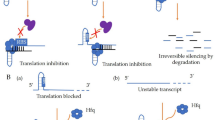
Abstract
Small RNAs (sRNAs) exert important functions in pseudomonads. Classical sRNAs comprise the 4.5S, 6S, 10Sa and 10Sb RNAs, which are known in enteric bacteria as part of the signal recognition particle, a regulatory component of RNA polymerase, transfer–messenger RNA (tmRNA) and the RNA component of RNase P, respectively. Their homologues in pseudomonads are presumed to have analogous functions. Other sRNAs of pseudomonads generally have little or no sequence similarity with sRNAs of enteric bacteria. Numerous sRNAs repress or activate the translation of target mRNAs by a base-pairing mechanism. Examples of this group in Pseudomonas aeruginosa are the iron-repressible PrrF1 and PrrF2 sRNAs, which repress the translation of genes encoding iron-containing proteins, and PhrS, an anaerobically inducible sRNA, which activates the expression of PqsR, a regulator of the Pseudomonas quinolone signal. Other sRNAs sequester RNA-binding proteins that act as translational repressors. Examples of this group in P. aeruginosa include RsmY and RsmZ, which are central regulatory elements in the GacS/GacA signal transduction pathway, and CrcZ, which is a key regulator in the CbrA/CbrB signal transduction pathway. These pathways largely control the extracellular activities (including virulence traits) and the selection of the energetically most favourable carbon sources, respectively, in pseudomonads.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aarons S, Abbas A, Adams C, Fenton A, O’Gara F (2000) A regulatory RNA (PrrB RNA) modulates expression of secondary metabolite genes in Pseudomonas fluorescens F113. J Bacteriol 182:3913–3919
Abdou L, Chou H-T, Haas D, Lu C-D (2011) Promoter recognition and activation by the global response regulator CbrB in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. doi:https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.00164-11
Altuvia S (2007) Identification of bacterial small non-coding RNAs: experimental approaches. Curr Opin Microbiol 10:257–261
Alvarez-Ortega C, Harwood CS (2007) Responses of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to low oxygen indicate that growth in the cystic fibrosis lung is by aerobic respiration. Mol Microbiol 65:153–165
Amador C, Canosa I, Govantes F, Santero E (2010) Lack of CbrB in Pseudomonas putida affects not only amino acid metabolism but also different stress responses and biofilm development. Environ Microbiol 12:1748–1761
Aranda-Olmedo I, Ramos JL, Marqués S (2005) Integration of signals through Crc and PtsN in catabolite repression of Pseudomonas putida TOL plasmid pWW0. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:4191–4198
Babitzke P, Romeo T (2007) CsrB sRNA family: sequestration of RNA-binding regulatory proteins. Curr Opin Microbiol 10:156–163
Backofen R, Hess WR (2010) Computational prediction of sRNAs and their targets in bacteria. RNA Biol 7:33–42
Barrick JE, Sudarsan N, Weinberg Z, Ruzzo WL, Breaker RR (2005) 6S RNA is a widespread regulator of eubacterial RNA polymerase that resembles an open promoter. RNA 11:774–784
Beisel CL, Storz G (2010) Base pairing small RNAs and their roles in global regulatory networks. FEMS Microbiol Rev 34:866–882
Blumer C, Haas D (2000a) Iron regulation of the hcnABC genes encoding hydrogen cyanide synthase depend on the anaerobic regulator ANR rather than on the global activator GacA in Pseudomonas fluorescens CHA0. Microbiology 146:2417–2424
Blumer C, Haas D (2000b) Multicopy suppression of a gacA mutation by the infC operon in Pseudomonas fluorescens CHA0: competition with the global translational regulator RsmA. FEMS Microbiol Lett 187:53–58
Blumer C, Heeb S, Pessi G, Haas D (1999) Global GacA-steered control of cyanide and exoprotease production in Pseudomonas fluorescens involves specific ribosome binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:14073–14078
Boisset S, Geissmann T, Huntzinger E, Fechter P, Bendridi N, Possedko M, Chevalier C, Helfer AC, Benito Y, Jacquier A, Gaspin C, Vandenesch F, Romby P (2007) Staphylococcus aureus RNAIII coordinately represses the synthesis of virulence factors and the transcription regulator Rot by an antisense mechanism. Genes Dev 21:1353–1366
Bordi C, Lamy M-C, Ventre I, Termine E, Hachani A, Fillet S, Roche B, Bleves S, Méjean V, Lazdunski A, Filloux A (2010) Regulatory RNAs and the HptB/RetS signalling pathways fine tune Pseudomonas aeruginosa pathogenesis. Mol Microbiol 76:1427–1443
Brencic A, Lory S (2009) Determination of the regulon and identification of novel mRNA targets of Pseudomonas aeruginosa RsmA. Mol Microbiol 72:612–632
Brencic A, McFarland KA, McManus HR, Castang S, Mogno I, Dove SL, Lory S (2009) The GacS/GacA signal transduction system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa acts exclusively through its control over the transcription of the RsmY and RsmZ regulatory small RNAs. Mol Microbiol 73:434–445
Bronstein PA, Filiatrault MJ, Myers CR, Rutzke M, Schneider DJ, Cartinhour SW (2008) Global transcriptional responses of Pseudomonas syringae DC3000 to changes in iron bioavailability in vitro. BMC Microbiol 8:209
Brown D (2010) A mathematical model of the Gac/Rsm quorum sensing network in Pseudomonas fluorescens. Biosystems 101:200–212
Burrowes E, Abbas A, O’Neill A, Adams C, O’Gara F (2005) Characterisation of the regulatory RNA RsmB from Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Res Microbiol 156:7–16
Burrowes E, Baysse C, Adams C, O’Gara F (2006) Influence of the regulatory protein RsmA on cellular functions in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1, as revealed by transcriptome analysis. Microbiology 152:405–418
Cases I, Pérez-Martín J, de Lorenzo V (1999) The IIANtr (PtsN) protein of Pseudomonas putida mediates the C source inhibition of the σ54-dependent Pu promoter of the TOL plasmid. J Biol Chem 274:15562–15568
Collier DN, Hager PW, Phibbs PV Jr (1996) Catabolite repression control in the pseudomonads. Res Microbiol 147:551–561
Comolli JC, Donohue TJ (2004) Differences in two Pseudomonas aeruginosa cbb 3 cytochrome oxidases. Mol Microbiol 51:1193–1203
Cornelis P (2010) Iron uptake and metabolism in pseudomonads. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 86:1637–1645
Dubey AK, Baker CS, Romeo T, Babitzke P (2005) RNA sequence and secondary structure participate in high-affinity CsrA–RNA interaction. RNA 11:1579–1587
Dubuis C, Keel C, Haas D (2007) Dialogues of root-colonizing biocontrol pseudomonads. Eur J Plant Pathol 119:311–328
Filiatrault MJ, Stodghill PV, Bronstein PA, Moll S, Lindeberg M, Grills G, Schweitzer P, Wang W, Schroth GP, Luo S, Khrebtukova I, Yang Y, Thannhauser T, Butcher BG, Cartinhour S, Schneider DJ (2010) Transcriptome analysis of Pseudomonas syringae identifies new genes, noncoding RNAs, and antisense activity. J Bacteriol 192:2359–2372
Gaffney TD, Lam ST, Ligon J, Gates K, Frazelle A, Di Maio J, Hill S, Goodwin S, Torkewitz N, Allshouse AM, Kempf H-J, Becker JO (1994) Global regulation of antifungal factors by a Pseudomonas fluorescens biological control strain. Mol Plant-Microb Interact 7:455–463
Gallagher LA, Manoil C (2001) Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 kills Caenorhabditis elegans by cyanide poisoning. J Bacteriol 183:6207–6214
González N, Heeb S, Valverde C, Kay E, Reimmann C, Junier T, Haas D (2008) Genome-wide search reveals a novel GacA-regulated small RNA in Pseudomonas species. BMC Genomics 9:167
Goodman AL, Kulasekara B, Rietsch A, Boyd D, Smith RS, Lory S (2004) A signaling network reciprocally regulates genes associated with acute infection and chronic persistence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Dev Cell 7:745–754
Goodman AL, Merighi M, Hyodo M, Ventre I, Filloux A, Lory S (2009) Direct interaction between sensor kinase proteins mediates acute and chronic disease phenotypes in a bacterial pathogen. Genes Dev 23:249–259
Görke B, Stülke J (2008) Carbon catabolite repression in bacteria: many ways to make the most out of nutrients. Nat Rev Microbiol 6:613–624
Haas D, Défago G (2005) Biological control of soil-borne pathogens by fluorescent pseudomonads. Nat Rev Microbiol 3:307–319
Haas D, Gamper M, Zimmermann A (1992) Anaerobic control in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. In: Galli E, Silver S, Witholt B (eds) Pseudomonas, molecular biology and biotechnology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, pp 177–187
Hassan KA, Johnson A, Shaffer BT, Ren Q, Kidarsa TA, Elbourne LDH, Hartney S, Duboy R, Goebel NC, Zabriskie MT, Paulsen IT, Loper JE (2010) Inactivation of the GacA response regulator in Pseudomonas fluorescens Pf-5 has far-reaching transcriptomic consequences. Environ Microbiol 12:899–915
Heeb S, Blumer C, Haas D (2002) Regulatory RNA as mediator in GacA/RsmA-dependent global control of exoproduct formation in Pseudomonas fluorescens CHA0. J Bacteriol 184:1046–1056
Heeb S, Heurlier K, Valverde C, Cámara M, Haas D, Williams P (2004) Post-transcriptional regulation in Pseudomonas spp. via the Gac/Rsm regulatory network. In: Ramos J-L (ed) Pseudomonas—virulence and gene regulation, vol 2. Kluwer Academic, New York, pp 239–255
Heeb S, Valverde C, Gigot-Bonnefoy C, Haas D (2005) Role of the stress sigma factor RpoS in GacA/RsmA-controlled secondary metabolism and resistance to oxidative stress in Pseudomonas fluorescens CHA0. FEMS Microbiol Lett 243:251–258
Heeb S, Kuehne SA, Bycroft M, Crivii S, Allen MD, Haas D, Cámara M, Williams P (2006) Functional analysis of the post-transcriptional regulator RsmA reveals a novel RNA-binding site. J Mol Biol 355:1026–1036
Heeb S, Fletcher MP, Chhabra SR, Diggle SP, Williams P, Camara M (2011) Quinolones: from antibiotics to autoinducers. FEMS Microbiol Rev 35:247–274
Hemm MR, Paul BJ, Schneider TD, Storz G, Rudd KE (2008) Small membrane proteins found by comparative genomics and ribosome binding site models. Mol Microbiol 70:1487–1501
Heurlier K, Williams F, Heeb S, Dormond C, Pessi G, Singer D, Cámara M, Williams P, Haas D (2004) Positive control of swarming, rhamnolipid synthesis, and lipase production by the posttranscriptional RsmA/RsmZ system in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. J Bacteriol 186:2936–2945
Hobbs EC, Astarita JL, Storz G (2010) Small RNAs and small proteins involved in resistance to cell envelope stress and acid shock in Escherichia coli: analysis of a bar-coded mutant collection. J Bacteriol 192:59–67
Hood RD, Singh P, Hsu F, Güvener T, Carl MA, Trinidad RR, Silverman JM, Ohlson BB, Hicks KG, Plemel RL, Li M, Schwarz S, Wang WY, Merz AJ, Goodlett DR, Mougous JD (2010) A type VI secretion system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa targets a toxin to bacteria. Cell Host Microbe 7:25–37
Hrabak EM, Willis DK (1992) The lemA gene required for pathogenicity of Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae on bean is a member of a family of two-component regulators. J Bacteriol 174:3011–3020
Hsu J-L, Chen H-C, Peng H-L, Chang H-Y (2008) Characterization of the histidine-containing phosphotransfer protein B-mediated multistep phosphorelay system in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. J Biol Chem 283:9933–9944
Humair B, González N, Mossialos D, Reimmann C, Haas D (2009) Temperature-responsive sensing regulates biocontrol factor expression in Pseudomonas fluorescens CHA0. ISME J 3:955–965
Humair B, Wackwitz B, Haas D (2010) GacA-controlled activation of promoters for small RNA genes in Pseudomonas fluorescens. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:1497–1506
Itoh Y, Nishijyo T, Nakada Y (2007) Histidine catabolism and catabolic regulation. In: Ramos J-L, Filloux A (eds) Pseudomonas–a model system in biology, vol 5. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 371–395
Jacobs MA, Alwood A, Thaipisuttikul I, Spencer D, Haugen E, Ernst S, Will O, Kaul R, Raymond C, Levy R, Chun-Rong L, Guenthner D, Bovee D, Olson MV, Manoil C (2003) Comprehensive transposon mutant library of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:14339–14344
James BD, Olsen GJ, Liu JS, Pace NR (1988) The secondary structure of ribonuclease P RNA, the catalytic element of a ribonucleoprotein enzyme. Cell 52:19–26
Jing X, Jaw J, Robinson HH, Schubot FD (2010) Crystal structure and oligomeric state of the RetS signaling kinase sensory domain. Proteins 78:1631–1640
Juhas M, Eberl L, Tümmler B (2005) Quorum sensing: the power of cooperation in the world of Pseudomonas. Environ Microbiol 7:459–471
Jung YS, Kwon YM (2008) Small RNA ArrF regulates the expression of sodB and feSII genes in Azotobacter vinelandii. Curr Microbiol 57:593–597
Kawakami T, Kuroki M, Ishii M, Igarashi Y, Arai H (2010) Differential expression of multiple terminal oxidases for aerobic respiration in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Environ Microbiol 12:1399–1412
Kay E, Dubuis C, Haas D (2005) Three small RNAs jointly ensure secondary metabolism and biocontrol in Pseudomonas fluorescens CHA0. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:17136–17141
Kay E, Humair B, Dénervaud V, Riedel K, Spahr S, Eberl L, Valverde C, Haas D (2006) Two GacA-dependent small RNAs modulate the quorum sensing response in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 188:6026–6033
Keenan RJ, Freymann DM, Stroud RM, Walter P (2001) The signal recognition particle. Annu Rev Biochem 70:755–775
Keiler KC (2007) Physiology of tmRNA: what gets tagged and why? Curr Opin Microbiol 10:169–175
Kitten T, Willis DK (1996) Suppression of a sensor kinase-dependent phenotype in Pseudomonas syringae by ribosomal proteins L35 and L20. J Bacteriol 178:1548–1555
Kulkarni PR, Cui X, Williams JW, Stevens AM, Kulkarni RV (2006) Prediction of CsrA-regulating small RNAs in bacteria and their experimental verification in Vibrio fischeri. Nucleic Acids Res 34:3361–3369
Lapouge K, Sineva E, Lindell M, Starke K, Baker CS, Babitzke P, Haas D (2007) Mechanism of hcnA mRNA recognition in the Gac/Rsm signal transduction pathway of Pseudomonas fluorescens. Mol Microbiol 66:341–356
Lapouge K, Schubert M, Allain FHT, Haas D (2008) Gac/Rsm signal transduction pathway of γ-proteobacteria: from RNA recognition to regulation of social behaviour. Mol Microbiol 67:241–253
Laskowski MA, Kazmierczak BI (2006) Mutational analysis of RetS, an unusual sensor kinase-response regulator hybrid required for Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence. Infect Immun 74:4462–4473
Laville J, Voisard C, Keel C, Maurhofer M, Défago G, Haas D (1992) Global control in Pseudomonas fluorescens mediating antibiotic synthesis and suppression of black root rot of tobacco. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:1562–1566
Lazdunski AM, Ventre I, Bleves S (2007) Cell-cell communication: quorum sensing and regulatory circuits in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. In: Ramos J-L, Filloux A (eds) Pseudomonas, a model system in biology, vol 5. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 279–310
Li Y, Altman S (2004) In search of RNase P RNA from microbial genomes. RNA 10:1533–1540
Li W, Lu C-D (2007) Regulation of carbon and nitrogen utilization by CbrAB and NtrBC two-component systems in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 189:5413–5420
Linares JF, Moreno R, Fajardo A, Martínez L, Escalante R, Rojo F, Martínez JL (2010) The global regulator Crc modulates metabolism, susceptibility to antibiotics and virulence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Environ Microbiol 12:3196–3212
Liu JM, Camilli A (2010) A broadening world of bacterial small RNAs. Curr Opin Microbiol 13:18–23
Livny J, Brencic A, Lory S, Waldor MK (2006) Identification of 17 Pseudomonas aeruginosa sRNAs and prediction of sRNA-encoding genes in 10 diverse pathogens using the bioinformatic tool sRNAPredict2. Nucleic Acids Res 34:3484–3493
Loper JE, Kobayashi DY, Paulsen IT (2007) The genomic sequence of Pseudomonas fluorescens Pf-5: insights into biological control. Phytopathology 97:233–238
MacGregor CH, Wolff JA, Arora SK, Phibbs PV Jr (1991) Cloning of a catabolite repression control (crc) gene from Pseudomonas aeruginosa, expression of the gene in Escherichia coli, and identification of the gene product in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 173:7204–7212
Massé E, Gottesman S (2002) A small RNA regulates the expression of genes involved in iron metabolism in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:4620–4625
Moreno R, Rojo F (2008) The target for the Pseudomonas putida Crc global regulator in the benzoate degradation pathway is the BenR transcriptional regulator. J Bacteriol 190:1539–1545
Moreno R, Ruiz-Manzano A, Yuste L, Rojo F (2007) The Pseudomonas putida Crc global regulator is an RNA binding protein that inhibits translation of the AlkS transcriptional regulator. Mol Microbiol 64:665–675
Moreno R, Marzi S, Romby P, Rojo F (2009) The Crc global regulator binds to an unpaired A-rich motif at the Pseudomonas putida alkS mRNA coding sequence and inhibits translation initiation. Nucleic Acids Res 37:7678–7690
Moreno R, Fonseca P, Rojo F (2010) The Crc global regulator inhibits the Pseudomonas putida pWW0 toluene/xylene assimilation pathway by repressing translation of regulatory and structural genes. J Biol Chem 285:24412–24419
Mougous JD, Cuff ME, Raunser S, Shen A, Zhou M, Gifford CA, Goodman AL, Joachimiak G, Ordoñez CL, Lory S, Walz T, Joachimiak A, Mekalanos JJ (2006) A virulence locus of Pseudomonas aeruginosa encodes a protein secretion apparatus. Science 312:1526–1530
Müsken M, Di Fiore S, Dötsch A, Fischer R, Häussler S (2010) Genetic determinants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm establishment. Microbiology 156:431–441
Nishijyo T, Haas D, Itoh Y (2001) The CbrA–CbrB two-component regulatory system controls the utilization of multiple carbon and nitrogen sources in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol Microbiol 40:917–931
Oglesby AG, Farrow JM 3rd, Lee JH, Tomaras AP, Greenberg EP, Pesci EC, Vasil ML (2008) The influence of iron on Pseudomonas aeruginosa physiology: a regulatory link between iron and quorum sensing. J Biol Chem 283:15558–15567
Oglesby-Sherrouse AG, Vasil ML (2010) Characterization of a heme-regulated non-coding RNA encoded by the prrF locus of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. PLoS ONE 5:e9930
O’Toole GA, Gibbs KA, Hager PW, Phibbs PV Jr, Kolter R (2000) The global carbon metabolism regulator Crc is a component of a signal transduction pathway required for biofilm development by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 182:425–431
Parkins MD, Ceri H, Storey DG (2001) Pseudomonas aeruginosa GacA, a factor in multihost virulence, is also essential for biofilm formation. Mol Microbiol 40:1215–1226
Pernestig AK, Melefors O, Georgellis D (2001) Identification of UvrY as the cognate response regulator for the BarA sensor kinase in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 276:225–231
Pessi G, Haas D (2001) Dual control of hydrogen cyanide biosynthesis by the global activator GacA in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. FEMS Microbiol Lett 200:73–78
Pessi G, Williams F, Hindle Z, Heurlier K, Holden MT, Cámara M, Haas D, Williams P (2001) The global posttranscriptional regulator RsmA modulates production of virulence determinants and N-acylhomoserine lactones in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 183:6676–6683
Petrova OE, Sauer K (2010) The novel two-component regulatory system BfiSR regulates biofilm development by controlling the small RNA rsmZ through CafA. J Bacteriol 192:5275–5288
Petruschka L, Burchhardt G, Müller C, Weihe C, Herrmann H (2001) The cyo operon of Pseudomonas putida is involved in catabolic repression of phenol degradation. Mol Genet Genomics 266:199–206
Pyla R, Kim TJ, Silva JL, Jung YS (2009) Overproduction of poly-β-hydroxybutyrate in the Azotobacter vinelandii mutant that does not express small RNA ArrF. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 84:717–724
Rahme LG, Ausubel FM, Cao H, Drenkard E, Goumnerov BC, Lau GW, Mahajan-Miklos S, Plotnikova J, Tan MW, Tsongalis J, Walendziewicz CL, Tompkins RG (2000) Plants and animals share functionally common bacterial virulence factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:8815–8821
Reimmann C, Beyeler M, Latifi A, Winteler H, Foglino M, Lazdunski A, Haas D (1997) The global activator GacA of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 positively controls the production of the autoinducer N-butyryl-homoserine lactone and the formation of the virulence factors pyocyanin, cyanide, and lipase. Mol Microbiol 24:309–319
Reimmann C, Valverde C, Kay E, Haas D (2005) Posttranscriptional repression of GacS/GacA-controlled genes by the RNA-binding protein RsmE acting together with RsmA in the biocontrol strain Pseudomonas fluorescens CHA0. J Bacteriol 187:276–285
Rich JJ, Kinscherf TG, Kitten T, Willis DK (1994) Genetic evidence that the gacA gene encodes the cognate response regulator for the lemA sensor in Pseudomonas syringae. J Bacteriol 176:7468–7475
Rojo F (2010) Carbon catabolite repression in Pseudomonas: optimizing metabolic versatility and the interaction with the environment. FEMS Microbiol Rev 34:658–784
Rowley KB, Clements DE, Mandel M, Humphreys T, Patil SS (1993) Multiple copies of a DNA sequence from Pseudomonas syringae pathovar phaseolicola abolish thermoregulation of phaseolotoxin production. Mol Microbiol 8:625–635
Ruiz-Manzano A, Yuste L, Rojo F (2005) Levels and activity of the Pseudomonas putida global regulatory protein Crc vary according to growth conditions. J Bacteriol 187:3678–3686
Sabra W, Kim EJ, Zeng AP (2002) Physiological responses of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 to oxidative stress in controlled microaerobic and aerobic cultures. Microbiology 148:3195–3202
Schobert M, Tielen P (2010) Contribution of oxygen-limiting conditions to persistent infection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Future Microbiol 5:603–621
Schubert M, Lapouge K, Duss O, Oberstrass FC, Jelesarov I, Haas D, Allain FH (2007) Molecular basis of messenger RNA recognition by the specific bacterial repressing clamp RsmA/CsrA. Nat Struct Mol Biol 14:807–813
Sharma CM, Vogel J (2009) Experimental approaches for the discovery and characterization of regulatory small RNA. Curr Opin Microbiol 12:536–546
Siegel LS, Hylemon PB, Phibbs PV Jr (1977) Cyclic adenosine 3′,5′-monophosphate levels and activities of adenyl cyclase and cyclic adenosine 3′,5′-monophosphate phosphodiesterase in Pseudomonas and Bacteroides. J Bacteriol 129:87–96
Silby MW, Rainey PB, Levy SB (2004) IVET experiments in Pseudomonas fluorescens reveal cryptic promoters at loci associated with recognizable overlapping genes. Microbiology 150:518–520
Smyth PF, Clarke PH (1975) Catabolite repression of Pseudomonas aeruginosa amidase: the effect of carbon source on amidase synthesis. J Gen Microbiol 90:81–90
Sonnleitner E, Schuster M, Sorger-Domenigg T, Greenberg EP, Bläsi U (2006) Hfq-dependent alterations of the transcriptome profile and effects on quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol Microbiol 59:1542–1558
Sonnleitner E, Sorger-Domenigg T, Madej MJ, Findeiss S, Hackermüller J, Hüttenhofer A, Stadler PF, Bläsi U, Moll I (2008) Detection of small RNAs in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by RNomics and structure-based bioinformatic tools. Microbiology 154:3175–3187
Sonnleitner E, Abdou L, Haas D (2009) Small RNA as global regulator of carbon catabolite repression in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:21866–21871
Sonnleitner E, González N, Haas D (2010) Small RNAs of Pseudomonas spp. In: Ramos J-L, Filloux A (eds) Pseudomonas—molecular microbiology, infection and biodiversity, vol 6. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 3–28
Sonnleitner E, Gonzalez N, Sorger-Domenigg T, Heeb S, Richter AS, Backofen R, Williams P, Hüttenhofer A, Haas D, Bläsi U (2011) The small RNA PhrS stimulates synthesis of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa quinolone signal. Mol Microbiol. doi:https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.2011.07620.x
Soper T, Mandin P, Majdalani N, Gottesman S, Woodson SA (2010) Positive regulation by small RNAs and the role of Hfq. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:9602–9607
Sorek R, Cossart P (2010) Prokaryotic transcriptomics: a new view on regulation, physiology and pathogenicity. Nat Rev Genet 11:9–16
Sorger-Domenigg T, Sonnleitner E, Kaberdin VR, Bläsi U (2007) Distinct and overlapping binding sites of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Hfq and RsmA proteins on the non-coding RNA RsmY. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 352:769–773
Soscia C, Hachani A, Bernadac A, Filloux A, Bleves S (2007) Cross talk between type III secretion and flagellar assembly systems in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 189:3124–3132
Suh S-J, Runyen-Janecky LJ, Maleniak TC, Hager P, MacGregor CH, Zielinski-Mozny NA, Phibbs PV Jr, West SHE (2002) Effect of vfr mutation on global gene expression and catabolite repression control of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbiology 148:1561–1569
Takeuchi K, Kiefer P, Reimmann C, Keel C, Dubuis C, Rolli J, Vorholt JA, Haas D (2009) Small RNA-dependent expression of secondary metabolism is controlled by Krebs cycle function in Pseudomonas fluorescens. J Biol Chem 284:34976–34985
Toschka HY, Struck JC, Erdmann VA (1989) The 4.5S RNA gene from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Nucleic Acids Res 17:31–36
Toyofuku M, Nomura N, Kuno E, Tashiro Y, Nakajima T, Uchiyama HJ (2008) Influence of the Pseudomonas quinolone signal on denitrification in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 190:7947–7956
Valverde C, Heeb S, Keel C, Haas D (2003) RsmY, a small regulatory RNA, is required in concert with RsmZ for GacA-dependent expression of biocontrol traits in Pseudomonas fluorescens CHA0. Mol Microbiol 50:1361–1379
Valverde C, Lindell M, Wagner EG, Haas D (2004) A repeated GGA motif is critical for the activity and stability of the riboregulator RsmY of Pseudomonas fluorescens. J Biol Chem 279:25066–25074
Vasil ML (2007) How we learnt about iron acquisition in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a series of very fortunate events. Biometals 20:587–601
Ventre I, Goodman AL, Valley-Gely I, Vasseur P, Soscia C, Molin S, Bleves S, Lazdunski A, Lory S, Filloux A (2006) Multiple sensors control reciprocal expression of Pseudomonas aeruginosa regulatory RNA and virulence genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:171–176
Ventre I, Goodman AL, Filloux A, Lory S (2007) Modulation of bacterial lifestyles via two-component regulatory networks. In: Ramos J-L, Filloux A (eds) Pseudomonas—a model system in biology, vol 5. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 311–340
Vincent F, Round A, Reynaud A, Bordi C, Filloux A, Bourne Y (2010) Distinct oligomeric forms of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa RetS sensor domain modulate accessability to the ligand binding site. Environ Microbiol 12:1775–1786
Visca P (2004) Iron regulation and siderophore signalling in virulence by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. In: Ramos J-L (ed) Pseudomonas—virulence and gene regulation, vol 2. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 69–123
Vogel J (2009) A rough guide to the non-coding RNA world of Salmonella. Mol Microbiol 71:1–11
Vogel DW, Hartmann RK, Struck JC, Ulbrich N, Erdmann VA (1987) The sequence of the 6S RNA gene of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Nucleic Acids Res 15:4583–4591
Wadler CS, Vanderpool CK (2007) A dual function for a bacterial small RNA: SgrS performs base pairing-dependent regulation and encodes a functional polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:20454–20459
Wassarman KM (2007) 6S RNA: a regulator of transcription. Mol Microbiol 65:1425–1431
Wassarman KM, Zhang A, Storz G (1999) Small RNAs in Escherichia coli. Trends Microbiol 7:37–45
Waters LS, Storz G (2009) Regulatory RNAs in bacteria. Cell 136:615–628
Whistler CA, Corbell NA, Sarniguet A, Ream W, Loper JE (1998) The two-component regulators GacS and GacA influence accumulation of the stationary-phase sigma factor σS and the stress response in Pseudomonas fluorescens Pf-5. J Bacteriol 180:6635–6641
Wilderman PJ, Sowa NA, FitzGerald DJ, FitzGerald PC, Gottesman S, Ochsner UA, Vasil ML (2004) Identification of tandem duplicate regulatory small RNAs in Pseudomonas aeruginosa involved in iron homeostasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:9792–9797
Williams KP, Bartel DP (1996) Phylogenetic analysis of tmRNA secondary structure. RNA 2:1306–1310
Winteler HV, Haas D (1996) The homologous regulators ANR of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and FNR of Escherichia coli have overlapping but distinct specificities for anaerobically inducible promoters. Microbiology 142:685–693
Workentine M-L, Chang L, Ceri H, Turner RJ (2009) The GacS–GacA two-component regulatory system of Pseudomonas fluorescens: a bacterial two-hybrid analysis. FEMS Microbiol Lett 292:50–56
Ye RW, Haas D, Ka JO, Krishnapillai V, Zimmermann A, Baird C, Tiedje JM (1995) Anaerobic activation of the entire denitrification pathway in Pseudomonas aeruginosa requires Anr, an analog of Fnr. J Bacteriol 177:3606–3609
Zhang X-X, Liu Y-H, Rainey PB (2010) CbrAB-dependent regulation of pcnB, a pola(A) polymerase gene involved in polyadenylation of RNA in Pseudomonas fluorescens. Environ Microbiol 12:1674–1683
Zimmermann A, Reimmann C, Galimand M, Haas D (1991) Anaerobic growth and cyanide synthesis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa depend on anr, a regulatory gene homologous with fnr of Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol 5:1483–1490
Zolfaghar I, Evans DJ, Ronaghi R, Fleiszig SM (2006) Type III secretion-dependent modulation of innate immunity as one of multiple factors regulated by Pseudomonas aeruginosa RetS. Infect Immun 74:3880–3889
Zuber S, Carruthers F, Keel C, Mattart A, Blumer C, Pessi G, Gigot-Bonnefoy C, Schnider-Keel U, Heeb S, Reimmann C, Haas D (2003) GacS sensor domains pertinent to the regulation of exoproduct formation and to the biocontrol potential of Pseudomonas fluorescens CHA0. Mol Plant-Microb Interact 16:634–644
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Swiss National Foundation, the Hertha-Firnberg Research fellowship from the Austrian Science Fund (to E.S.) and a genomics project of the University of Lausanne. We thank Cornelia Reimmann and Karine Lapouge for critically reading the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sonnleitner, E., Haas, D. Small RNAs as regulators of primary and secondary metabolism in Pseudomonas species. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 91, 63–79 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3332-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3332-1