Abstract
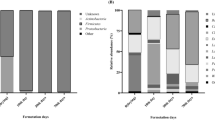
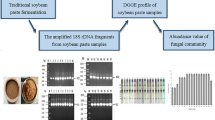
Soy sauce is a traditional condiment manufactured by natural inoculation and mixed culture fermentation. As is well known, it is the microbial community that plays an important role in the formation of its flavors. However, to date, its dynamic changes during the long period of fermentation process are still unclear, intensively constraining the improvement and control of the soy sauce quality. In this work, we revealed the dynamic changes of the microbial community by combining a cultured dependent method and a cultured independent method of polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Results indicated that the two methods verified and complemented each other in profiling microbial community, and that significant dynamics of the microbial community existed during the fermentation process, especially the strong inhibition of the growth of most of the microbes when entering into the mash stage from the koji stage. In the analysis of bacterial community, Staphylococcus and Bacillus were found to be the dominant bacteria and detected in the whole fermentation process. Kurthia and Klebsiella began to appear in the koji stage and then fade away in the early stage of the mash fermentation. In the analysis of fungal community, Aspergillus sojae and Zygosaccharomyces rouxii were found to be the dominant fungi in the koji and mash fermentation, respectively. It was clearly shown that when A. sojae decreased and disappeared in the middle stage of the mash fermentation, Z. rouxii appeared and increased at the meantime. Aspergillus parasiticus, Trichosporon ovoides and Trichosporon asahii also appeared in the koji and the early period of the mash fermentation and disappeared thereafter. Similar to Z. rouxii, Millerozyma farinosa and Peronospora farinosa were also found spontaneously which appeared in the mid-late period of the mash fermentation. The principal component analysis suggested that the microbial community underwent significant changes in the early period of the fermentation and, thereafter, tended to the stabilization in the mid-late periods. This study gave us important clues to understand the fermentation process and can serve as a foundation for improving the quality of soy sauce in the future.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akopyanz N, Bukanov NO, Westblom TU, Kresovich S, Berg DE (1992) DNA diversity among clinical isolates of Helicobacter pylori detected by PCR-based RAPD fingerprinting. Nucleic Acids Res 20(19):5137–5142
Cocolin L, Aggio D, Manzano M, Cantoni C, Comi G (2002) An application of PCR-DGGE analysis to profile the yeast populations in raw milk. Int Dairy J 12(5):407–411
De Vero L, Gala E, Gullo M, Solieri L, Landi S, Giudici P (2006) Application of denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) analysis to evaluate acetic acid bacteria in traditional balsamic vinegar. Food Microbiol 23(8):809–813
Endo A, Okada S (2005) Monitoring the lactic acid bacterial diversity during shochu fermentation by PCR-denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. J Biosci Bioeng 99(3):216–221
Fell JW, Boekhout T, Fonseca A, Scorzetti G, Statzell-Tallman A (2000) Biodiversity and systematics of basidiomycetous yeasts as determined by large-subunit rDNA D1/D2 domain sequence analysis. Int J Syst Evol Micr 50(3):1351–1371
Garcia-Armisen T, Papalexandratou Z, Hendryckx H, Camu N, Vrancken G, De Vuyst L, Cornelis P (2010) Diversity of the total bacterial community associated with Ghanaian and Brazilian cocoa bean fermentation samples as revealed by a 16S rRNA gene clone library. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 87(6):2281–2292
Goodfellow M, Collins M, Minnikin D (1980) Fatty acid and polar lipid composition in the classification of Kurthia. J Appl Microbiol 48(2):269–276
Gordon JL, Wolfe KH (2008) Recent allopolyploid origin of Zygosaccharomyces rouxii strain ATCC 42981. Yeast 25(6):449–456
Guan L, Cho KH, Lee J-H (2011) Analysis of the cultivable bacterial community in jeotgal, a Korean salted and fermented seafood, and identification of its dominant bacteria. Food Microbiol 28(1):101–113
Ito H, Dou K (1994) Microorganisms of Miso and Soysauce. Japanese Journal of Food Microbiology 11(3):151–157
Janse I, Bok J, Zwart G (2004) A simple remedy against artifactual double bands in denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. J Microbiol Meth 57(2):279–281
Leejeerajumnean A, Duckham SC, Owens JD, Ames JM (2001) Volatile compounds in Bacillus-fermented soybeans. J Sci Food Agr 81(5):525–529
Mamlouk D, Hidalgo C, Torija MJ, Gullo M (2011) Evaluation and optimisation of bacterial genomic DNA extraction for no-culture techniques applied to vinegars. Food Microbiol 28(7):1374–1379
Marsh TL (1999) Terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism (T-RFLP): an emerging method for characterizing diversity among homologous populations of amplification products. Curr Opin Microbiol 2(3):323–327
Muyzer G, Smalla K (1998) Application of denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) and temperature gradient gel electrophoresis (TGGE) in microbial ecology. Anton Leeuw Int J G 73(1):127–141
Muyzer G, De Waal EC, Uitterlinden AG (1993) Profiling of complex microbial populations by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified genes coding for 16S rRNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 59(3):695–700
Ni Z, Xu W, Dou W, Xu H, Xu Z (2010) Comparison of total microbial DNA extraction methods from solid-culture of Zhenjiang vinegar. Acta Microbiologica Sinica 50(1):119
Oguntoyinbo FA, Tourlomousis P, Gasson MJ, Narbad A (2011) Analysis of bacterial communities of traditional fermented West African cereal foods using culture independent methods. Int J Food Microbiol 145(1):205–210
Röling WFM, Apriyantono A, Van Verseveld HW (1996) Comparison between traditional and industrial soy sauce (kecap) fermentation in Indonesia. J fermentation and bioengineering 81(3):275–278
Steele DB, Fiske MJ, Steele BP, Kelley VC (1992) Production of a low-molecular-weight, alkaline-active, thermostable protease by a novel, spiral-shaped bacterium, Kurthia spiroforme, sp. nov. Enzyme Microb Tech 14(5):358–360
Strauss MJ, Prinsloo NM (2007) Real-time principal component analysis of in-line NIR spectroscopic data as applied to heterogeneous catalysis research. Appl Catal A-Gen 320:16–23
Suezawa Y, Kimura I, Inoue M, Gohda N, Suzuki M (2006) Identification and typing of miso and soy sauce fermentation yeasts, Candida etchellsii and C. versatilis, based on sequence analyses of the D1/D2 domain of the 26S ribosomal RNA gene, and the region of internal transcribed spacer 1, 5.8S ribosomal RNA gene and internal transcribed spacer 2. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 70(2):348–354
Takazane S, Endo T, Shida O, Tagami H, Takagi H, Kadowaki K (1998) Influence of Bacillus species in Shoyu Koji on Shoyu brewing (part 1) isolation and identification of antifungal antibiotics producing bacteria. Shoyu Kenkyujyo Kenkyu Houkoku 24:77–82
Tanasupawat S, Thongsanit J, Okada S, Komagata K (2002) Lactic acid bacteria isolated from soy sauce mash in Thailand. J Gen Appl Microbiol 48(4):201–209
Uchida K (2000) Diversity and ecology of salt tolerant lactic acid bacteria: Tetragenococcus halophilus in Soy Sauce fermentation. Japanese Journal of Lactic Acid Bacteria 11:60–65
Wah TT, Walaisri S, Assavanig A, Niamsiri N, Lertsiri S (2013) Co-culturing of Pichia guilliermondii enhanced volatile flavor compound formation by Zygosaccharomyces rouxii in the model system of Thai soy sauce fermentation. Int J Food Microbiol 160(3):282–289
Wei CL, Chao SH, Tsai WB, Lee PS, Tsau NH, Chen JS, Lai WL, Tu JC, Tsai YC (2013) Analysis of bacterial diversity during the fermentation of inyu, a high-temperature fermented soy sauce, using nested PCR-denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis and the plate count method. Food Microbiol 33(2):252–261
Whiteley AS, Jenkins S, Waite I, Kresoje N, Payne H, Mullan B, Allcock R, O’Donnell A (2012) Microbial 16S rRNA Ion Tag and community metagenome sequencing using the Ion Torrent (PGM) Platform. J Microbiol Meth 91(1):80–88
Wu J, Gullo M, Chen F, Giudici P (2010) Diversity of Acetobacter pasteurianus strains isolated from solid-state fermentation of cereal vinegars. Curr Microbiol 60(4):280–286
Xie J, Jiang H, Liu X, Liu X, Zhou J, Qiu G (2011) 16s rDNA based microbial diversity analysis of eleven acid mine drainages obtained from three Chinese copper mines. J Cent South Univ T 18(6):1930–1939
Yan YZ, Qian YL, Ji FD, Chen JY, Han BZ (2013) Microbial composition during Chinese soy sauce koji-making based on culture dependent and independent methods. Food Microbiol 34(1):189–195
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University (IRT1166), National High-Tech Research and Development Plan (‘863’ Plan) (No. 2011AA100905-4). We thank Zhiqiang Nie of the College of Bioengineering, Tianjin University of Science and Technology for providing help in using the technique.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Quanzeng Wei and Hongbin Wang contributed equally as the first author.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, Q., Wang, H., Chen, Z. et al. Profiling of dynamic changes in the microbial community during the soy sauce fermentation process. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97, 9111–9119 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-5146-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-5146-9