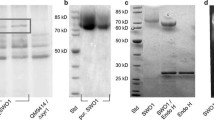
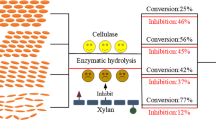
Abstract
For the efficient degradation and bioconversion of cellulosic biomass, it is important to efficiently disrupt and convert crystalline regions of cellulose into easily hydrolyzable regions than to simply hydrolyze cellulose. Expansin-like proteins such as swollenins have disruptive functions on lignocellulose, including crystalline cellulose, via non-hydrolytic mechanisms. In this work, we produced the swollenin from Trichoderma asperellum in Escherichia coli. The recombinant protein was then refolded into the bioactive form with simultaneous purification via a novel cellulose-assisted process. We devised a novel, simple, and efficient method to quantitatively determine the non-hydrolytic disruptive activity of swollenin on crystalline cellulose. This method is based on the synergism of the swollenin and the endoglucanase FnCel5A from Fervidobacterium nodosum. The change from crystalline regions into easily hydrolyzable forms, due to non-hydrolytic disruption, might be slight and not easily be observed. However, disrupted regions of cellulose could be hydrolyzed by FnCel5A, and reducing sugars were formed by the synergism. The disruptive function of the swollenin was quantitatively characterized by measuring the release of reducing sugars. These methods and processes will be useful for further research on non-hydrolytic disruptive bioactivities and provide novel approaches for the efficient and economical bioconversion of cellulosic biomass.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arantes V, Saddler JN (2010) Access to cellulose limits the efficiency of enzymatic hydrolysis: the role of amorphogenesis. Biotechnol Biofuels 3:4
Berdichevsky Y, Lamed R, Frenkel D, Gophna U, Bayer EA, Yaron S, Shoham Y, Benhar I (1999) Matrix-assisted refolding of single-chain Fv-cellulose binding domain fusion proteins. Protein Expr Purif 17:249–259
Boraston AB, Bolam DN, Gilbert HJ, Davies GJ (2004) Carbohydrate-binding modules: fine-tuning polysaccharide recognition. Biochem J 382(Pt 3):769–781
Brotman Y, Briff E, Viterbo A, Chet I (2008) Role of swollenin, an expansin-like protein from Trichoderma, in plant root colonization. Plant Physiol 147:779–789
Carrard G, Koivula A, Soderlund H, Beguin P (2000) Cellulose-binding domains promote hydrolysis of different sites on crystalline cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:10342–10347
Chang MC (2007) Harnessing energy from plant biomass. Curr Opin Chem Biol 11:677–684
Chen XA, Ishida N, Todaka N, Nakamura R, Maruyama J, Takahashi H, Kitamoto K (2010) Promotion of efficient saccharification of crystalline cellulose by Aspergillus fumigatus Swo1. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:2556–2561
Cosgrove DJ (2000) Loosening of plant cell walls by expansins. Nature 407:321–326
Cosgrove DJ, Li LC, Cho HT, Hoffmann-Benning S, Moore RC, Blecker D (2002) The growing world of expansins. Plant Cell Physiol 43:1436–1444
Geng X, Wang C (2007) Protein folding liquid chromatography and its recent developments. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 849:69–80
Gilbert HJ, Stålbrand H, Brumer H (2008) How the walls come crumbling down: recent structural biochemistry of plant polysaccharide degradation. Curr Opin Plant Biol 11:338–348
Gräslund S, Nordlund P, Weigelt J, Hallberg BM, Bray J, Gileadi O, Knapp S, Oppermann U, Arrowsmith C, Hui R, Ming J et al (2008) Protein production and purification. Nat Methods 5:135–146
Guillén D, Sánchez S, Rodríguez-Sanoja R (2010) Carbohydrate-binding domains: multiplicity of biological roles. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 85:1241–1249
Himmel ME, Ding SY, Johnson DK, Adney WS, Nimlos MR, Brady JW, Foust TD (2007) Biomass recalcitrance: engineering plants and enzymes for biofuels production. Science 315:804–807
Jungbauer A, Kaar W (2007) Current status of technical protein refolding. J Biotechnol 128:587–596
Jungbauer A, Kaar W, Schlegl R (2004) Folding and refolding of proteins in chromatographic beds. Curr Opin Biotechnol 15:487–494
Kerff F, Amoroso A, Herman R, Sauvage E, Petrella S, Filee P, Charlier P, Joris B, Tabuchi A, Nikolaidis N, Cosgrove DJ (2008) Crystal structure and activity of Bacillus subtilis YoaJ (EXLX1), a bacterial expansin that promotes root colonization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:16876–16881
Kim ES, Lee HJ, Bang WG, Choi IG, Kim KH (2009) Functional characterization of a bacterial expansin from Bacillus subtilis for enhanced enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose. Biotechnol Bioeng 102:1342–1353
Lee HJ, Lee S, Ko HJ, Kim KH, Choi IG (2010) An expansin-like protein from Hahella chejuensis binds cellulose and enhances cellulase activity. Mol Cells 29:379–385
Levasseur A, Saloheimo M, Navarro D, Andberg M, Monot F, Nakari-Setala T, Asther M, Record E (2006) Production of a chimeric enzyme tool associating the Trichoderma reesei swollenin with the Aspergillus niger feruloyl esterase A for release of ferulic acid. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 73:872–880
Levy I, Shoseyov O (2002) Cellulose-binding domains: biotechnological applications. Biotechnol Adv 20:191–213
Li Y, Jones L, McQueen-Mason S (2003) Expansins and cell growth. Curr Opin Plant Biol 6:603–610
Li M, Su ZG, Janson JC (2004) In vitro protein refolding by chromatographic procedures. Protein Expr Purif 33:1–10
Lynd LR, Weimer PJ, van Zyl WH, Pretorius IS (2002) Microbial cellulose utilization: fundamentals and biotechnology. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 66:506–577
Mattinen ML, Kontteli M, Kerovuo J, Linder M, Annila A, Lindeberg G, Reinikainen T, Drakenberg T (1997) Three-dimensional structures of three engineered cellulose-binding domains of cellobiohydrolase I from Trichoderma reesei. Protein Sci 6:294–303
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal Chem 31:426–428
Moser F, Irwin D, Chen S, Wilson DB (2008) Regulation and characterization of Thermobifida fusca carbohydrate-binding module proteins E7 and E8. Biotechnol Bioeng 100:1066–1077
Pauly M, Keegstra K (2008) Cell-wall carbohydrates and their modification as a resource for biofuels. Plant J 54:559–568
Qoronfleh MW, Hesterberg LK, Seefeldt MB (2007) Confronting high-throughput protein refolding using high pressure and solution screens. Protein Expr Purif 55:209–224
Ragauskas AJ, Williams CK, Davison BH, Britovsek G, Cairney J, Eckert CA, Frederick WJ Jr, Hallett JP, Leak DJ, Liotta CL, Mielenz JR, Murphy R, Templer R, Tschaplinski T (2006) The path forward for biofuels and biomaterials. Science 311:484–489
Rubin EM (2008) Genomics of cellulosic biofuels. Nature 454:841–845
Saloheimo M, Paloheimo M, Hakola S, Pere J, Swanson B, Nyyssönen E, Bhatia A, Ward M, Penttilä M (2002) Swollenin, a Trichoderma reesei protein with sequence similarity to the plant expansins, exhibits disruption activity on cellulosic materials. Eur J Biochem 269:4202–4211
Sampedro J, Cosgrove DJ (2005) The expansin superfamily. Genome Biol 6:242
Shoseyov O, Shani Z, Levy I (2006) Carbohydrate binding modules: biochemical properties and novel applications. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 70:283–295
Singh SM, Panda AK (2005) Solubilization and refolding of bacterial inclusion body proteins. J Biosci Bioeng 99:303–310
Somerville C, Bauer S, Brininstool G, Facette M, Hamann T, Milne J, Osborne E, Paredez A, Persson S, Raab T, Vorwerk S, Youngs H (2004) Toward a systems approach to understanding plant cell walls. Science 306:2206–2211
Swietnicki W (2006) Folding aggregated proteins into functionally active forms. Curr Opin Biotechnol 17:367–372
Wang Y, Wang X, Tang R, Yu S, Zheng B, Feng Y (2010) A novel thermostable cellulase from Fervidobacterium nodosum. J Mol Catal B Enzym 66:294–301
Yennawar NH, Li LC, Dudzinski DM, Tabuchi A, Cosgrove DJ (2006) Crystal structure and activities of EXPB1 (Zea m 1), a β-expansin and group-1 pollen allergen from maize. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:14664–14671
Zhang Y-HP, Himmel ME, Mielenz JR (2006a) Outlook for cellulase improvement: screening and selection strategies. Biotechnol Adv 24:452–481
Zhang Y-HP, Cui J, Lynd LR, Kuang LR (2006b) A transition from cellulose swelling to cellulose dissolution by o-phosphoric acid: evidence from enzymatic hydrolysis and supramolecular structure. Biomacromolecules 7:644–648
Acknowledgements
The research has been supported by National Basic Research Program of China (973 program), Natural Science Foundation of China, and Jilin Province Science and Technology Institute of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 1396 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Tang, R., Tao, J. et al. Quantitative investigation of non-hydrolytic disruptive activity on crystalline cellulose and application to recombinant swollenin. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 91, 1353–1363 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3421-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3421-1