Abstract
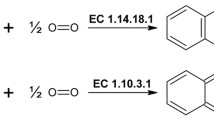
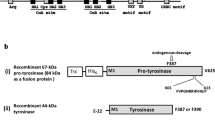
A homology search against public fungal genome sequences was performed to discover novel secreted tyrosinases. The analyzed proteins could be divided in two groups with different lengths (350–400 and 400–600 residues), suggesting the presence of a new class of secreted enzymes lacking the C-terminal domain. Among them, a sequence from Aspergillus oryzae (408 aa, AoCO4) was selected for production and characterization. AoCO4 was expressed in Trichoderma reesei under the strong cbh1 promoter. Expression of AoCO4 in T. reesei resulted in high yields of extracellular enzyme, corresponding to 1.5 g L−1 production of the enzyme. AoCO4 was purified with a two-step purification procedure, consisting of cation and anion exchange chromatography. The N-terminal analysis of the protein revealed N-terminal processing taking place in the Kex2/furin-type protease cleavage site and removing the first 51 amino acids from the putative N-terminus. AoCO4 activity was tested on various substrates, and the highest activity was found on 4-tert-butylcatechol. Because no activity was detected on L-tyrosine and on l-dopa, AoCO4 was classified as a catechol oxidase. AoCO4 showed the highest activity within an acidic and neutral pH range, having an optimum at pH 5.6. AoCO4 showed good pH stability within a neutral and alkaline pH range and good thermostability up to 60°C. The UV–visible and circular dichroism spectroscopic analysis suggested that the folding of the protein was correct.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aberg CM, Chen T, Olumide A, Raghavan SR, Payne GF (2004) Enzymatic grafting of peptides from casein hydrolysate to chitosan. Potential for value-added byproducts from food-processing wastes. J Agric Food Chem 52:788–793
Anghileri A, Lantto R, Kruus K, Arosio C, Freddi G (2007) Tyrosinase-catalyzed grafting of sericin peptides onto chitosan and production of protein-polysaccharide bioconjugates. J Biotechnol 127:508–519
Arvas M, Kivioja T, Mitchell A, Saloheimo M, Ussery D, Penttilä M, Oliver S (2007) Comparison of protein coding gene contents of the fungal phyla Pezizomycotina and Saccharomycotina. BMC Genomics 8:325
Beltramini M, Lerch K (1982) Fluorescence properties of Neurospora tyrosinase. Biochem J 205:173–180
Boer H, Koivula A (2003) The relationship between thermal stability and pH optimum studied with wild-type and mutant Trichoderma reesei cellobiohydrolase Cel7A. Eur J Biochem 270:841–848
Claus H, Decker H (2006) Bacterial tyrosinases. Syst Appl Microbiol 29:3–14
Cuff ME (1998) Crystal structure of a functional unit from Octopus hemocyanin. J Mol Biol 278(4):855–870
Decker H, Schweikardt T, Tuczek F (2006) The first crystal structure of tyrosinase: all questions answered? Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 45:4546–4550
Eicken C, Zippel F, Buldt-Karentzopoulos K, Krebs B (1998) Biochemical and spectroscopic characterization of catechol oxidase from sweet potatoes (Ipomoea batatas) containing a type-3 dicopper center. FEBS Lett 436:293–299
Emanuelsson O, Brunak S, von Heijne G, Nielsen H (2007) Locating proteins in the cell using TargetP, SignalP and related tools. Nat Protoc 2:953–971
Enright AJ, Van Dongen S, Ouzounis CA (2002) An efficient algorithm for large-scale detection of protein families. Nucleic Acids Res 30:1575–1584
Flurkey WH, Inlow JK (2008) Proteolytic processing of polyphenol oxidase from plants and fungi. J Inorg Biochem 102:2160–2170
Freddi G, Anghileri A, Sampaio S, Buchert J, Monti P, Taddei P (2006) Tyrosinase-catalyzed modification of Bombyx mori silk fibroin: grafting of chitosan under heterogeneous reaction conditions. J Biotechnol 125:281–294
Fujita Y, Uraga Y, Ichisima E (1995) Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of the protyrosinase gene, melO, from Aspergillus oryzae and expression of the gene in yeast cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1261:151–154
García-Borrón JC, Solano F (2002) Molecular anatomy of tyrosinase and its related proteins: beyond the histidine-bound metal catalytic center. Pigment Cell Res 15:162–173
Garcia-Molina F, Munoz JL, Varon R, Rodriguez-Lopez JN, Garcia-Canovas F, Tudela J (2007) A review on spectrophotometric methods for measuring the monophenolase and diphenolase activities of tyrosinase. J Agric Food Chem 55:9739–9749
Gerdemann C, Eicken C, Krebs B (2002) The crystal structure of catechol oxidase: new insight into the function of type-3 copper proteins. Acc Chem Res 35:183–191
Gheibi N, Saboury AA, Haghbeen K, Moosavi-Movahedi AA (2005) Activity and structural changes of mushroom tyrosinase induced by n-alkyl sulfates. Colloids and surfaces B, Biointerfaces 45:104–107
Goller SP, Schoisswohl D, Baron M, Parriche M, Kubicek CP (1998) Role of endoproteolytic dibasic proprotein processing in maturation of secretory proteins in Trichoderma reesei. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:3202–3208
Goloboff PA (1999) Analyzing large data sets in reasonable times: solutions for composite optima. Cladistics 15:415–428
Halaouli S, Asther M, Kruus K, Guo L, Hamdi M, Sigoillot JC, Asther M, Lomascolo A (2005) Characterization of a new tyrosinase from Pycnoporus species with high potential for food technological applications. J Appl Microbiol 98:332–343
Halaouli S, Asther M, Sigoillot JC, Hamdi M, Lomascolo A (2006) Fungal tyrosinases: new prospects in molecular characteristics, bioengineering and biotechnological applications. J Appl Microbiol 100:219–232
Hearing VJ, Tsukamoto K (1991) Enzymatic control of pigmentation in mammals. FASEB J 5(14):2902–2909
James TY, Kauff F, Schoch CL, Matheny PB, Hofstetter V, Cox CJ, Celio G, Gueidan C, Fraker E, Miadlikowska J, Lumbsch HT, Rauhut A, Reeb V, Arnold AE, Amtoft A, Stajich JE, Hosaka K, Sung GH, Johnson D, O’Rourke B, Crockett M, Binder M, Curtis JM, Slot JC, Wang Z, Wilson AW, Schüssler A, Longcore JE, O’Donnell K, Mozley-Standridge S, Porter D, Letcher PM, Powell MJ, Taylor JW, White MM, Griffith GW, Davies DR, Humber RA, Morton JB, Sugiyama J, Rossman AY, Rogers JD, Pfister DH, Hewitt D, Hansen K, Hambleton S, Shoemaker RA, Kohlmeyer J, Volkmann-Kohlmeyer B, Spotts RA, Serdani M, Crous PW, Hughes KW, Matsuura K, Langer E, Langer G, Untereiner WA, Lücking R, Büdel B, Geiser DM, Aptroot A, Diederich P, Schmitt I, Schultz M, Yahr R, Hibbett DS, Lutzoni F, McLaughlin DJ, Spatafora JW, Vilgalys R (2006) Reconstructing the early evolution of Fungi using a six-gene phylogeny. Nature 443:818–822
Karbassi F, Haghbeen K, Saboury AA, Ranjbar B, Moosavi-Movahedi AA (2003) Activity, structural and stability changes of mushroom tyrosinase by sodium dodecyl sulfate. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces 32:137–143
Kiiskinen LL, Viikari L, Kruus K (2002) Purification and characterisation of a novel laccase from the ascomycete Melanocarpus albomyces. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 59:198–204
Klabunde T, Eicken C, Sacchettini JC, Krebs B (1998) Crystal structure of a plant catechol oxidase containing a dicopper center. Nat Struct Biol 5:1084–1090
Kwon BS, Haq AK, Pomerantz SH, Halaban R (1987) Isolation and sequence of a cDNA clone for human tyrosinase that maps at the mouse c-albino locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 84:7473–7477
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Lantto R, Puolanne E, Kruus K, Buchert J, Autio K (2007) Tyrosinase-aided protein cross-linking: effects on gel formation of chicken breast myofibrils and texture and water-holding of chicken breast meat homogenate gels. J Agric Food Chem 55:1248–1255
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, Valentin F, Wallace IM, Wilm A, Lopez R, Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Higgins DG (2007) Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23:2947–2948
Lerch K (1982) Primary structure of tyrosinase from Neurospora crassa. II. Complete amino acid sequence and chemical structure of a tripeptide containing an unusual thioether. J Biol Chem 257(11):6414–6419
Marchler-Bauer A, Anderson JB, Derbyshire MK, DeWeese-Scott C, Gonzales NR, Gwadz M, Hao L, He S, Hurwitz DI, Jackson JD, Ke Z, Krylov D, Lanczycki CJ, Liebert CA, Liu C, Lu F, Lu S, Marchler GH, Mullokandov M, Song JS, Thanki N, Yamashita RA, Yin JJ, Zhang D, Bryant SH (2007) CDD: a conserved domain database for interactive domain family analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 35:D237–40
Martınez MV, Whitaker JR (1995) The biochemistry and control of enzymatic browning. Trends Food Sci Tech 6:195–200
Marusek CM, Trobaugh NM, Flurkey WH, Inlow JK (2006) Comparative analysis of polyphenol oxidase from plant and fungal species. J Inorg Biochem 100:108–123
Masayuki M, Takayoshi A, Katsuya G, Kiyoshi A, Motoaki S, Taishin K, Hidaki N, Satoru H, Osamu A, Naoki O, Satoru K, Obata H, Yukihiro N, Yoji H, Shoji K, Yasuhisa A (2004) New tyrosinase gene melD. Patent JP2004201545
Matoba Y, Kumagai T, Yamamoto A, Yoshitsu H, Sugiyama M (2006) Crystallographic evidence that the dinuclear copper center of tyrosinase is flexible during catalysis. J Biol Chem 281:8981–8990
Mattinen M, Lantto R, Selinheimo E, Kruus K, Buchert J (2008) Oxidation of peptides and proteins by Trichoderma reesei and Agaricus bisporus tyrosinases. J Biotechnol 133:395–402
Mayer AM (2006) Polyphenol oxidases in plants and fungi: going places? A review. Phytochemistry 67:2318–2331
Obata H, Ishida H, Hata Y, Kawato A, Abe Y, Akao T, Akita O, Ichishima E (2004) Cloning of a novel tyrosinase-encoding gene (melB) from Aspergillus oryzae and its overexpression in solid-state culture (Rice Koji). J Biosci Bioeng 97(6):400–405
Paradis E, Claude J, Strimmer K (2004) Analyses of phylogenetics and evolution in R language. Bioinformatics 20:289–290
Penttilä M, Nevalainen H, Ratto M, Salminen E, Knowles J (1987) A versatile transformation system for the cellulolytic filamentous fungus Trichoderma reesei. Gene 61:155–164
Quevillon E, Silventoinen V, Pillai S, Harte N, Mulder N, Apweiler R, Lopez R (2005) InterProScan: protein domains identifier. Nucleic Acids Res 33:W116–W120
Robb DA (1984) Tyrosinase. In: Lontie R (ed) Copper proteins and copper enzymes, vol 2. CRC, Boca Raton, pp 207–241
Rompel A, Fischer H, Meiwes D, Buldt-Karentzopoulos K, Dillinger R, Tuczek F, Witzel H, Krebs B (1999) Purification and spectroscopic studies on catechol oxidases from Lycopus europaeus and Populus nigra: evidence for a dinuclear copper center of type 3 and spectroscopic similarities to tyrosinase and hemocyanin. J Biol Inorg Chem 4:56–63
Rosenfeld J, Capdevielle J, Guillemot JC, Ferrara P (1992) In-gel digestion of proteins for internal sequence analysis after one- or two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem 203:173–179
Saboury AA, Karbassi F, Haghbeen K, Ranjbar B, Moosavi-Movahedi AA, Farzami B (2004) Stability, structural and suicide inactivation changes of mushroom tyrosinase after acetylation by N-acetylimidazole. Int J Biol Macromol 34:257–262
Selinheimo E, Saloheimo M, Ahola E, Westerholm-Parvinen A, Kalkkinen N, Buchert J, Kruus K (2006) Production and characterization of a secreted, C-terminally processed tyrosinase from the filamentous fungus Trichoderma reesei. FEBS J 273:4322–4335
Selinheimo E, Autio K, Kruus K, Buchert J (2007a) Elucidating the mechanism of laccase and tyrosinase in wheat bread making. J Agric Food Chem 55:6357–6365
Selinheimo E, NiEidhin D, Steffensen C, Nielsen J, Lomascolo A, Halaouli S, Record E, O’Beirne D, Buchert J, Kruus K (2007b) Comparison of the characteristics of fungal and plant tyrosinases. J Biotechnol 130:471–480
Te Biesebeke R, Record E (2008) Scientific advances with Aspergillus species that are used for food and biotech applications. Microbes Environ 23:177–181
Acknowledgments
The work was carried out with financial support from the Marie Curie EU-project “Enzymatic tailoring of protein interactions and functionalities in food matrix” PRO-ENZ (MEST-CT-2005-020924). Harry Boer, Päivi Mantikainen, and Evanthia Monogioudi are acknowledged for their assistance at MALDI-TOF MS and CD instruments. Also, the skilful technical assistance of Hanna Kuusinen, Riitta Isoniemi, Michael Bailey, and Gunilla Rönnholm is acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Chiara Gasparetti and Greta Faccio contributed equally to this work.
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3110-0
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gasparetti, C., Faccio, G., Arvas, M. et al. Discovery of a new tyrosinase-like enzyme family lacking a C-terminally processed domain: production and characterization of an Aspergillus oryzae catechol oxidase. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 86, 213–226 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-009-2258-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-009-2258-3