Abstract
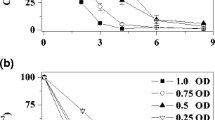
In this work, we investigated the anaerobic decolorization of methyl orange (MO), a typical azo dye, by Shewanella oneidensis MR-1, which can use various organic and inorganic substances as its electron acceptor in natural and engineered environments. S. oneidensis MR-1 was found to be able to obtain energy for growth through anaerobic respiration accompanied with dissimilatory azo-reduction of MO. Chemical analysis shows that MO reduction occurred via the cleavage of azo bond. Block of Mtr respiratory pathway, a transmembrane electron transport chain, resulted in a reduction of decolorization rate by 80%, compared to the wild type. Knockout of cymA resulted in a substantial loss of its azo-reduction ability, indicating that CymA is a key c-type cytochrome in the electron transfer chain to MO. Thus, the MtrA-MtrB-MtrC respiratory pathway is proposed to be mainly responsible for the anaerobic decolorization of azo dyes such as MO by S. oneidensis.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bretschger O, Obraztsova A, Sturm CA, Chang IS, Gorby YA, Reed SB, Culley DE, Reardon CL, Barua S, Romine MF, Zhou J, Beliaev AS, Bouhenni R, Saffarini D, Mansfeld F, Kim BH, Fredrickson JK, Nealson KH (2007) Current production and metal oxide reduction by Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 wild type and mutants. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:7003–7012
Brigé A, Motte B, Borloo J, Buysschaert G, Devreese B, Van Beeumen JJ (2008) Bacterial decolorization of textile dyes is an extracellular process requiring a multicomponent electron transfer pathway. Microb Biotechnol 1:40–52
Burns JL, Ginn BR, Bates DJ, Dublin SN, Taylor JV, Apkarian RP, Samary AG, Neal AL, Dichristina TJ (2010) Outer membrane-associated serine protease involved in adhesion of Shewanella oneidensis to Fe(III) oxides. Environ Sci Technol 44:68–73
Chang JS, Chou C, Lin YC, Lin PJ, HO JY, Hu TL (2001) Kinetic characteristics of bacterial azo-dye decolorization by Pseudomonas luteola. Water Res 35:2841–2851
Chen XJ, Xu MY, Wei HB, Sun GP (2010) Two different electron transfer pathways may involve in azoreduction in Shewanella decolorationis S12. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 86:743–751
Coursolle D, Baron DB, Bond DR, Gralnick JA (2010) The Mtr respiratory pathway is essential for reducing flavins and electrodes in Shewanella oneidensis. J Bacteriol 192:467–474
Coursolle D, Gralnick JA (2010) Modularity of the Mtr respiratory pathway of Shewanella oneidensis strain MR-1. Mol Microbiol 77:995–1008
Gralnick JA, Vali H, Lies DP, Newman DK (2006) Extracellular respiration of dimethyl sulfoxide by Shewanella oneidensis strain MR-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:4669–4674
Hartshorne RS, Reardon CL, Ross D, Nuester J, Clarke TA, Gates AJ, Mills PC, Fredrickson JK, Zachara JM, Shi L, Beliaev AS, Marshall MJ, Tien M, Brantley S, Butt JN, Richardson DJ (2009) Characterization of an electron conduit between bacteria and the extracellular environment. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:22169–22174
Hau HH, Gralnick JA (2007) Ecology and biotechnology of the genus Shewanella. Annu Rev Microbiol 61:237–258
Heidelberg JF, Paulsen IT, Nelson KE, Gaidos EJ, Nelson WC, Read TD, Eisen JA, Seshadri R, Ward N, Methe B, Clayton RA, Meyer T, Tsapin A, Scott J, Beanan M, Brinkac L, Daugherty S, DeBoy RT, Dodson RJ, Durkin AS, Haft DH, Kolonay JF, Madupu R, Peterson JD, Umayam LA, White O, Wolf AM, Vamathevan J, Weidman J, Impraim M, Lee K, Berry K, Lee C, Mueller J, Khouri H, Gill J, Utterback TR, McDonald LA, Feldblyum TV, Smith HO, Venter JC, Nealson KH (2002) Genome sequence of the dissimilatory metal ion–reducing bacterium Shewanella oneidensis. Nat Biotechnol 20:1118–1123
Hong YG, Guo J, Xu ZC, Mo CY, Xu MY, Sun GP (2007a) Reduction and partial degradation mechanisms of naphthylaminesulfonic azo dye amaranth by Shewanella decolordtionis S12. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 75:647–654
Hong Y, Xu MY, Guo J, Xu ZC, Chen XJ, Sun GP (2007b) Respiration and growth of Shewanella decolorationis S12 with an azo compound as the sole electron acceptor. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:64–72
Jiao YQ, Qian F, Li Y, Wang GM, Saltikov CW, Granick JA (2011) Deciphering the electron transport pathway for graphene oxide reduction by Shewanella oneidensis MR-1. J Bacteriol 193:3662–3665
Khalid A, Arshad M, Crowley DE (2008) Decolorization of azo dyes by Shewanella sp. under saline conditions. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 79:1053–1059
Kudlich M, Keck A, Klein J, Stolz A (1997) Localization of the enzyme system involved in anaerobic reduction of azo dyes by Sphingomonas sp. strain BN6 and effect of artificial redox mediators on the rate of azo dye reduction. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:3691–3694
Lambert DA, Shurvell HF, Lightner DA, Cooks RG (1998) Organic structural spectroscopy. Prentice-Hall, London
Li T, Guthrie JT (2010) Colour removal from aqueous solutions of metal-complex azo dyes using bacterial cells of Shewanella strain J18 143. Bioresour Technol 101:4291–4295
Logan BE (2009) Exoelectrogenic bacteria that power microbial fuel cells. Nat Rev Microbiol 7:375–381
Luan FB, Burgos WD, Xie L, Zhou Q (2010) Bioreduction of nitrobenzene, natural organic matter, and hematite by Shewanella putrefaciens CN32. Environ Sci Technol 44:184–190
Marsili E, Baron DB, Shikhare ID, Coursolle D, Gralnick JA, Bond DR (2008) Shewanella secretes flavins that mediate extracellular electron transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:3968–3973
Mu Y, Rabaey K, Rozendal RA, Yuan ZG, Keller J (2009) Decolorization of azo dyes in bioelectrochemical systems. Environ Sci Technol 43:5137–5143
Myers CR, Myers JM (1997) Cloning and sequence of cymA a gene encoding a tetraheme cytochrome c required for reduction of iron(III), fumarate, and nitrate by Shewanella putrefaciens MR-1. J Bacteriol 179:1143–1152
Pearce CI, Christie R, Boothman C, Canstein HV, Guthrie JT, Lloyd JR (2006) Reactive azo dye reduction by Shewanella strain J18 143. Biotechnol Bioeng 95:692–703
Pierce J, Suelter CH (1977) An evaluation of the Coomassie brilliant blue G-250 dye-binding method for quantitative protein determination. Anal Biochem 81:478–480
Salas EC, Sun ZZ, Lüttge A, Tour JM (2010) Reduction of graphene oxide via bacterial respiration. ACS Nano 4:4852–4856
Schuetz B, Schicklberger M, Kuermann J, Spormann AM, Gescher J (2009) Periplasmic electron transfer via the c-type cytochromes MtrA and FccA of Shewanella oneidensis MR-1. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:7789–7796
Schwalb C, Chapman SK, Reid GA (2003) The tetraheme cytochrome CymA is required for anaerobic respiration with dimethyl sulfoxide and nitrite in Shewanella oneidensis. Biochemistry 42:9491–9497
Seesuriyachan P, Takenaka S, Kuntiya A, Klayraung S, Murakami S, Aoki K (2007) Metabolism of azo dyes by Lactobacillus casei TISTR 1500 and effects of various factors on decolorization. Water Res 41:985–992
Shi L, Squier TC, Zachara JM, Fredrickson JK (2007) Respiration of metal (hydr)oxides by Shewanella and Geobacter: a key role for multihaem c-type cytochromes. Mol Microbiol 65:12–20
Shi L, Deng S, Marshall MJ, Wang ZM, Kennedy DW, Dohnalkova AC, Mottaz HM, Hill EA, Gorby YA, Beliaev AS, Richardson DJ, Zachara JM, Fredrickson K (2008) Direct involvement of type II secretion system in extracellular translocation of Shewanella oneidensis outer membrane cytochromes MtrC and OmcA. J Bacteriol 190:5512–5516
Skong DA, Holler FJ, Crouch SR (2006) Principles of instrumental analysis, 6th edn. Brooks/Cole, New York
Stolz A (2001) Basic and applied aspects in the microbial degradation of azo dyes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 56:69–80
van der Zee FP, Villaverde S (2005) Combined anaerobic-aerobic treatment of azo dyes-A short review of bioreactor studies. Water Res 39:1425–1440
Wu J, Kim KS, Sung NC, Kim CH, Lee YC (2009) Isolation and characterization of Shewanella oneidensis WL-7 capable of decolorizing azo dye Reactive Black 5. J Gen Appl Microbiol 55:51–55
Zhang SJ, Yu HQ, Li QR (2005) Radiolytic degradation of acid orange 7: a mechanistic study. Chemosphere 61:1003–1011
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (20907050) and the Outstanding Young Scientists Foundation of Anhui Province, China (10040606Y27). The authors wish to thank Professor K. H. Nealson from University of Southern California for providing the bacteria used in this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 125 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, PJ., Xiao, X., He, YR. et al. Anaerobic biodecolorization mechanism of methyl orange by Shewanella oneidensis MR-1. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 93, 1769–1776 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3508-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3508-8