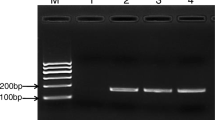
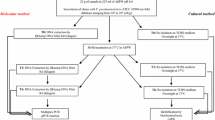
Abstract
A multiplex polymerase chain reaction (MPCR)-based assay was developed for the simultaneous detection of Vibrios using the genus-specific RNA polymerase subunit A (rpoA) gene and specific detection of toxin-producing Vibrio cholerae strains using two sets of primer based on cholera toxin subunit A (ctxA) and repeat in toxin subunit A (RtxA)-producing genes. The MPCR method developed is applicable to both the simultaneous and the two-step detection of genus Vibrio total and toxigenic V. cholerae species. This assay was specific as no amplification occurred with the other bacterial pathogens tested. The sensitivity of the assay was tested by artificially spiking the shrimp homogenate with the toxigenic strain of V. cholerae (NICED 16582) in different dilutions. The developed MPCR assay could detect three cells of V. cholerae in 12 h pre-enrichment in APW. The proposed method is rapid, sensitive, and specific for the detection of Vibrio genus as well as toxin-producing V. cholerae strains in environmental samples.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott SL, Seli LS, Catino MJ, Hartley MA, Janda JM (1998) Misidentification of unusual Aeromonas species as members of the genus Vibrio: a continuing problem. J Clin Microbiol 36:1103–1104
Aono E, Sugita J, Kawasaki J, Sakakibara H, Takahashi T, Endo K, Deguchi Y (1997) Evaluation of the polymerase chain reaction method for identification of Vibrio vulnificus isolated from marine environments. J Food Prot 60:81–83
Bej AK, Patterson DP, Brasher CW, Vickery MCL, Jones DD, Kaysner CA (1999) Detection of total and hemolysin-producing Vibrio parahaemolyticus in shellfish using multiplex PCR amplification of tl, tdh and trh. J Microbiol Methods 36:215–225
Blackstone GM, Nordstrom JL, Bowen MD, Meyer RF, Imbro P, DePaola A (2007) Use of a real time PCR assay for detection of the ctxA gene of Vibrio cholerae in an environmental survey of Mobile Bay. J Microbiol Methods 68:254–259
Brasher CW, DePaola A, Jones DD, Bej AK (1998) Detection of microbial pathogens in shellfish with multiplex PCR. Curr Microbiol 37:01–107
Castroverde CDM, San Luis BB, Monsalud RG, Hedreyda CT (2006) Differential detection of Vibrios pathogenic to shrimp by multiplex PCR. J Gen Appl Microbiol 52:273–280
Chow KH, Ng TK, Yuen KY, Yam WC (2001) Detection of RTX toxin gene in Vibrio cholerae by PCR. J Clin Microbiol 39:2594–2597
Colwell RR, Seidler RJ, Kaper J, Joseph SW, Garges S, Lockman H, Maneval D, Bradford H, Roberts N, Remmers E, Huq I, Huq A (1981) Occurrence of Vibrio cholerae serotype O1 in Maryland and Louisiana estuaries. Appl Environ Microbiol 41:555–558
Coster TS, Killeen KP, Waldor MK, Beattie DT, Spriggs DR, Kenner JR, Trofa A, Sadoff JC, Mekalanos JJ, Taylor DN (1995) Safety, immunogenicity, and efficacy of live attenuated Vibrio cholerae O139 vaccine prototype. Lancet 345:949–952
Dalmasso A, Neve FL, Suffredini E, Croci L, Seracca L, Bottero MT, Civera T (2009) Development of a PCR assay targeting the rpoA gene for the screening of Vibrio genus. Food Anal Methods 2:317–324
Espineria M, Atanassova M, Vieites JM, Santaclara FJ (2009) Validation of a method for the detection of five species, serogroups, biotypes and virulence factors of Vibrio by multiplex PCR in fish and seafood. Food Microbiol 27:122–131
Fields PI, Popovic T, Wachsmuth K, Olsvik O (1992) Use of polymerase chain reaction for detection of toxigenic Vibrio cholerae O1 strains from the Latin American cholera epidemic. J Clin Microbiol 30:2118–2121
Finkelstein RA (1988) Cholera, the cholera enterotoxins, and the cholera enterotoxin-related enterotoxin family. In: Owen P, Foster TJ (eds) Immunological and molecular genetic analysis of bacterial pathogens. Elsevier Science Publisher, Amsterdam, pp 85–102
Ghittino C, Latini M, Agnetti F, Panzieri C, Lauro L, Ciappelloni R, Petracca G (2003) Emerging pathologies in aquaculture: effects on production and food safety. Vet Res Commun 27:471–479
Goel AK, Ponmariappan S, Kamboj DV, Singh L (2007) Single multiplex polymerase chain reaction for environmental surveillance of toxigenic-pathogenic O1 and non-O1 Vibrio cholerae. Folia Microbiol 52:81–85
Gubala AJ (2006) Multiplex real-time PCR detection of Vibrio cholerae. J Microbiol Methods 65:278–293
Hall RH, Khambaty FM, Kothary MH, Keasler SP, Tall BD (1994) Vibrio cholerae non-O1 serogroup associated with cholera gravis genetically and physiologically resembles O1 E1 Tor cholera strains. Infect Immunol 62:3859–3863
Hong GE, Kim DG, Bae JY, Ahn SH, Bai SC, Kong IS (2007) Species-specific PCR detection of the fish pathogen, Vibrio anguillarum, using the amiB gene, which encodes N-acetylmuramoyl-l-alanine amidase. FEMS Microbiol Lett 269:201–206
Hoshino K, Yamasaki S, Mukhopadhyay AK, Chakraborty S, Basu A, Bhattacharya SK, Nair GB, Shimada T, Takeda Y (1998) Development and evaluation of a multiplex PCR assay for rapid detection of toxigenic Vibrio cholerae O1 and O139. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 20:201–207
Kapley A, Lampel K, Purohit HJ (2000) Thermocycling steps and optimization of multiplex PCR. Biotechnol Lett 22:1913–1918
Karunasagar I, Sugumar G, Karunasagar I, Reilly A (1995) Rapid detection of Vibrio cholerae contamination of seafood by polymerase chain reaction. Mol Mar Bio Biotechnol 4:365–368
Koch WH, Payne WL, Wentz BA, Cebula TA (1993) Rapid polymerase chain reaction method for detection of Vibrio cholerae in foods. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:556–560
Kurazono H, Pal A, Bag PK, Nair GB, Karasawa T, Mihara T, Takeda Y (1995) Distribution of genes encoding cholera toxin, zonula occludens toxin, accessory cholera toxin, and El Tor hemolysin in Vibrio cholerae of diverse origins. Microb Pathog 18:231–235
Kwok AY, Wilson JT, Coulthart M, Ng LK, Mutharia L, Chow AW (2002) Phylogenetic study and identification of human pathogenic Vibrio species based on partial hsp60 gene sequences. Can J Microbiol 48:903–910
Lin W, Fullner KJ, Clayton R, Sexton JA, Rogers MB, Calia KE, Calderwood SB, Fraser C, Mekalanos JJ (1999) Identification of a Vibrio cholerae RTX toxin gene cluster that is tightly linked to the cholera toxin prophage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:1071–1076
Lipp EK, Rivera ING, Gill AI, Espeland EM, Choopun N, Louis VR, Russek-Cohen E, Huq A, Colwell RR (2003) Direct detection of Vibrio cholerae and ctxA in Peruvian coastal waters and plankton by PCR. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:3676–3680
Markoulatos P, Siafakas N, Moncany M (2002) Multiplex polymerase chain reaction: a practical approach. J Clin Lab Anal 16:47–51
Noguerola I, Blanch AR (2008) Identification of Vibrio spp. with a set of dichotomous keys. J Appl Microbiol 105:175–185
Ramamurthy T, Bhattacharya SK, Uesaka Y, Horigome K, Paul MD, Sen S, Pal C, Takeda T, Takeda Y, Nair GB (1992) Evaluation of the bead enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of cholera toxin directly from stool specimens. J Clin Microbiol 30:1783–1786
Rivera ING, Chun J, Huq A, Sack RB, Colwell RR (2001) Genotypes associated with virulence in environmental isolates of Vibrio cholerae. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:2421–2429
Sack D, Sack RB, Nair GB, Siddique AK (2004) Cholera. Lancet 363:223–233
Satchell KJ (2003) Activation and suppression of the pro inflammatory immune response by Vibrio cholerae toxins. Microbes Infect 5:1241–1247
Shangkuan YH, Show YS, Wang TM (1995) Multiplex polymerase chain reaction to detect toxigenic Vibrio cholerae and to biotype Vibrio cholerae O1. J Appl Bacteriol 79:264–273
Singh DV, Matte MH, Matte GR, Jiang S, Sabeena F, Shukala SC, Sanyal SC, Huq A, Colwell RR (2001) Molecular analysis of Vibrio cholerae O1, O139, non-O1, and non-O139 strains: clonal relationships between clinical and environmental isolates. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:910–921
Singh DV, Isac SR, Colwell RR (2002) Development of hexaplex PCR assay for rapid detection of virulence and regulatory genes in Vibrio cholerae and Vibrio mimicus. J Clin Microbiol 40:4321–4324
Tang Y, Elis NM, Hopkins MK, Smith DH, Dodge DE, Persing DH (1998) Comparison of phenotyphic and genotyphic techniques for identification of unusal aerobic pathogenic gram-negative bacilli. J Clin Microbiol 36:3674–3679
Taniguchi H, Hirano H, Kubomura S, Higashi K, Mizuguchi Y (1986) Comparison of the nucleotide-sequences of the genes for the thermostable direct hemolysins and the thermolabile hemolysin from Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Microb Pathog 1:425–432
Tarr CL, Patel JS, Puhr ND, Sowers E, Bopp CA, Strockbine NA (2007) Identification of Vibrio isolates by a multiplex PCR assay and rpoB sequence determination. J Clin Microbiol 45:134–140
Theron J, Cilliers J, Du Preez M, Brözel VS, Venter SN (2000) Detection of toxigenic Vibrio cholerae from environmental water samples by an enrichment broth cultivation-pit-stop semi-nested PCR procedure. J Appl Microbiol 89:539–546
Thompson FL, Iida T, Swings JG (2004) Biodiversity of Vibrios. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 68:403–431
Thompson CC, Hoste B, Munn CB, Thompson FL, Dawyndt P, Swings J, Gevers D, Naser S (2005) Phylogeny and molecular identification of Vibrios on the basis of multilocus sequence analysis. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:5107–5115
Acknowledgements
The financial assistance extended by the Department of Biotechnology, Government of India, New Delhi, India for conducting this project work is gratefully acknowledged. The authors wish to thank the dean of the Fisheries College and Research Institute, Tamil Nadu Veterinary and Animal Sciences University, Tuticorin, India for having provided the necessary support for carrying out this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeyasekaran, G., Thirumalai Raj, K., Jeya Shakila, R. et al. Multiplex polymerase chain reaction-based assay for the specific detection of toxin-producing Vibrio cholerae in fish and fishery products. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 90, 1111–1118 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3175-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3175-9