Abstract
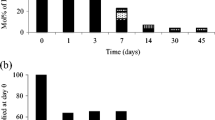
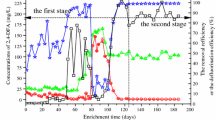
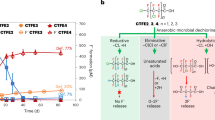
The accumulation of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) has been detected in wildlife, soil, and water. Further, 8:2 fluorotelomer alcohol (8:2 FTOH) is used for the industrial synthesis of other fluorotelomer compounds, surfactants, and polymeric materials; however, it was recently found to be a potential source of PFOA contamination in the environment. 1H,1H,2H,2H,8H,8H-perfluorododecanol (degradable telomer fluoroalcohol (DTFA)), which is a newly developed fluorotelomer, contains the –CH2– group in the fluorinated carbon backbone, making it potentially degradable through biological reactions. In this study, we investigated the biodegradation of DTFA in a mixed bacterial culture obtained from activated sludge. Optimized quantitative liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry analysis of the predicted metabolites generated in the culture revealed accumulations of the transformation products from DTFA to 2H,2H,8H,8H-PFDoA and 2H,8H,8H-2-PFUDoA via multiple processes. Furthermore, the production of short fluorinated compounds, perfluorobutanoic acid, perfluoropentanoic acid, and perfluoropentanedioic acid, which are believed to have lower accumulation potential and toxicity toward organisms than PFOA, was determined.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdellatif AG, Preat V, Taper HS, Roberfroid M (1991) The modulation of rat-liver carcinogenesis by perfluorooctanoic acid, a peroxisome proliferator. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 111:530–537
Apelberg BJ, Witter FR, Herbstman JB, Calafat AM, Halden RU, Needham LL, Goldman LR (2007) Cord serum concentrations of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoate (PFOA) in relation to weight and size at birth. Environ Health Perspect 115:1670–1676
Barber JL, Berger U, Chaemfa C, Huber S, Jahnke A, Temme C, Jones KC (2007) Analysis of per- and polyfluorinated alkyl substances in air samples from Northwest Europe. J Environ Monit 9:530–541
D’eon JC, Mabury SA (2007) Production of perfluorinated carboxylic acids (PFCAs) from the biotransformation of polyfluoroalkyl phosphate surfactants (PAPS): exploring routes of human contamination. Environ Sci Technol 41:4799–4805
de Voogt P, Saez M (2006) Analytical chemistry of perfluoroalkylated substances. Trends Anal Chem 25:326–342
Dinglasan MJA, Ye Y, Edwards EA, Mabury SA (2004) Fluorotelomer alcohol biodegradation yields poly- and perfluorinated acids. Environ Sci Technol 38:2857–2864
Ellis DA, Martin JW, De Silva AO, Mabury SA, Hurley MD, Andersen MPS, Wallington TJ (2004) Degradation of fluorotelomer alcohols: a likely atmospheric source of perfluorinated carboxylic acids. Environ Sci Technol 38:3316–3321
Houde M, Martin JW, Letcher RJ, Solomon KR, Muir DCG (2006) Biological monitoring of polyfluoroalkyl substances: a review. Environ Sci Technol 40:3463–3473
Kennedy GL, Butenhoff JL, Olsen GW, O’Connor JC, Seacat AM, Perkins RG, Biegel LB, Murphy SR, Farrar DG (2004) The toxicology of perfluorooctanoate. Crit Rev Toxicol 34:351–384
Kudo N, Bandai N, Suzuki E, Katakura M, Kawashima Y (2000) Induction by perfluorinated fatty acids with different carbon chain length of peroxisomal beta-oxidation in the liver of rats. Chem Biol Interact 124:119–132
Lau C, Butenhoff JL, Rogers JM (2004) The developmental toxicity of perfluoroalkyl acids and their derivatives. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 198:231–241
Liu J, Lee LS, Nies LF, Nakatsu CH, Turco RF (2007) Biotransformation of 8:2 fluorotelorner alcohol in soil and by soil bacteria isolates. Environ Sci Technol 41:8024–8030
Liu J, Wang N, Szostek B, Buck RC, Panciroli PK, Folsom PW, Sulecki LM, Bellin CA (2010) 6-2 Fluorotelomer alcohol aerobic biodegradation in soil and mixed bacterial culture. Chemosphere 78:437–444
Marasco EK, Schmidt-Dannert C (2008) Identification of bacterial carotenoid cleavage dioxygenase homologues that cleave the interphenyl alpha, beta double bond of stilbene derivatives via a monooxygenase reaction. ChemBioChem 9:1450–1461
Nabb DL, Szostek B, Himmelstein MW, Mawn MP, Gargas ML, Sweeney LM, Stadler JC, Buck RC, Fasano WJ (2007) In vitro metabolism of 8-2 fluorotelomer alcohol: interspecies comparisons and metabolic pathway refinement. Toxicol Sci 100:333–344
Nguyen HP, Schug KA (2008) The advantages of ESI-MS detection in conjunction with HILIC mode separations: fundamentals and applications. J Sep Sci 31:1465–1480
Olsen GW, Burris JM, Ehresman DJ, Froehlich JW, Seacat AM, Butenhoff JL, Zobel LR (2007) Half-life of serum elimination of perfluorooctanesulfonate, perfluorohexanesulfonate, and perfluorooctanoate in retired fluorochemical production workers. Environ Health Perspect 115:1298–1305
Prevedouros K, Cousins IT, Buck RC, Korzeniowski SH (2006) Sources, fate and transport of perfluorocarboxylates. Environ Sci Technol 40:32–44
Sauveplane V, Kandel S, Kastner PE, Ehlting J, Compagnon V, Werck-Reichhart D, Pinot F (2009) Arabidopsis thaliana CYP77A4 is the first cytochrome P450 able to catalyze the epoxidation of free fatty acids in plants. FEBS J 276:719–735
Senthilkumar K, Ohi E, Sajwan K, Takasuga T, Kannan K (2007) Perfluorinated compounds in river water, river sediment, market fish, and wildlife samples from Japan. Bullet Environ Contam Toxicol 79:427–431
Wallington TJ, Hurley MD, Xia J, Wuebbles DJ, Sillman S, Ito A, Penner JE, Ellis DA, Martin J, Mabury SA, Nielsen OJ, Andersen MPS (2006) Formation of C7F15COOH (PFOA) and other perfluorocarboxylic acids during the atmospheric oxidation of 8:2 fluorotelomer alcohol. Environ Sci Technol 40:924–930
Wang N, Szostek B, Buck RC, Folsom PW, Sulecki LM, Capka V, Berti WR, Gannon JT (2005a) Fluorotelomer alcohol biodegradation—direct evidence that perfluorinated carbon chains breakdown. Environ Sci Technol 39:7516–7528
Wang N, Szostek B, Folsom PW, Sulecki LM, Capka V, Buck RC, Berti WR, Gannon JT (2005b) Aerobic biotransformation of C-14-labeled 8-2 telomer B alcohol by activated sludge from a domestic sewage treatment plant. Environ Sci Technol 39:531–538
Wang N, Szostek B, Buck RC, Folsom PW, Sulecki LM, Gannon JT (2009) 8-2 Fluorotelomer alcohol aerobic soil biodegradation: pathways, metabolites, and metabolite yields. Chemosphere 75:1089–1096
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Fig. S1
1H-NMR (a) and 19F-NMR (b) spectra of DTFA (PPT 176 kb)
Fig. S2
1H-NMR (a) and 19F-NMR (b) spectra of 2H,2H,8H,8H-perfluorododecanoic acid (2H,2H,8H,8H-PFDoA) (PPT 173 kb)
Fig. S3
1H-NMR (a) and 19F-NMR (b) spectra of 2H,8H,8H-2-perfluorododecenoic acid (2H,8H,8H-2-PFUDoA) (PPT 202 kb)
Fig. S4
Time course of metabolite formation in the a activated sludge culture. b Zoom view of part a, showing short-chained metabolites resulting from long-term biodegradation in the presence of air flow (PPT 87 kb)
Fig. S5
Time course of metabolite formation in the E. coli culture in the presence of air flow (PPT 79 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arakaki, A., Ishii, Y., Tokuhisa, T. et al. Microbial biodegradation of a novel fluorotelomer alcohol, 1H,1H,2H,2H,8H,8H-perfluorododecanol, yields short fluorinated acids. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 88, 1193–1203 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2815-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2815-9