Abstract
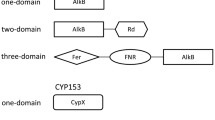
Alcanivorax hongdengensis A-11-3 is a newly identified type strain isolated from the surface water of the Malacca and Singapore Straits that can degrade a wide range of alkanes. To understand the degradation mechanism of this strain, the genes encoding alkane hydroxylases were obtained by PCR screening and shotgun sequencing of a genomic fosmid library. Six genes involved in alkane degradation were found, including alkB1, alkB2, p450-1, p450-2, p450-3 and almA. Heterogeneous expression analysis confirmed their functions as alkane oxidases in Pseudomonas putida GPo12 (pGEc47ΔB) or Pseudomonas fluorescens KOB2Δ1. Q-PCR revealed that the transcription of alkB1 and alkB2 was enhanced in the presence of n-alkanes C12 to C24; three p450 genes were up-regulated by C8–C16 n-alkanes at different levels, whereas enhanced expression of almA was observed when strain A-11-3 grew with long-chain alkanes (C24 to C36). In the case of branched alkanes, pristane significantly enhanced the expression of alkB1, p450-3 and almA. The six genes enable strain A-11-3 to degrade short (C8) to long (C36) alkanes that are straight or branched. The ability of A. hongdengensis A-11-3 to thrive in oil-polluted marine environments may be due to this strain’s multiple systems for alkane degradation and its range of substrates.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ditta G, Stanfield S, Corbin D, Helinski DR (1980) Broad host range DNA cloning system for gram-negative bacteria: construction of a gene bank of Rhizobium meliloti. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77:7347–7351
Dower WJ, Miller JF, Ragsdale CW (1988) High efficiency transformation of E. coli by high voltage electroporation. Nucleic Acids Res 16:6127–6145
Feng L, Wang W, Cheng J, Ren Y, Zhao G, Gao C (2007) Genome and proteome of long-chain alkane degrading Geobacillus thermodenitrificans NG80-2 isolated from a deep-subsurface oil reservoir. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:5602–5607
Hara A, Baik SH, Syutsubo K, Misawa N, Smits TH, van Beilen JB, Harayama S (2004) Cloning and functional analysis of alkB genes in Alcanivorax borkumensis SK2. Environ Microbiol 6:191–197
Hara A, Syutsubo K, Harayama S (2003) Alcanivorax which prevails in oil-contaminated seawater exhibits broad substrate specificity for alkane degradation. Environ Microbiol 5:746–753
Head IM, Jones DM (2006) Marine microorganisms make a meal of oil. Nat Rev Microbiol 4(3):173–82
Kloos K, Munch JC, Schloter M (2006) A new method for the detection of alkane-monooxygenase homologous genes (alkB) in soils based on PCR-hybridization. J Microbiol Methods 66:486–496
Koopmans MP, Rijpstra WIC, Klapwijk MM, de Leeuw JW, Lewan MD, Damste JSS (1999) A thermal and chemical degradation approach to decipher pristine and phytane precursors in sedimentary organic matter. Org Geochem 30:1089–1104
Kubota MM, Nodate M (2005) Isolation and functional analysis of cytochrome P450 CYP153A genes from various environments. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 69(12):2421–30
Liu C, Wang W, Wu Y, Zhou Z, Lai Q, Shao Z (2011) Multiple alkane hydroxylase systems in a marine alkane degrader, Alcanivorax dieselolei B-5. Environ Microbiol 13(5):1168–78
Liu C, Shao Z (2005) Alcanivorax dieselolei sp. nov., a novel alkane-degrading bacterium isolated from sea water and deep-sea sediment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:1181–1186
Liu YC, Zhou TT, Zhang J, Xu L, Zhang ZH, Shen QR, Shen B (2009) Molecular characterization of the alkB gene in the thermophilic Geobacillus sp. strain MH-1. Research in Microbiology 160(8):560–6
Luria SE, Adams JN, Ting RC (1960) Transduction of lactose-utilizing ability among strains of E. coli and S. dysenteriae and the properties of the transducing phage particles. Virology 12:348–390
Maier T, Forster HH (2001) Molecular characterization of the 56-kDa CYP153 from Acinetobacter sp. EB104. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 286(3):652–8
Pirnik MP, Atlas RM, Bratha R (1974) Hydrocarbon metabolism by Brevibacterium erythrogenes: normal and branched alkanes. J Bacteriol 119(3):868–78
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA
Schneiker S, Martins dos Santos VA, Bartels D, Bekel T, Brecht M, Buhrmester J (2006) Genome sequence of the ubiquitous hydrocarbon-degrading marine bacterium Alcanivorax borkumensis. Nat Biotechnol 24:997–1004
Smits TH, Balada SB, Witholt B, van Beilen JB (2002) Functional analysis of alkane hydroxylases from gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria. J Bacteriol 184:1733–1742
Smits TH, Seeger MA, Witholt B, van Beilen JB (2001) New alkane-responsive expression vectors for Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas. Plasmid 46:16–24
Solano-Serena F, Marchal R, Heiss SV, Vandecasteele JP (2004) Degradation of isooctane by Mycobacterium austroafricanum IFP 2173: growth and catabolic pathway. J Appl Microbiol 97(3):629–39
Throne-Holst M, Wentzel A, Ellingsen TE, Kotlar HK, Zotchev SB (2007) Identification of novel genes involved in long-chain n-alkane degradation by Acinetobacter sp. strain DSM 17874. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:3327–3332
van Beilen JB, Eggink G, Enequist H, Bos R, Witholt B (1992) DNA sequence determination and functional characterization of the OCT-plasmid-encoded alkJKL genes of Pseudomonas oleovorans. Mol Microbiol 6:3121–3136
van Beilen JB, Funhoff EG, van Loon A, Just A, Kaysser L, Bouza M (2006) Cytochrome P450 alkane hydroxylases of the CYP153 family are common in alkane-degrading eubacteria lacking integral membrane alkane hydroxylases. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:59–65
van Beilen JB, Marin MM, Smits TH, Rothlisberger M, Franchini AG, Witholt B, Rojo F (2004) Characterization of two alkane hydroxylase genes from the marine hydrocarbonoclastic bacterium Alcanivorax borkumensis. Environ Microbiol 6:264–273
van Beilen JB, Wubbolts MG, Witholt B (1994) Genetics of alkane oxidation by Pseudomonas oleovorans. Biodegradation 5:161–174
Wang L, Wang W, Shao Z (2010) Gene diversity of CYP153A and AlkB alkane hydroxylases in oil-degrading bacteria isolated from the Atlantic Ocean. Environ Microbiol 12(5):1230–1242
Whyte LG, Smits TH (2002) Gene cloning and characterization of multiple alkane hydroxylase systems in Rhodococcus strains Q15 and NRRL B-16531. Appl Environ Microbiol 68(12):5933–42
Wu Y, Lai Q, Zhou Z, Nan Q, Liu C, Shao Z (2009) Alcanivorax hongdengensis sp. nov., an alkane degrading bacterium isolated from surface seawater of the straits of Malacca and Singapore, producing a lipopeptide as its biosurfactant. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:1474–1479
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Dr. Daniela Näther and Dr. Montri Yasawong (Environmental Microbiology Group, Helmholtz Centre for Infection Research) for their help with genomic fosmid library construction and analysis. We would like to thank Dr. Jan B. van Beilen (Institute of Biotechnology, Zurich, Switzerland) for kindly providing P. fluorescens KOB2D1, P. putida Gpo12, E. coli CC118 (RK600) and plasmids pGEc47DB, pCom8 and pRK2017. This work was financially supported by The Project Sponsored by the National Science Foundation of China (41176154, 41106151), the International Sci & Tech cooperation Program of China (2010DFB93670), and the Sci & Tech Program of Fujian Province of China (2009H0029).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Table S1
List of predicted ORFs retrieved from 826 fosmid clone (DOC 72.5 kb)
Table S2
List of predicted ORFs retrieved from 118 fosmid clone (DOC 81.5 kb)
Table S3
List of predicted ORFs retrieved from 517 fosmid clone (DOC 88 kb)
Table S4
List of predicted ORFs retrieved from 208 fosmid clone (DOC 66.5 kb)
Table S5
List of predicted ORFs retrieved from 336 fosmid clone (DOC 74.5 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, W., Shao, Z. Genes involved in alkane degradation in the Alcanivorax hongdengensis strain A-11-3. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 94, 437–448 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3818-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3818-x