Abstract
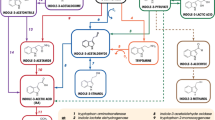
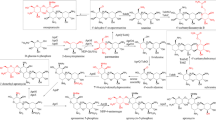
XlnR is a Zn(II)2Cys6 transcriptional activator of xylanolytic and cellulolytic genes in Aspergillus. Overexpression of the aoxlnR gene in Aspergillus oryzae (A. oryzae xlnR gene) resulted in elevated xylanolytic and cellulolytic activities in the culture supernatant, in which nearly 40 secreted proteins were detected by two-dimensional electrophoresis. DNA microarray analysis to identify the transcriptional targets of AoXlnR led to the identification of 75 genes that showed more than fivefold increase in their expression in the AoXlnR overproducer than in the disruptant. Of these, 32 genes were predicted to encode a glycoside hydrolase, highlighting the biotechnological importance of AoXlnR in biomass degradation. The 75 genes included the genes previously identified as AoXlnR targets (xynF1, xynF3, xynG2, xylA, celA, celB, celC, and celD). Thirty-six genes were predicted to be extracellular, which was consistent with the number of proteins secreted, and 61 genes possessed putative XlnR-binding sites (5′-GGCTAA-3′, 5′-GGCTAG-3′, and 5′-GGCTGA-3′) in their promoter regions. Functional annotation of the genes revealed that AoXlnR regulated the expression of hydrolytic genes for degradation of β-1,4-xylan, arabinoxylan, cellulose, and xyloglucan and of catabolic genes for the conversion of d-xylose to xylulose-5-phosphate. In addition, genes encoding glucose-6-phosphate 1-dehydrogenase and l-arabinitol-4-dehydrogenase involved in d-glucose and l-arabinose catabolism also appeared to be targets of AoXlnR.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen MR, Vongsangnak W, Panagiotou G, Salazar MP, Lehmann L, Nielsen J (2008) A trispecies Aspergillus microarray: comparative transcriptomics of three Aspergillus species. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:4387–4392
Bauer S, Vasu P, Persson S, Mort AJ, Somerville CR (2006) Development and application of a suite of polysaccharide-degrading enzymes for analyzing plant cell walls. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:11417–11422
de Groot MJ, Prathumpai W, Visser J, Ruijter GJ (2005) Metabolic control analysis of Aspergillus niger L-arabinose catabolism. Biotechnol Prog 21:1610–1616
de Groot MJL, van den Dool C, Wosten HAB, Levisson M, vanKuyk PA, Ruijter GJG, de Vries RP (2007) Regulation of pentose catabolic pathway genes of Aspergillus niger. Food Technol Biotechnol 45:134–138
de Vries RP, Visser J (1999) Regulation of the feruloyl esterase (faeA) gene from Aspergillus niger. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:5500–5503
de Vries RP, Flipphi MJ, Witteveen CF, Visser J (1994) Characterization of an Aspergillus nidulans L-arabitol dehydrogenase mutant. FEMS Microbiol Lett 123:83–90
de Vries RP, van den Broeck HC, Dekkers E, Manzanares P, de Graaff LH, Visser J (1999a) Differential expression of three α-galactosidase genes and a single β-galactosidase gene from Aspergillus niger. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:2453–2460
de Vries RP, Visser J, de Graaff LH (1999b) CreA modulates the XlnR-induced expression on xylose of Aspergillus niger genes involved in xylan degradation. Res Microbiol 150:281–285
de Vries RP, van de Vondervoort PJ, Hendriks L, van de Belt M, Visser J (2002) Regulation of the α-glucuronidase-encoding gene (aguA) from Aspergillus niger. Mol Genet Genomics 268:96–102
Frey PA (1996) The Leloir pathway: a mechanistic imperative for three enzymes to change the stereochemical configuration of a single carbon in galactose. FASEB J 10:461–470
Furukawa T, Shida Y, Kitagami N, Ota Y, Adachi M, Nakagawa S, Shimada R, Kato M, Kobayashi T, Okada H, Ogasawara W, Morikawa Y (2008) Identification of the cis-acting elements involved in regulation of xylanase III gene expression in Trichoderma reesei PC-3–7. Fungal Genet Biol 45:1094–1102
Furukawa T, Shida Y, Kitagami N, Mori K, Kato M, Kobayashi T, Okada H, Ogasawara W, Morikawa Y (2009) Identification of specific binding sites for XYR1, a transcriptional activator of cellulolytic and xylanolytic genes in Trichoderma reesei. Fungal Genet Biol 46:564–574
Gielkens MM, Dekkers E, Visser J, de Graaff LH (1999) Two cellobiohydrolase-encoding genes from Aspergillus niger require D-xylose and the xylanolytic transcriptional activator XlnR for their expression. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:4340–4345
Hasper AA, Visser J, de Graaff LH (2000) The Aspergillus niger transcriptional activator XlnR, which is involved in the degradation of the polysaccharides xylan and cellulose, also regulates D-xylose reductase gene expression. Mol Microbiol 36:193–200
Ito T, Yokoyama E, Sato H, Ujita M, Funaguma T, Furukawa K, Hara A (2003) Xylosidases associated with the cell surface of Penicillium herquei IFO 4674. J Biosci Bioeng 96:354–359
Kawaguchi T, Enoki T, Tsurumaki S, Sumitani J, Ueda M, Ooi T, Arai M (1996) Cloning and sequencing of the cDNA encoding β-glucosidase 1 from Aspergillus aculeatus. Gene 173:287–288
Marui J, Kitamoto N, Kato M, Kobayashi T, Tsukagoshi N (2002a) Transcriptional activator, AoXlnR, mediates cellulose-inductive expression of the xylanolytic and cellulolytic genes in Aspergillus oryzae. FEBS Lett 528:279–282
Marui J, Tanaka A, Mimura S, de Graaff LH, Visser J, Kitamoto N, Kato M, Kobayashi T, Tsukagoshi N (2002b) A transcriptional activator, AoXlnR, controls the expression of genes encoding xylanolytic enzymes in Aspergillus oryzae. Fungal Genet Biol 35:157–169
Metz B, de Vries RP, Polak S, Seidl V, Seiboth B (2009) The Hypocrea jecorina (syn. Trichoderma reesei) lxr1 gene encodes a D-mannitol dehydrogenase and is not involved in L-arabinose catabolism. FEBS Lett 583:1309–1313
Miyazaki K, Miyamoto H, Mercer DK, Hirase T, Martin JC, Kojima Y, Flint HJ (2003) Involvement of the multidomain regulatory protein XynR in positive control of xylanase gene expression in the ruminal anaerobe Prevotella bryantii B(1)4. J Bacteriol 185:2219–2226
Nelson N (1944) A photometric adaptation of the Somogyi method for the determination of glucose. J Biol Chem 153:375–380
Pail M, Peterbauer T, Seiboth B, Hametner C, Druzhinina I, Kubicek CP (2004) The metabolic role and evolution of L-arabinitol 4-dehydrogenase of Hypocrea jecorina. Eur J Biochem 271:1864–1872
Richard P, Putkonen M, Väänänen R, Londesborough J, Penttilä M (2002) The missing link in the fungal L-arabinose catabolic pathway, identification of the L-xylulose reductase gene. Biochemistry (Mosc) 41:6432–6437
Seiboth B, Gamauf C, Pail M, Hartl L, Kubicek CP (2007) The D-xylose reductase of Hypocrea jecorina is the major aldose reductase in pentose and D-galactose catabolism and necessary for β-galactosidase and cellulase induction by lactose. Mol Microbiol 66:890–900
Shida Y, Furukawa T, Ogasawara W, Kato M, Kobayashi T, Okada H, Morikawa Y (2008) Functional analysis of the egl3 upstream region in filamentous fungus Trichoderma reesei. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 78:514–524
Stricker AR, Grosstessner-Hain K, Würleitner E, Mach RL (2006) Xyr1 (xylanase regulator 1) regulates both the hydrolytic enzyme system and D-xylose metabolism in Hypocrea jecorina. Eukaryotic Cell 5:2128–2137
Takada G, Kawaguchi T, Sumitani J, Arai M (1998) Expression of Aspergillus aculeatus No. F-50 cellobiohydrolase I (cbhI) and β-glucosidase 1 (bgl1) genes by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 62:1615–1618
Tamano K, Sano M, Yamane N, Terabayashi Y, Toda T, Sunagawa M, Koike H, Hatamoto O, Umitsuki G, Takahashi T, Koyama Y, Asai R, Abe K, Machida M (2008) Transcriptional regulation of genes on the non-syntenic blocks of Aspergillus oryzae and its functional relationship to solid-state cultivation. Fungal Genet Biol 45:139–151
van Peij NN, Gielkens MMC, de Vries RP, Visser J, de Graaff LH (1998a) The transcriptional activator XlnR regulates both xylanolytic and endoglucanase gene expression in Aspergillus niger. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:3615–3619
van Peij NN, Visser J, de Graaf JH (1998b) Isolation and analysis of xlnR, encoding a transcriptional activator co-ordinating xylanolytic expression in Aspergillus niger. Mol Microbiol 27:131–142
vanKuyk PA, de Groot MJ, Ruijter GJ, de Vries RP, Visser J (2001) The Aspergillus niger D-xylulose kinase gene is co-expressed with genes encoding arabinan degrading enzymes, and is essential for growth on D-xylose and L-arabinose. Eur J Biochem 268:5414–5423
Acknowledgment
This work was partially supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (B) and a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Priority Areas, Applied Genomics, from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology of Japan, and also by New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Noguchi, Y., Sano, M., Kanamaru, K. et al. Genes regulated by AoXlnR, the xylanolytic and cellulolytic transcriptional regulator, in Aspergillus oryzae . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 85, 141–154 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-009-2236-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-009-2236-9