Abstract
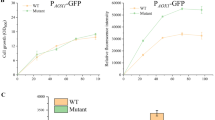
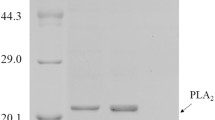
Increased copy number of foreign gene can result in the alteration of normal metabolism in Pichia pastoris. To better understand the effect of foreign gene dosage on the cellular physiology of P. pastoris cells, comparative transcriptional analysis was performed among three P. pastoris strains carrying 0, 6, and 18 copies of porcine insulin precursor (PIP) expression cassettes, respectively. mRNA levels of 13 selected genes involved in methanol metabolic pathway, central metabolic pathway, protein folding, and oxidative stress were determined by real-time PCR. Results showed that enhanced PIP copy number resulted in an increase in PIP mRNA and also in folding stress on the yeast cells’ endoplasmic reticulum. The metabolism of 6-copy P. pastoris strain was not significantly changed as compared to 0-copy strain (control). In contrast, physiology of 18-copy strain was remarkably affected, characterized by the upregulation of antioxidative genes and readjusted expression level of methanol metabolic pathway genes. These data suggested that high copy P. pastoris strain might be suffering from protein folding-related oxidative stress and insufficient supply of carbon and energy sources.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cos O, Serrano A, Montesinos JL, Ferrer P, Cregg JM, Valero F (2005) Combined effect of the methanol utilization (Mut) phenotype and gene dosage on recombinant protein production in Pichia pastoris fed-batch cultures. J Biotechnol 116:321–335
Curvers S, Linnemann J, Klauser T, Wandrey C, Takors R (2002) Recombinant protein production with Pichia pastoris in continuous fermentation—kinetic analysis of growth and product formation. Eng Life Sci 8:229–235
Daly R, Hearn MT (2005) Expression of heterologous proteins in Pichia pastoris: a useful experimental tool in protein engineering and production. J Mol Recognit 18:119–138
d'Anjou MC, Daugulis AJ (2001) A rational approach to improving productivity in recombinant Pichia pastoris fermentation. Biotechnol Bioeng 72:1–11
Dragosits M, Stadlmann J, Albiol J, Baumann K, Maurer M, Gasser B, Sauer M, Altmann F, Ferrer P, Mattanovich D (2009) The effect of temperature on the proteome of recombinant Pichia pastoris. J Proteome Res 8:1380–1392
Gasser B, Maurer M, Rautio J, Sauer M, Bhattacharyya A, Saloheimo M, Penttila M, Mattanovich D (2007) Monitoring of transcriptional regulation in Pichia pastoris under protein production conditions. BMC Genomics 8:179
Gasser B, Saloheimo M, Rinas U, Dragosits M, Rodriguez-Carmona E, Baumann K, Giuliani M, Parrilli E, Branduardi P, Lang C, Porro D, Ferrer P, Tutino ML, Mattanovich D, Villaverde A (2008) Protein folding and conformational stress in microbial cells producing recombinant proteins: a host comparative overview. Microb Cell Fact 7:11
Gellissen G (2000) Heterologous protein production in methylotrophic yeasts. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 54:741–750
Haynes CM, Titus EA, Cooper AA (2004) Degradation of misfolded proteins prevents ER-derived oxidative stress and cell death. Mol Cell 15:767–776
Hohenblum H, Gasser B, Maurer M, Borth N, Mattanovich D (2004) Effects of gene dosage, promoters, and substrates on unfolded protein stress of recombinant Pichia pastoris. Biotechnol Bioeng 85:367–375
Huo XD, Liu YY, Wang X, Ouyang PK, Niu ZD, Shi YH, Qiu BS (2007) Co-expression of human protein disulfide isomerase (hPDI) enhances secretion of bovine follicle-stimulating hormone (bFSH) in Pichia pastoris. Protein Expr Purif 54:234–239
Inan M, Aryasomayajula D, Sinha J, Meagher MM (2006) Enhancement of protein secretion in Pichia pastoris by overexpression of protein disulfide isomerase. Biotechnol Bioeng 93:771–778
Jungo C, Rerat C, Marison IW, Von Stockar U (2006) Quantitative characterization of the regulation of the synthesis of alcohol oxidase and of the expression of recombinant avidin in a Pichia pastoris Mut+ strain. Enzyme Microb Technol 39:936–944
Jungo C, Marison I, von Stockar SU (2007) Regulation of alcohol oxidase of a recombinant Pichia pastoris Mut+ strain in transient continuous cultures. J Biotechnol 130:236–246
Kimata Y, Ishiwata-Kimata Y, Yamada S, Kohno K (2006) Yeast unfolded protein response pathway regulates expression of genes for anti-oxidative stress and for cell surface proteins. Genes Cells 11:59–69
Kohrer K, Domdey H (1991) Preparation of high molecular weight RNA. Methods Enzymol 194:398–405
Liu SH, Chou WI, Sheu CC, Chang MD (2005) Improved secretory production of glucoamylase in Pichia pastoris by combination of genetic manipulations. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 326:817–824
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔ method. Methods 25:402–408
Ma Y, Hendershot LM (2001) The unfolding tale of the unfolded protein response. Cell 107:827–830
Malhotra JD, Miao H, Zhang K, Wolfson A, Pennathur S, Pipe SW, Kaufman RJ (2008) Antioxidants reduce endoplasmic reticulum stress and improve protein secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci 105:18525–18530
Mansur M, Cabello C, Hernandez L, Pais J, Varas L, Valdes J, Terrero Y, Hidalgo A, Plana L, Besada V, Garcia L, Lamazares E, Castellanos L, Martinez E (2005) Multiple gene copy number enhances insulin precursor secretion in the yeast Pichia pastoris. Biotechnol Lett 27:339–345
Mattanovich D, Gasser B, Hohenblum H, Sauer M (2004) Stress in recombinant protein producing yeasts. J Biotechnol 113:121–135
Penninckx MJ (2002) An overview on glutathione in Saccharomyces versus non-conventional yeasts. FEMS Yeast Res 2:295–305
Perrone GG, Tan SX, Dawes IW (2008) Reactive oxygen species and yeast apoptosis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1783:1354–1368
Resina D, Bollok M, Khatri NK, Valero F, Neubauer P, Ferrer P (2007) Transcriptional response of Pichia pastoris in fed-batch cultivations to Rhizopus oryzae lipase production reveals UPR induction. Microb Cell Fact 6:21
Scorer CA, Clare JJ, Mccombie WR, Romanos MA, Sreekrishna K (1994) Rapid selection using g418 of high copy number transformants of Pichia pastoris for high-level foreign gene-expression. Biotechnology 12:181–184
Sunga AJ, Cregg JM (2004) The Pichia pastoris formaldehyde dehydrogenase gene (FLD1) as a marker for selection of multicopy expression strains of P. pastoris. Gene 330:39–47
Travers KJ, Patil CK, Wodicka L, Lockhart DJ, Weissman JS, Walter P (2000) Functional and genomic analyses reveal an essential coordination between the unfolded protein response and ER-associated degradation. Cell 101:249–258
Vad R, Nafstad E, Dahl LA, Gabrielsen OS (2005) Engineering of a Pichia pastoris expression system for secretion of high amounts of intact human parathyroid hormone. J Biotechnol 116:251–260
Vassileva A, Chugh DA, Swaminathan S, Khanna N (2001) Effect of copy number on the expression levels of hepatitis B surface antigen in the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris. Protein Expr Purif 21:71–80
Wen SH, Zhang T, Tan TW (2005) Optimization of the amino acid composition in glutathione fermentation. Process Biochem 40:3474–3479
Xiao AF, Zhou XS, Zhou L, Zhang YX (2006) Improvement of cell viability and hirudin production by ascorbic acid in Pichia pastoris fermentation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 72:837–844
Yano T, Takigami E, Yurimoto H, Sakai Y (2009) Yap1-regulated glutathione redox system curtails accumulation of formaldehyde and reactive oxygen species in methanol metabolism of Pichia pastoris. Eukaryot Cell 8:540–549
Yurimoto H, Kato N, Sakai Y (2005) Assimilation, dissimilation, and detoxification of formaldehyde, a central metabolic intermediate of methylotrophic metabolism. Chem Rec 5:367–375
Zhu T, Guo M, Sun C, Qian J, Zhuang Y, Chu J, Zhang S (2009a) A systematical investigation on the genetic stability of multi-copy Pichia pastoris strains. Biotechnol Lett 31:679–684
Zhu T, Guo M, Tang Z, Zhang M, Zhuang Y, Chu J, Zhang S (2009b) Efficient generation of multi-copy strains for optimizing secretory expression of porcine insulin precursor in yeast Pichia pastoris. J Appl Microbiol 107:954–963
Acknowledgments
We thank Professor James M. Gregg (Keck Graduate Institute of Applied Life Sciences) for providing sequence information. This research was supported by a grant from National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 30560006) and by National Basic Research Program of China (no. 2007CB714303).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, T., Guo, M., Zhuang, Y. et al. Understanding the effect of foreign gene dosage on the physiology of Pichia pastoris by transcriptional analysis of key genes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 89, 1127–1135 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2944-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2944-1