Abstract
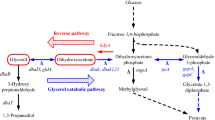
In the Klebsiella pneumoniae reduction pathway for 1,3-propanediol (1,3-PD) synthesis, glycerol is first dehydrated to 3-hydroxypropionaldehyde (3-HPA) and then reduced to 1,3-PD with NADH consumption. Rapid conversion of 3-HPA to 1,3-PD is one of the ways to improve the yield of 1,3-PD from glycerol and to avoid 3-HPA accumulation, which depends on enzyme activity of the reaction and the amount of reducing equivalents available from the oxidative pathway of glycerol. In the present study, the yqhD gene, encoding 3-propanediol oxidoreductase isoenzyme from Escherichia coli and the dhaT gene, encoding 3-propanediol oxidoreductase from K. pneumoniae were expressed individually and co-expressed in K. pneumoniae using the double tac promoter expression plasmid pEtac-dhaT-tac-yqhD. The three resultant recombinant strains (K. pneumoniae/pEtac-yqhD, K. pneumoniae/pEtac-dhaT, and K. pneumoniae/pEtac-dhaT-tac-yqhD) were used for fermentation studies. Experimental results showed that the peak values for 3-HPA production in broth of the three recombinant strains were less than 25% of that of the parent strain. Expression of dhaT reduced formation of by-products (ethanol and lactic acid) and increased molar yield of 1,3-PD slightly, while expression of yqhD did not enhance molar yield of 1,3-PD, but increased ethanol concentration in broth as NADPH participation in transforming 3-HPA to 1,3-PD allowed more cellular NADH to be used to produce ethanol. Co-expression of both genes therefore decreased by-products and increased the molar yield of 1,3-PD by 11.8%, by catalyzing 3-HPA conversion to 1,3-propanediol using two cofactors (NADH and NADPH). These results have important implications for further studies involving use of YqhD and DhaT for bioconversion of glycerol into 1,3-PD.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidman JG, Smith JA, Struhl K (1987) Current protocols in molecular microbiology. Wiley, New York
Barbirato F, Grivet JP, Soucaille P, Bories A (1996) 3-HPA, an inhibitory metabolite of glycerol fermentation to 1, 3-propanediol by enterobacterial species. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:1448–1451
Bentley WE, Mirjalili N, Andersen DC, Davis RH, Kompala DS (1990) Plasmid encoded protein: the principal factor in the “metabolic burden” associated with recombinant bacteria. Biotechnol Bioeng 35:668–681
Biebl H, Menzel K, Zeng AP, Deckwer WD (1999) Microbial production of 1, 3-propanediol. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 52:289–297
Cirde SJ, Stone L, Boruv CS (1945) Acrolein determination by means of tryptophane. Ind Eng Chem Anal Ed 17:259–262
Emptage M, Haynie SL, Laffend LA, Pucci JP, White G (2003) Process for the biological production of 1,3-propanediol with high titer. US patent no 651473
Fang HY, Zhang C, Zhuge B, Zhuge J (2009) Construction of novel recombinant strains capable of producing 1, 3-propanediol. Chin J Appl Environ Biol 15(5):708–712
Forage RG, Foster AM (1982) Glycerol fermentation in Klebsiella pneumoniae: functions of the coenzyme B12-dependent glycerol and diol dehydratases. J Bacteriol 149:413–419
Forage R, Lin ECC (1982) dha system mediating aerobic and anaerobic dissimilation of glycerolin Klebsiella pneumoniae NCIB418. J Bacteriol 15:591–593
Fournet-Fayard S, Joly B, Forestier C (1995) Transformation of wild type Klebsiella pneumoniae with plasmid DNA by electroporation. J Microbiol Methods 24:49–54
Gonzlez-Pajuedo M, Andrade JC, Vasconcelos I (2004) Production of 1,3-propanediol by Clostridium butyricum VPI 3266 using a synthetic medium and raw glycerol. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 31:442–446
Kurian JV (2005) A new polymer platform for the future—Sorona from corn derived 1,3-propanediol. J Polym Environ 44:857–862
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Ma Z, Rao Z, Xu L, Liao X, Fang H, Zhuge B, Zhuge J (2009) Expression of dha operon required for 1,3-PD formation in Escherichia coli and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Curr Microbiol. doi:10.1007/s00284-009-9528-2
Menzel K, Zeng AP, Deckwer WD (1997) High concentration and productivity of 1,3-propanediol from continuous fermentation of glycerol by Klebsiella pneumoniae. Enzyme Microb Technol 20:82–86
Mu Y, Teng H, Zhang DJ, Wang W, Xiu ZL (2006) Microbial production of 1,3-propanediol by Klebsiella pneumoniae using crude glycerol from biodiesel preparations. Biotechnol Lett 28:1755–1759
Nemeth A, Sevella B (2008) Development of a new bioprocess for production of 1,3-propanediol: modeling of glycerol bioconversion to 1,3-propanediol with Klebsiella pneumoniae enzymes. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 144:47–58
Rao Z, Ma Z, Shen W, Fang H, Zhuge J, Wang X (2008) Engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae that produces 1,3-propanediol from d-glucose. J Appl Microbiol 105:1768–1776
Ruch FE, Lengeler J, Lin ECC (1974) Regulation of glycerol catabolism in Klebsiella aerogenes. J Bacteriol 119:50–56
Saxena RK, Anand P, Saran S, Isar J (2009) Microbial production of 1,3-propanediol: recent developments and emerging opportunities. Biotechnol Adv. doi:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2009.07.003
Yang G, Tian J, Li J (2007) Fermentation of 1,3-propanediol by a lactate deficient mutant of Klebsiella oxytoca under microaerobic conditions. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 73:1017–1024
Zhang XM, Zhuge J (2007) Construction of novel recombinant strain harboring glycerol dehydratase reactivating factor capable of producing 1,3-propanediol. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao 23:841–845
Zhang XM, Tang XM, Zhuge B, Shen W, Rao ZM, Fang HY, Zhuge J (2005) Construction of novel recombinant Escherichia coli capable of production 1,3-propanediol. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao 21:743–747
Zhang Z, Li Y, Du C, Liu M, Cao Z (2006) Inactivation of aldehyde ehydrogenase: a key factor for engineering 1,3-propanediol production by Klebsiella pneumoniae. Metab Eng 8:578–586
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Programs for High Technology Research and Development of China (2006AA020103 and 2009AA02Z210).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhuge, B., Zhang, C., Fang, H. et al. Expression of 1,3-propanediol oxidoreductase and its isoenzyme in Klebsiella pneumoniae for bioconversion of glycerol into 1,3-propanediol. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 87, 2177–2184 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2678-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2678-0