3171–3182
Lee CL, Kuo TF, Wu CL, Wang JJ, Pan TM (2010) Red mold rice promotes neuroprotective sAPPalpha secretion instead of Alzheimer's risk factors and amyloid beta expression in hyperlipidemic Abeta40-infused rats. J Agric Food Chem 58:2230–2238
Lee CL, Kung YH, Wang JJ, Lung TY, Pan TM (2011) Enhanced hypolipidemic effect and safety of red mold dioscorea cultured in deep ocean water. J Agric Food Chem 59:8199–8207
Lu ZM, Tao WY, Xu HY, Ao ZH, Zhang XM, Xu ZH (2011) Further studies on the hepatoprotective effect of Antrodia camphorata in submerged culture on ethanol-induced acute liver injury in rats. Nat Prod Res 25:684–695
Manna SK, Mukhopadhyay A, Van NT, Aggarwal BB (1999) Silymarin suppresses TNF-induced activation of NF-kappa B, c-Jun N-terminal kinase, and apoptosis. J Immunol 163:6800–6809
Mizumoto M, Arii S, Furutani M, Nakamura T, Ishigami S, Monden K, Ishiguro S, Fujita S, Imamura M (1997) NO as an indicator of portal hemodynamics and the role of iNOS in increased NO production in CCl4-induced liver cirrhosis. J Surg Res 70:124–133
Nakajima M, Iwata K, Yamamoto T, Funae Y, Yoshida T, Kuroiwa Y (1998) Nicotine metabolism in liver microsomes from rats with acute hepatitis or cirrhosis. Drug Metab Dispos 26:36–41
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:351–358
Othmer DF, Roels OA (1973) Power, fresh water, and food from cold, deep sea water. Science 182:121–125
Phadnis SV, Atilade A, Bowring J, Kyrgiou M, Young MP, Evans H, Paraskevaidis E, Walker P (2011) Regeneration of cervix after excisional treatment for cervical intraepithelial neoplasia: a study of collagen distribution. BJOG 118:1585–1591
Rockey DC, Boyles JK, Gabbiani G, Friedman SL (1992) Rat hepatic lipocytes express smooth muscle actin upon activation in vivo and in culture. J Submicrosc Cytol Pathol 24:193–203
Sanz N, Diez-Fernandez C, Andres D, Cascales M (2002) Hepatotoxicity and aging: endogenous antioxidant systems in hepatocytes from 2-, 6-, 12-, 18- and 30-month-old rats following a necrogenic dose of thioacetamide. Biochim Biophys Acta 1587:12–20
Shaker ME, Zalata KR, Mehal WZ, Shiha GE, Ibrahim TM (2011) Comparison of imatinib, nilotinib and silymarin in the treatment of carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic oxidative stress, injury and fibrosis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 252:165–175
Shen YC, Yang SW, Lin CS, Chen CH, Kuo YH, Chen CF (1997) Zhankuic acid F: a new metabolite from a formosan fungus Antrodia cinnamomea. Planta Med 63:86–88
Sugiyama A, Suzuki K, Mitra S, Arashida R, Yoshida E, Nakano R, Yabuta Y, Takeuchi T (2009) Hepatoprotective effects of paramylon, a beta-1, 3-d-glucan isolated from Euglena gracilis Z, on acute liver injury induced by carbon tetrachloride in rats. J Vet Med Sci 71:885–890
Toyama T, Nakamura H, Harano Y, Yamauchi N, Morita A, Kirishima T, Minami M, Itoh Y, Okanoue T (2004) PPARalpha ligands activate antioxidant enzymes and suppress hepatic fibrosis in rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 324:697–704
Tsukamoto H, Rippe R, Niemela O, Lin M (1995) Roles of oxidative stress in activation of Kupffer and Ito cells in liver fibrogenesis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 10(Suppl 1):S50–S53
Ueno T, Sata M, Sakata R, Torimura T, Sakamoto M, Sugawara H, Tanikawa K (1997) Hepatic stellate cells and intralobular innervation in human liver cirrhosis. Hum Pathol 28:953–959
Wang T, Fontenot RD, Soni MG, Bucci TJ, Mehendale HM (2000) Enhanced hepatotoxicity and toxic outcome of thioacetamide in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 166:92–100
Wang H, Wu G, Park HJ, Jiang PP, Sit WH, van Griensven LJ, Wan JM (2012a) Protective effect of Phellinus linteus polysaccharide extracts against thioacetamide-induced liver fibrosis in rats: a proteomics analysis. Chin Med 7:23
Wang LC, Wang SE, Wang JJ, Tsai TY, Lin CH, Pan TM, Lee CL (2012b) In vitro and in vivo comparisons of the effects of the fruiting body and mycelium of Antrodia camphorata against amyloid beta-protein-induced neurotoxicity and memory impairment. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 94:1505–1519
Yu YL, Chen IH, Shen KY, Huang RY, Wang WR, Chou CJ, Chang TT, Chu CL (2009) A triterpenoid methyl antcinate K isolated from Antrodia cinnamomea promotes dendritic cell activation and Th2 differentiation. Eur J Immunol 39:2482–2491
Zhu YZ, Huang SH, Tan BK, Sun J, Whiteman M, Zhu YC (2004) Antioxidants in Chinese herbal medicines: a biochemical perspective. Nat Prod Rep 21:478–489
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a grant from the National Science Council, Republic of China (NSC-98-2313-B-143-002-MY3), Industrial Technology Research Institute of Taiwan, Republic of China (B200-101-YG-02), and Ministry of Economic Affairs, Republic of China (102-EC-17-A-32-S1-230).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, LC., Kuo, IU., Tsai, TY. et al. Antrodia camphorata-fermented product cultured in deep ocean water has more liver protection against thioacetamide-induced fibrosis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97, 9955–9967 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-5214-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-5214-1