Abstract
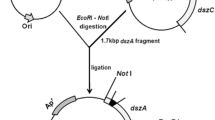
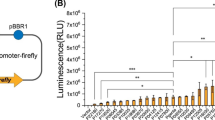
The bacterium Gordonia alkanivorans RIPI90A has been previously reported as dibenzothiophene-desulfurizing strain. The present study provides a complete investigation of the dsz operon including dsz promoter analysis from desulfurization competent strain belonging to the genus Gordonia. PCR was used to amplify the dszABC genes and adaptor ligation-based PCR-walking strategy used to isolate the dsz promoter. Unlike the dsz operon of Rhodococcus erythropolis, the operon of RIPI90A was located on chromosome. Despite the remarkably high homology between dsz genes of G. alkanivorans RIPI90A and R. erythropolis IGST8, promoter sequences of the strains were not very similar. The dsz promoter of G. alkanivorans RIPI90A shows only 52.5% homology to that of R. erythropolis IGTS8 and Gordonia nitida. Deletion analysis of the dsz promoter from RIPI90A using luciferase as a reporter gene revealed that the dsz promoter was located in regions from −156 to −50.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schäffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Alves L, Melo M, Mendonca D, Simoes F, Matos J, Tenreiro R, Girio FM (2007) Sequencing, cloning and expression of the dsz genes required for dibenzothiophene sulfone desulfurization from Gordonia alkanivorans strain 1B. Enzyme Microb Technol 40:1598–1603
Arenskötter M, Baumeister D, Kalscheuer R, Steinbüchel A (2003) Identification and application of plasmids suitable for transfer of foreign DNA to members of the genus Gordonia. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:4971–4974
Caro A, Boltes K, Calvo LP (2007) Dibenzothiophene biodesulfurization in resting cell conditions by aerobic bacteria. Biochem Eng J 35:191–197
Chen H, Zhang W, Cai Y, Zhang Y, Li W (2008) Elucidation of 2-hydroxybiphenyl effect on dibenzothiophene desulfurization by Microbacterium sp. strain ZD-M2. Bioresour Technol 99:6928–6933
Denis-Larose C, Bergeron H, Labbe D, Greer CW, Hawari J, Grossman MJ, Sankey BM, Lau PCK (1998) Characterization of the basic replicon of Rhodococcus plasmid pSOX and development of a Rhodococcus–Escherichia coli shuttle vector. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:4363–4367
Denome SA, Oldfield C, Nash LJ, Young KD (1994) Characterization of the desulfurization genes from Rhodococcus sp. strain IGTS8. J Bacteriol 176:6707–6716
Emamzadeh A, Hosseinkhani S, Sadeghizadeh M, Nikkhah M, Chaichi MJ, Mortazavi M (2006) cDNA cloning, expression and homology modeling of luciferase from the firefly Lampyroidea maculata. J Biochem Mol Biolo 39:578–585
Gallardo ME, Ferrandez A, Lorenzo VD, Garcia JL, Diaz E (1997) Designing recombinant Pseudomonas strains to enhance biodesulfurization. J Bacteriol 179:7156–7160
Gray KA, Mrachko GT, Squires CH (2003) Biodesulfurization of fossil fuels. Curr Opin Microbiol 6:229–235
Gupta N, Roychoudhury PK, Deb JK (2005) Biotechnology of desulfurization of diesel: prospects and challenges. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 66:356–366
Hirasawa K, Ishii Y, Kobayashi M, Koizumi K (2001) Improvement of desulfurizing activity in Rhodococcus erythropolis KA2-5-1 by genetic engineering. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 65:239–246
Ishii Y, Konishi J, Okada H, Hirasawa K, Onaka T, Suzuki M (2000) Operon structure and functional analysis of the genes encoding thermophilic desulfurizing enzymes of Paenibacillus sp. A11-2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 270:81–88
Kilbane JJ (2006) Microbial biocatalyst development to upgrade fossil fuels. Curr Opin Biotechnol 17:305–314
Kilbane JJ, Robbins J (2007) Characterization of the dszABC genes of Gordonia amicalis F.5.25.8 and identification of conserved protein and DNA sequences. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 75:843–851
Li GQ, Ting MA, Li SS, Li H, Liang F, Liu R (2007) Improvement of dibenzothiophene biodesulfurization activity by removing the gene overlap in the dsz operon. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 71:849–854
Li GQ, Li SS, Li H, Zhang ML, Wang J, Zhu L, Liang F, Liu R, Ting MA (2008) Genetic rearrangement strategy for optimizing the dibenzothiophene biodesulfurization pathway in Rhodococcus erythropolis. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:971–976
Li ZM, Charles HS, Monticello DJ, Childs JD (1996) Genetic analysis of the dsz promoter and associated regulatory regions of Rhodococcus erythropolis IGTS8. J Bacteriol 178:6409–6418
Matsui T, Saeki H, Shinzato N, Matsuda H (2007) Analysis of the 7.6-kb cryptic plasmid pNC500 from Rhodococcus rhodochrous B-276 and construction of Rhodococcus–E. coli shuttle vector. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 74:169–175
McFarland BL (1999) Biodesulfurization. Curr Opin Microbiol 2:257–264
Mohebali G, Ball AS (2008) Biocatalytic desulfurization (BDS) of petrodiesel fuels. Microbiology 154:2169–2183
Mohebali G, Ball AS, Rasekh B, Keytash A (2007) Biodesulfurization potential of a newly isolated bacterium, Gordonia alkanivorans RIPI90A. Enzyme Microb Technol 40:578–584
Monticello DJ (2000) Biodesulfurization and the upgrading of petroleum distillates. Curr Opin Biotechnol 11:540–546
Oldfield C, Pogrebinsky O, Simmonds J, Olson ES, Kulpa CF (1997) Elucidation of the metabolic pathway for dibenzothiophene desulphurization by Rhodococcus sp. strain IGTS8 (ATCC 53968). Microbiology 143:2961–2973
Park SJ, Lee I, Chang YK, Lee SY (2003) Desulfurization of dibenzothiophene and diesel oil by metabolically engineered E. coli. J Microbial Biotechnol 13:578–583
Piddington CS, Kovacevich BR, Rambosek J (1995) Sequence and molecular characterization of a DNA region encoding the dibenzothiophene desulfurization operon of Rhodococcus sp. strain IGTS8. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:468–475
Rishi AS, Nelson ND, Goyal A (2004) Genome walking of large fragments: an improved method. J Biotech 111:9–15
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning, a laboratory manual, 3rd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor
Santos SCC, Alviano DS, Alviano CS, Pádula M, Leitao AC, Martins OB, Ribeiro CMS, Sassaki MYM, Matta CPS, Bevilaqua J, Sebastián GV, Seldin L (2006) Characterization of Gordonia sp. strain F.5.25.8 capable of dibenzothiophene desulfurization and carbazole utilization. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 71:355–362
Shavandi M, Sadeghizadeh M, Zomorodipour A, Khajeh K (2009) Biodesulfurization of dibenzothiophene by recombinant Gordonia alkanivorans RIPI90A. Bioresour Technol 100:475–479
Soleimani M, Bassi A, Margaritis A (2007) Biodesulfurization of refractory organic sulfur compounds in fossil fuels. Biotechnol Adv 25:570–596
Vasicova P, Patek M, Nesvera J, Sahm H, Eikmanns B (1999) Analysis of the Corynebacterium glutamicum dapA promoter. J Bacteriol 181:6188–6191
Yu B, Xu P, Zhu S, Cai X, Wang Y, Li L, Li F, Liu X, Ma C (2006) Selective biodegradation of S and N heterocycles by a recombinant Rhodococcus erythropolis strain containing carbazole dioxygenase. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:2235–2238
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a fund from Iranian Research Institute of Petroleum Industry (R.I.P.I.). We gratefully thank M. Takeo for kindly donating the pRSG43 plasmid. The authors are grateful to Dr. S. Hoseinkhani for providing us with luciferase reporter gene and members of his laboratory for technical assistance in luciferase activity measurement.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shavandi, M., Sadeghizadeh, M., Khajeh, K. et al. Genomic structure and promoter analysis of the dsz operon for dibenzothiophene biodesulfurization from Gordonia alkanivorans RIPI90A. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 87, 1455–1461 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2605-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2605-4