Abstract
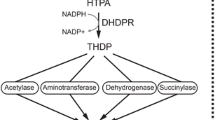
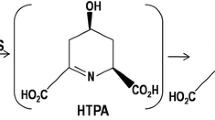
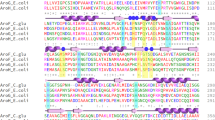
Dihydrodipicolinate synthase (DHDPS, EC 4.2.1.52) catalyzes the first committed reaction of l-lysine biosynthesis in bacteria and plants and is allosterically regulated by l-lysine. In previous studies, DHDPSs from different species were proved to have different sensitivity to l-lysine inhibition. In this study, we investigated the key determinants of feedback regulation between two industrially important DHDPSs, the l-lysine-sensitive DHDPS from Escherichia coli and l-lysine-insensitive DHDPS from Corynebacterium glutamicum, by sequence and structure comparisons and site-directed mutation. Feedback inhibition of E. coli DHDPS was successfully alleviated after substitution of the residues around the inhibitor’s binding sites with those of C. glutamicum DHDPS. Interestingly, mutagenesis of the lysine binding sites of C. glutamicum DHDPS according to E. coli DHDPS did not recover the expected feedback inhibition but an activation of DHDPS by l-lysine, probably due to differences in the allosteic signal transduction in the DHDPS of these two organisms. Overexpression of l-lysine-insensitive E. coli DHDPS mutants in E. coli MG1655 resulted in an improvement of l-lysine production yield by 46 %.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bearer CF, Neet KE (1978) Threonine inhibition of aspartokinase-homoserine dehydrogenase-I of Escherichia-coli—slow transient and cooperativity of inhibition of aspartokinase activity. Biochem 17:3523–3530. doi:10.1021/bi00610a016
Becker J, Wittmann C (2012) Systems and synthetic metabolic engineering for amino acid production—the heartbeat of industrial strain development. Curr Opinion Biotechnol
Bittel DC, Shaver JM, Somers DA, Gengenbach BG (1996) Lysine accumulation in maize cell cultures transformed with a lysine-insensitive form of maize dihydrodipicolinate synthase. Theor Appl Genet 92:70–77
Blagova E, Levdikov V, Milioti N, Fogg MJ, Kalliomaa AK, Brannigan JA, Wilson KS, Wilkinson AJ (2006) Crystal structure of dihydrodipicolinate synthase (BA3935) from Bacillus anthracis at 1.94 angstrom resolution. Proteins 62:297–301. doi:10.1002/Prot.20684
Blickling S, Beisel HG, Bozic D, Knablein J, Laber B, Huber R (1997) Structure of dihydrodipicolinate synthase of Nicotiana sylvestris reveals novel quaternary structure. J Mol Biol 274:608–621
Blickling S, Knablein J (1997) Feedback inhibition of dihydrodipicolinate synthase enzymes by L-lysine. Biol Chem 378:207–210
Chen Z, Meyer W, Rappert S, Sun J, Zeng A-P (2011a) Coevolutionary analysis enabled rational deregulation of allosteric enzyme inhibition in Corynebacterium glutamicum for lysine production. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:4352–4360. doi:10.1128/aem.02912-10
Chen Z, Rappert S, Sun J, Zeng A-P (2011b) Integrating molecular dynamics and co-evolutionary analysis for reliable target prediction and deregulation of the allosteric inhibition of aspartokinase for amino acid production. J Biotech 154:248–254. doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2011.05.005
Chen Z, Wilmanns M, Zeng A-P (2010) Structural synthetic biotechnology: from molecular structure to predictable design for industrial strain development. Trends Biotech 28:534–542. doi:10.1016/j.tibtech.2010.07.004
Cremer J, Eggeling L, Sahm H (1991) Control of the lysine biosynthesis sequence in Corynebacterium-glutamicum as analyzed by overexpression of the individual corresponding genes. Appl Environ Microb 57:1746–1752
Dobson RCJ, Griffin MDW, Jameson GB, Gerrard JA (2005) The crystal structures of native and (S)-lysine-bound dihydrodipicolinate synthase from Escherichia coli with improved resolution show new features of biological significance. Acta Crystallogr D 61:1116–1124. doi:10.1107/S0907444905016318
Dobson RCJ, Griffin MDW, Roberts SJ, Gerrard JA (2004) Dihydrodipicolinate synthase (DHDPS) from Escherichia coli displays partial mixed inhibition with respect to its first substrate, pyruvate. Biochimie 86:311–315. doi:10.1016/j.biochi.2004.03.008
Domigan LJ, Scally SW, Fogg MJ, Hutton CA, Perugini MA, Dobson RCJ, Muscroft-Taylor AC, Gerrard JA, Devenish SRA (2009) Characterisation of dihydrodipicolinate synthase (DHDPS) from Bacillus anthracis. Bba-Proteins Proteom 1794:1510–1516. doi:10.1016/j.bbapap.2009.06.020
Ghislain M, Frankard V, Jacobs M (1996) A dinucleotide mutation in dihydrodipicolinate synthase of Nicotiana sylvestris leads to lysine overproduction. Plant J 9:135–135
Griffin MDW, Dobson RCJ, Gerrard JA, Perugini MA (2010) Exploring the dihydrodipicolinate synthase tetramer: how resilient is the dimer–dimer interface? Arch Biochem Biophys 494:58–63. doi:10.1016/j.abb.2009.11.014
Kefala G, Evans GL, Griffin MDW, Devenish SRA, Pearce FG, Perugini MA, Gerrard JA, Weiss MS, Dobson RCJ (2008) Crystal structure and kinetic study of dihydrodipicolinate synthase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Biochem J 411:351–360. doi:10.1042/Bj20071360
Laber B, Gomisruth FX, Romao MJ, Huber R (1992) Escherichia-coli dihydrodipicolinate synthase—identification of the active-site and crystallization. Biochem J 288:691–695
Ma C, Xiu Z, Zeng A-P (2011) A new concept to reveal protein dynamics based on energy dissipation. PLoS One 6:e26453
Mazelis M, Creveling RK (1979) Studies of the regulatory properties of dihydrodipicolinate synthase. Plant Physiol 63:110–110
Mazelis M, Whatley FR, Whatley J (1977) Enzymology of lysine biosynthesis in higher-plants—occurrence, characterization and some regulatory properties of dihydrodipicolinate synthase. FEBS Lett 84:236–240
Padmanabhan B, Strange RW, Antonyuk SV, Ellis MJ, Hasnain SS, Iino H, Agari Y, Bessho Y, Yokoyama S (2009) Structure of dihydrodipicolinate synthase from Methanocaldococcus jannaschii. Acta Crystallogr F 65:1222–1226. doi:10.1107/S174430910904651X
Paris S, Wessel PM, Dumas R (2002) Overproduction, purification, and characterization of recombinant bifunctional threonine-sensitive aspartate kinase-homoserine dehydrogenase from Arabidopsis thaliana. Protein Expr Purif 24:105–110. doi:10.1006/prep.2001.1539
Pearce FG, Perugini MA, McKerchar HJ, Gerrard JA (2006) Dihydrodipicolinate synthase from Thermotoga maritima. Biochem J 400:359–366. doi:10.1042/Bj20060771
Reinscheid DJ, Eikmanns BJ, Sahm H (1991) Analysis of a Corynebacterium-glutamicum hom gene coding for a feedback-resistant homoserine dehydrogenase. J Bacteriol 173:3228–3230
Rice EA, Bannon GA, Glenn KC, Jeong SS, Sturman EJ, Rydel TJ (2008) Characterization and crystal structure of lysine insensitive Corynebacterium glutamicum dihydrodipicolinate synthase (cDHDPS) protein. Arch Biochem Biophys 480:111–121. doi:10.1016/j.abb.2008.09.018
Shaver JM, Bittel DC, Sellner JM, Frisch DA, Somers DA, Gengenbach BG (1996) Single-amino acid substitutions eliminate lysine inhibition of maize dihydrodipicolinate synthase. Proc Nat Acad Sci U S A 93:1962–1966
Shedlars J, Gilvarg C (1970) Pyruvate-aspartic semialdehyde condensing enzyme of Escherichia-coli. J Biol Chem 245:1362–1373
Thomas D, Barbey R, Surdinkerjan Y (1993) Evolutionary relationships between yeast and bacterial homoserine dehydrogenases. FEBS Lett 323:289–293. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(93)81359-8
Vold B, Szulmajster J, Carbone A (1975) Regulation of dihydrodipicolinate synthase and aspartate kinase in Bacillus-subtilis. J Bacteriol 121:970–974
Yugari Y, Gilvarg C (1965) The condensation step in diamino-pimelate synthesis. J Biol Chem 240:4710–4716
Acknowledgment
The authors FG, PZ, and JS gratefully thank the financial support from the 973 key basic research program with the project 2011CBA00804 and the Chinese Academy of Sciences with the project KSCX2-EW-G-14-1. CZ and AZE were supported by the German Research Foundation (DFG) through the project ZE 542/6-1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The authors Feng Geng and Zhen Chen contributed equally.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Geng, F., Chen, Z., Zheng, P. et al. Exploring the allosteric mechanism of dihydrodipicolinate synthase by reverse engineering of the allosteric inhibitor binding sites and its application for lysine production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97, 1963–1971 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4062-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4062-8