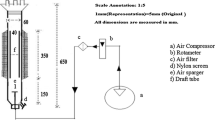
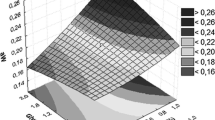
Abstract
In this work, fermentation and formulation aspects of the nematophagous fungus Hirsutella rhossiliensis BBA were investigated. When incubated in 2% (w/w) glucose and 0.5% (w/w) yeast extract medium in a 1-L Erlenmeyer flask without baffles, heavy pellet formation was observed. Only 40% of the mycelium had a size less than 500 μm. When a flask with three baffles was used, the portion of mycelium <500 μm rose to 95%. In the next step, the influence of aeration rate and stirrer speed on production of finely dispersed mycelium in a stirred tank reactor was investigated. The best fermentation results were obtained at 0.4 vvm and 400 rpm stirrer speed with 90% mycelium <500 μm and 5 g/L biomass. Then, mycelium was microencapsulated in hollow beads based on sulfoethylcellulose (SEC). Experiments on the capsule nutrient reservoir showed that 15% (w/w) corn gluten and 0.5% (w/w) yeast extract could be replaced with 3% (w/w) autoclaved baker's yeast which was never used as capsule additive before. Radial growth of mycelium out of dried hollow beads containing 1% (w/w) biomass and 3% (w/w) baker's yeast was faster than for alginate beads containing equivalent amounts of biomass and yeast indicating a higher bio-control potential.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burges HD (1998) Formulation of microbial pesticides. Kluwer, Dordrecht
Cayrol JC, Castet R, Samson RA (1986) Comparative activity of different Hirsutella species towards three plant parasitic nematodes. Revue Nématologique 12:331–336
Dautzenberg H, Loth F, Fechner K, Mehlis B, Pommerening K (1985) Preparation and performance of symplex capsules. Makromol Chem 9:203–210
Gutberlet V (2000) Dissertation Rheinische Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universität Bonn.
Hayes WA, Blackburn F (1966a) Studies on the nutrition of arthrobotrys oligospora Fes. and A. robusta Dudd. I. The saprophytic phase. Ann Appl Biol 58:43–50
Hayes WA, Blackburn F (1966b) Studies on the nutrition of arthrobotrys oligospora Fes. and A. robusta Dudd. II. The predaceous phase. Ann Appl Biol 58:51–60
Irvine TS (1990) Laboratory fermenters. In: McNeil B, Harvey LM (eds) Fermentation. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Jaffee BA (2000) Augmentation of soil with the nematophagous fungi Hirsutella rhossiliensis and Arthrobotrys haptotyla. Phytopathology 90:498–504
Jaffee BA, Zehr EI (1985) Parasitic and saprophytic abilities of the nematode-attacking fungus Hirsutella rhossiliensis. J Nematol 17:341–345
Kleespies RG, Zimmermann G (1998) Effect of additives on the production, viability and virulence of blastospores of Metarrhizium anisopliae. Biocontrol Sci Technol 8(2):207–214
Lackey BA, Jaffee BA, Muldoon AE (1992) Sporulation of the nematophagous fungus Hirsutella rhossiliensis from hyphae produced in vitro and added to soil. Phytopathology 82:1326–1330
Lackey BA, Muldoon AE, Jaffee BA (1993) Alginate pellet formulation of Hirsutella rhossiliensis for biological control of plant-parasitic nematodes. Biol Control 3:155–160
Liu XZ, Chen SY (2002) Nutritional requirements of the nematophagous fungus Hirsutella rhossiliensis. Biocontrol Sci Technol 12:381–393
MacLeod DM (1959a) Nutritional studies on the genus Hirsutella, I. Growth response in an enriched liquid medium. Can J Bot 37:695–714
MacLeod DM (1959b) Nutritional studies on the genus Hirsutella, II. Nitrogen utilization in a synthetic medium. Can J Bot 37:819–834
McInnis TM, Jaffee BA (1989) An assay for Hirsutella rhossiliensis spores and the importance of phialides for nematode inoculation. J Nematol 21:229–234
Milic S, Otenhajmer I (1974) Predicting the stability of freeze-dried suspensions of Lactobacillus acidophilus by the accelerated storage test. Cryobiology 11:116–120
Patel AV (1998) Verkapselungsverfahren für die biologische Schädlingsbekämpfung und zur Konstruktion von “vegetativen Samen”. Landbauforschung Völkenrode (Sonderheft) 188
Patel AV, Vorlop KD (1994) Entrapment of biological control agents applied to entomopathogenic nematodes. Biotechnol Tech 8(8):569–574
Patel AV, Pusch I, Mix-Wagner G, Vorlop KD (2000) A novel encapsulation technique for the construction of artificial seeds. Plant Cell Rep 19(9):868–874
Patel AV, Rose T, Vorlop KD (2001). Controlled release of Hirsutella rhossiliensis from hollow beads for biological control of phytopathogenic nematodes. In: Janssen FJJG (eds) COST 830—Microbial Inoculants for Agriculture and Environment Workgroup Meeting “Formulation of Microbial Inoculants” in Braunschweig, 05/02–06/02/1999, ISBN 92-894-0226-1, 50-52
Patel AV, Rose T, Vorlop KD (2002) Encapsulation of Hirsutella rhossiliensis in hollow beads based on sulfoethylcellulose to control plant-parasitic nematodes. Landbauforschung Völkenrode SH 241:145–150
Paul GC, Priede MA, Thomas CR (1999) Relationship between morphology and citric acid production in submerged Aspergillus niger fermentations. Biochem Eng J 3:121–129
Philipp B, Hong LT, Linow KJ, Dawydoff W, Arnold K (1980) Über Symplexe von Cellulosederivaten. 8. Mitt. Untersuchungen zur Wasserquellung unterschiedlicher Symplexfällungen. Acta Polym 31(10):654–658
Qadeer Choudhary A, Pirt J (1965) Metal-complexing agents as metal buffers in media for the growth of Aspergillus niger. J Gen Microbiol 41:99–107
Riley GL, Tucker KG, Paul GC, Thomas CR (2000) Effect of biomass concentration and mycelial morphology on fermentation broth rheology. Biotechnol Bioeng 68(2):160–172
Rose T, Neumann B, Thielking H, Koch W, Vorlop KD (2000) Hollow beads of sulfoethyl cellulose (SEC) on the basis of polyelectrolyte complexes. Chem Eng Technol 23(9):769–772
Sturhan D, Schneider R (1980) Hirsutella heteroderae, ein neuer nematodenparasitärer Pilz. Phytopathologische Zeitschrift 99:105–115
Tedford EC, Jaffee BA, Muldoon AE (1992) Effect of soil moisture on transmission of the nematophagous fungus Hirsutella rhossiliensis to cyst and root-knot nematodes. Phytopathology 82(10):1002–1007
Velvis H, Kamp P (1995) Infection of second stage juveniles of potato cyst nematodes by the nematophagous fungus Hirsutella rhossiliensis in Dutch potato fields. Nematologica 41:617–627
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by the Agency for Renewable Resources (FNR) of the German Ministry of Nutrition, Agriculture and Forestry (FKZ 98 NR 067) and by the “Gesellschaft der Freunde der FAL (GdF)” with a grant for junior scientists to Dr. A. Patel.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patel, A.V., Jakobs-Schönwandt, D., Rose, T. et al. Fermentation and microencapsulation of the nematophagous fungus Hirsutella rhossiliensis in a novel type of hollow beads. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 89, 1751–1760 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-3046-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-3046-9