Abstract
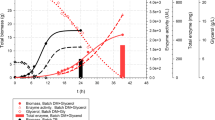
Recombinant Cupriavidus necator H 16 with a novel metabolic pathway using a cobalamin-dependent mutase was exploited to produce 2-hydroxyisobutyric acid (2-HIBA) from renewable resources through microbial fermentation. 2-HIBA production capacities of different strains of C. necator H 16 deficient in the PHB synthase gene and genetically engineered to enable the production of 2-HIBA from the intracellular PHB precursor (R)-3-hydroxybutyryl-CoA were evaluated in 48 parallel milliliter-scale stirred tank bioreactors (V = 11 mL). The effects of media composition, limitations, pH, and feed rate were studied with respect to the overall process performances of the different recombinant strains. 2-HIBA production was at a maximum at nitrogen limiting conditions and if the pH was controlled between 6.8 and 7.2 under fed-batch operating conditions (intermittent fructose addition). The final concentration of 2-HIBA was 7.4 g L−1 on a milliliter scale. Best reaction conditions identified on the milliliter scale were transferred to a laboratory-scale fed-batch process in a stirred tank bioreactor (V = 2 L). Two different process modes for the production of 2-HIBA, a single-phase and a dual-phase fermentation procedure, were evaluated and compared on a liter scale. The final concentration of 2-HIBA was 6.4 g L−1 on a liter scale after 2 days of cultivation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anastassiadis S (2007) l-lysine fermentation. Recent Pat Biotechnol 1:10–24
Hancock RD, Viola R (2002) Biotechnological approaches for l-ascorbic acid production. Trends Biotechnol 20:299–305
Khanna S, Srivastava AK (2005) Recent advances in microbial polyhydroxyalkanoates. Process Biochem 40:607–619
Kim BS, Lee SC, Lee SY, Chang HN, Chang YK, Woo SI (1994) Production of poly(3-hydroxybutyric acid) by fed-batch culture of AIcaIigenes eutrophus with glucose concentration control. Biotechnol Bioeng 43:892–898
Kovach ME, Elzer PH, Hill DS, Robertson GT, Farris MA, Roop RM, Peterson KM (1995) Four new derivatives of the broad-host-range cloning vector pBBR1MCS, carrying different antibiotic-resistance cassettes. Gene 166:175–176
Kusterer A, Krause C, Kaufmann K, Arnold M, Weuster-Botz D (2008) Fully automated single-use stirred-tank bioreactors for parallel microbial cultivations. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 31:207–215
Lechner U, Brodkorb D, Geyer R, Hause G, Hartig C, Auling G, Fayolle-Guichard F, Piveteau P, Müller RH, Rohwerder T (2007) Aquincola tertiaricarbonis gen. nov., sp nov., a tertiary butyl moiety-degrading bacterium. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:1295–1303
Lee SH, Park SJ, Lee SY, Hong SH (2008) Biosynthesis of enantiopure (S)-3-hydroxybutyric acid in metabolically engineered Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 79:633–641
Lee SY (1996) Bacterial polyhydroxyalkanoates. Biotechnol Bioeng 49:1–14
Link H, Anselment B, Weuster-Botz D (2010) Rapid media transition: an experimental approach for steady state analysis of metabolic pathways. Biotechnol Prog 26(1):1–10
Link H, Weuster-Botz D (2006) Genetic algorithm for multi-objective experimental optimization. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 29:385–390
Link H, Weuster-Botz D (2007) Steady-state analysis of metabolic pathways: Comparing the double modulation method and the lin-log approach. Metab Eng 9:433–441
Liu Q, Ouyang SP, Chung A, Wu Q, Chen GQ (2007) Microbial production of R-3-hydroxybutyric acid by recombinant E. coli harboring genes of phbA, phbB, and tesB. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 76:811–818
McKinlay JB, Vieille C, Zeikus JG (2007) Prospects for a bio-based succinate industry. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 76:727–740
Müller RH, Rohwerder T (2007) Method for the enzymatic production of 2-hydroxy-2-methyl carboxylic acids. C12P 7/42 (2006.01), C12N 9/90 (2006.01), C12P 7/52 (2006.01)
Pohlmann A, Fricke WF, Reinecke F, Kusian B, Liesegang H, Cramm R, Eitinger T, Ewering C, Potter M, Schwartz E, Strittmatter A, Voss I, Gottschalk G, Steinbüchel A, Friedrich B, Bowien B (2006) Genome sequence of the bioplastic-producing “Knallgas” bacterium Ralstonia eutropha H16. Nat Biotechnol 24:1257–1262
Puskeiler R, Kusterer A, John GT, Weuster-Botz D (2005) Miniature bioreactors for automated high-throughput bioprocess design (HTBD): reproducibility of parallel fed-batch cultivations with Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 42:227–235
Reinecke F (2007) Genome sequence of the PHA-Producing “Knallgas” bacterium Ralstonia eutropha H16: analysis with regard to PHA Metabolism. Dissertation, Münster
Reinecke F, Steinbüchel A (2009) Ralstonia eutropha strain H16 as model organism for PHA metabolism and for biotechnological production of technically interesting biopolymers. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 16:91–108
Reinecke L, Schaffer S, Marx A, Pötter M, Haas T (2009) Recombinant Cell producing 2-hydroxyisobutyric acid. C12P 7/42 (2006.01), C12N 15/63 (2006.01), C12N 15/70 (2006.01)
Reinecke L, Thiessenhusen A, Schaffer S, Buchhaupt M, Köhler T, Marx A (2010) Verwendung eines zu einem MeaB-Protein homologen Proteins zur Erhöhung der enzymatischen Aktivität einer 3-Hydroxycarbonsäure-CoA-Mutase. Submitted German patent application
Rohwerder T, Breuer U, Benndorf D, Lechner U, Müller RH (2006) The alkyl tert-butyl ether intermediate 2-hydroxyisobutyrate is degraded via a novel cobalamin-dependent mutase pathway. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:4128–4135
Rohwerder T, Müller RH (2010) Biosynthesis of 2-hydroxyisobutyric acid (2-HIBA) from renewable carbon. Microb Cell Fact 9:13
Ryu HW, Cho KS, Kim BS, Chang YK, Chang HN, Shim HJ (1999) Mass production of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) by fed-batch cultures of Ralstonia eutropha with nitrogen and phosphate limitation. J Microbiol Biotechnol 9:751–756
Sauer M, Porro D, Mattanovich D, Branduardi P (2008) Microbial production of organic acids: expanding the markets. Trends Biotechnol 26:100–108
Schlegel HG, Lafferty R, Krauss I (1970) The isolation of mutants not accumulating poly-β-hydroxybutyric acid. Arch Microbiol 71:283–294
Schubert P, Steinbüchel A, Schlegel HG (1988) Cloning of the Alcaligenes eutrophus genes for synthesis of poly-beta-hydroxybutyric acid (PHB) and synthesis of PHB in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 170:5837–5847
Soccol CR, Vandenberghe LP, Rodrigues C, Pandey A (2006) New perspectives for citric acid production and application. Food Technol Biotechnol 44:141–149
Verlinden RA, Hill DJ, Kenward MA, Williams CD, Radecka I (2007) Bacterial synthesis of biodegradable polyhydroxyalkanoates. J Appl Microbiol 102:1437–1449
Vester A, Hans M, Hohmann HP, Weuster-Botz D (2009) Discrimination of riboflavin producing Bacillus subtilis strains based on their fed-batch process performances on a millilitre scale. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 84:71–76
Vogel GH (2008) Change in raw material base in the chemical industry. Chem Eng Technol 31:730–735
Werpy T, Petersen G (2004) Top value added chemicals from biomass. http://www1.eere.energy.gov/biomass/pdfs/35523.pdf. Accessed 14 Jan 2010
Weuster-Botz D (2000) Experimental design for fermentation media development: statistical design or global random search? J Biosci Bioeng 90:473–483
Weuster-Botz D, Puskeiler R, Kusterer A, Kaufmann K, John GT, Arnold M (2005) Methods and milliliter scale devices for high-throughput bioprocess design. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 28:109–119
Willke T, Vorlop KD (2004) Industrial bioconversion of renewable resources as an alternative to conventional chemistry. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 66:131–142
Acknowledgments
This research was financed and supported by Evonik Degussa GmbH and funded by the Bundesministerium für Ernährung, Landwirtschaft und Verbraucherschutz (BMELV). Consulting and assistance from A. Marx (Evonik Degussa GmbH), A. Thiessenhusen (Evonik Degussa GmbH), F. Erhardt (Evonik Degussa GmbH), and G. Faust are gratefully appreciated. Furthermore, this work was carried out under mentoring of the TUM Graduate School.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hoefel, T., Wittmann, E., Reinecke, L. et al. Reaction engineering studies for the production of 2-hydroxyisobutyric acid with recombinant Cupriavidus necator H 16. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 88, 477–484 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2739-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2739-4