Abstract
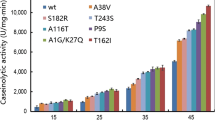
In proteins, a posttranslational deamidation process converts asparagine (Asn) and glutamine (Gln) residues into negatively charged aspartic (Asp) and glutamic acid (Glu), respectively. This process changes the protein net charge affecting enzyme activity, pH optimum, and stability. Understanding the principles which affect these enzyme properties would be valuable for protein engineering in general. In this work, three criteria for selecting amino acid substitutions of the deamidation type in the Bacillus gibsonii alkaline protease (BgAP) are proposed and systematically studied in their influence on pH-dependent activity and thermal resistance. Out of 113 possible surface amino acids, 18 (11 Asn and 7 Gln) residues of BgAP were selected and evaluated based on three proposed criteria: (1) The Asn or Gln residues should not be conserved, (2) should be surface exposed, and (3) neighbored by glycine. “Deamidation” in five (N97, N253, Q37, Q200, and Q256) out of eight (N97, N154, N250, N253, Q37, Q107, Q200, and Q256) amino acids meeting all criteria resulted in increased proteolytic activity. In addition, pH activity profiles of the variants N253D and Q256E and the combined variant N253DQ256E were dramatically shifted towards higher activity at lower pH (range of 8.5–10). Variant N253DQ256E showed twice the specific activity of wild-type BgAP and its thermal resistance increased by 2.4 °C at pH 8.5. These property changes suggest that mimicking surface deamidation by substituting Gln by Glu and/or Asn by Asp might be a simple and fast protein reengineering approach for modulating enzyme properties such as activity, pH optimum, and thermal resistance.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schäffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Ballinger MD, Tom J, Wells JA (1995) Designing subtilisin BPN' to cleave substrates containing dibasic residues. Biochemistry 34:13312–13319
Bischoff R, Schlüter H (2012) Amino acids: chemistry, functionality and selected non-enzymatic post-translational modifications. J Proteomics 75:2275–2296
Bodanszky M, Kwei JZ (1978) Side reactions in peptide synthesis VII. Sequence dependence in the formation of aminosuccinyl derivatives from beta-benzyl-aspartyl peptides. Int J Pept Protein Res 12:69–74
Brode PF, Erwin CR, Rauch DS, Barnett BL, Armpriester JM, Wang ESF, Rubingh DN (1996) Subtilisin BPN' variants: increased hydrolytic activity on surface-bound substrates via decreased surface activity. Biochemistry 35:3162–3169
Bryan PN (2000) Protein engineering of subtilisin. Biochim Biophys Acta 1543:203–222
Capasso S, Mazzarella L, Sica F, Zagari A (1989) Deamidation via cyclic imide in asparaginyl peptides. Pept Res 2:195–200
Catak S, Monard G, Aviyente V, Ruiz-Lopez MF (2009) Deamidation of asparagine residues: direct hydrolysis versus succinimide-mediated deamidation mechanisms. J Phys Chem A 113:1111–1120
Chavira R Jr, Burnett TJ, Hageman JH (1984) Assaying proteinases with azocoll. Anal Biochem 136:446–450
Craik CS, Page MJ, Madison EL (2011) Proteases as therapeutics. Biochem J 435:1–16
De Kreij A, Van den Burg B, Venema G, Vriend G, Eijsink VGH, Nielsen JE (2002) The effects of modifying the surface charge on the catalytic activity of a thermolysin-like protease. J Biol Chem 277:15432–15438
Di Cera E (2008) Engineering protease specificity made simple, but not simpler. Nat Chem Biol 4:270–271
Erwin CR, Barnett BL, Oliver JD, Sullivan JF (1990) Effects of engineered salt bridges on the stability of subtilisin BPN'. Protein Eng 4:87–97
Feller BE, Kellis JT Jr, Cascao-Pereira LG, Robertson CR, Frank CW (2010) The role of electrostatic interactions in protease surface diffusion and the consequence for interfacial biocatalysis. Langmuir 26:18916–18925
Goddette DW, Paech C, Yang SS, Mielenz JR, Bystroff C, Wilke ME, Fletterick RJ (1992) The crystal structure of the Bacillus lentus alkaline protease, subtilisin BL, at 1.4 A resolution. J Mol Biol 228:580–595
Inoue H, Nojima H, Okayama H (1990) High efficiency transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. Gene 96:23–28
Jaouadi B, Aghajari N, Haser R, Bejar S (2010) Enhancement of the thermostability and the catalytic efficiency of Bacillus pumilus CBS protease by site-directed mutagenesis. Biochimie 92:360–369
Kato A, Tanaka A, Lee Y, Matsudomi N, Kobayashi K (1987a) Effects of deamidation with chymotrypsin at pH 10 on the functional properties of proteins. J Agric Food Chem 35:285–288
Kato A, Tanaka A, Matsudomi N, Kobayashi K (1987b) Deamidation of food proteins by protease in alkaline pH. J Agric Food Chem 35:224–227
Kato A, Tanimoto S, Muraki Y, Kobayashi K, Kumagai I (1992) Structural and functional properties of hen egg-white lysozyme deamidated by protein engineering. Biosci Biotech Biochem 56:1424–1428
Kawamura F, Doi RH (1984) Construction of a Bacillus subtilis double mutant deficient in extracellular alkaline and neutral proteases. J Bacteriol 160:442–444
Knight ZA, Garrison JL, Chan K, King DS, Shokat KM (2007) A remodelled protease that cleaves phosphotyrosine substrates. J Am Chem Soc 129:11672–11673
Kossiakoff AA (1988) Tertiary structure is a principal determinant to protein deamidation. Science 240:191–194
Krieger E, Koraimann G, Vriend G (2002) Increasing the precision of comparative models with YASARA NOVA—a self-parameterizing force field. Proteins 47:393–402
Kuhn P, Knapp M, Soltis SM, Ganshaw G, Thoene M, Bott R (1998) The 0.78 A structure of a serine protease: Bacillus lentus subtilisin. Biochemistry 37:13446–13452
Leisola M, Turunen O (2007) Protein engineering: opportunities and challenges. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 75:1225–1232
Li Z, Roccatano D, Lorenz M, Schwaneberg U (2012) Directed evolution of subtilisin E into a highly active and guanidinium chloride- and sodium dodecylsulfate-tolerant protease. ChemBioChem 13:691–699
Loladze VV, Ibarra-Molero B, Sanchez-Ruiz JM, Makhatadze GI (1999) Engineering a thermostable protein via optimization of charge-charge interactions on the protein surface. Biochemistry 38:16419–16423
Martinez R, Schwaneberg U, Roccatano D (2011) Temperature effects on structure and dynamics of the psychrophilic protease subtilisin S41 and its thermostable mutants in solution. Protein Eng Des Sel 24:533–544
Maurer K-H (2004) Detergent proteases. Curr Opin Biotech 15:330–334
Miyazaki K, Wintrode PL, Grayling RA, Rubingh DN, Arnold FH (2000) Directed evolution study of temperature adaptation in a psychrophilic enzyme. J Mol Biol 297:1015–1026
Paech C, Christianson T, Maurer K-H (1993) Zymogram of proteases made with developed film from nondenaturing polyacrylamide gels after electrophoresis. Anal Biochem 208:249–254
Pogson M, Georgiou G, Iverson BL (2009) Engineering next generation proteases. Curr Opin Biotech 20:390–397
Robinson NE, Robinson AB (2004) Molecular clocks: deamidation of asparaginyl and glutaminyl residues in peptides and proteins. Althouse, Cave Junction
Russell AJ, Fersht AR (1987) Rational modification of enzyme catalysis by engineering surface charge. Nature 328:496–500
Sakoda H, Imanaka T (1992) Cloning and sequencing of the gene coding for alcohol dehydrogenase of Bacillus stearothermophilus and rational shift of the optimum pH. J Bacteriol 174:1397–1402
Sanchez-Ruiz JM, Makhatadze GI (2001) To charge or not to charge? Trends Biotechnol 19:132–135
Siegert P, Wieland S, Engelskirchen J, Merkel M, Maurer KH, Bessler C (2009) Novel alkaline protease from Bacillus gibsonii and washing and cleaning agents containing said novel alkaline protease. United States Patent, 2009
Siezen RJ, Leunissen JA (1997) Subtilases: the superfamily of subtilisin-like serine proteases. Protein Sci 6:501–523
Strub C, Alies C, Lougarre A, Ladurantie C, Czaplicki J, Fournier D (2004) Mutation of exposed hydrophobic amino acids to arginine to increase protein stability. BMC Biochem 5:9
Teshima G, Porter J, Yim K, Ling V, Guzzetta A (1991) Deamidation of soluble CD4 at asparagine-52 results in reduced binding capacity for the HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein gp120. Biochemistry 30:3916–3922
Van den Burg B, Vriend G, Veltman OR, Venema G, Eijsink VG (1998) Engineering an enzyme to resist boiling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:2056–2060
Vojcic L, Despotovic D, Martinez R, Maurer KH, Schwaneberg U (2012) An efficient transformation method for Bacillus subtilis DB104. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 94:487–493
Wang W, Malcolm BA (1999) Two-stage PCR protocol allowing introduction of multiple mutations, deletions and insertions using QuikChange Site-Directed Mutagenesis. Biotechniques 26:680–682
Wilson CR, Tang MR, Christianson T, Maurer KH, Weiss A (1999) Expression systems for commercial production of cellulase and xylanase in Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus licheniformis. United States Patent, 1999
Wright HT (1991) Sequence and structure determinants of the nonenzymatic deamidation of asparagine and glutamine residues in proteins. Protein Eng 4:283–294
Zhao H, Arnold FH (1999) Directed evolution converts subtilisin E into a functional equivalent of thermitase. Protein Eng 12:47–53
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the German Government through the Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung [FKZ, 0315035A to U.S.] and Henkel AG & Co. KGaA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 212 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jakob, F., Martinez, R., Mandawe, J. et al. Surface charge engineering of a Bacillus gibsonii subtilisin protease. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97, 6793–6802 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4560-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4560-8