Abstract
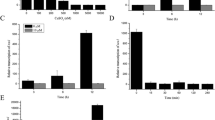
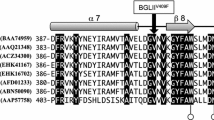
Comprehensive analyses on promoters of four cellulase and one xylanase genes of Trichoderma reesei were performed expressing a single reporter uidA from Escherichia coli to construct highly functional cellulase-overproducing strains. GUS amount expressed under each promoter correlated entirely with each mRNA amount, suggesting that GUS production was controlled at the transcriptional level. The uidA transcript levels were much lower than the native gene mRNAs, but they were produced in proportion to the mRNA of native cellulase and xylanase genes driven by the same promoters except for the cbh2 promoter. Cellulose-degrading activity and protein amount was reduced in cbh1 and cbh2 disruptant mutants compared to the wild-type T. reesei PC-3-7 and other uidA transformants. The cbh1 disruptant strain was observed to produce more CBH II, EG I, EG III, and xylanases than native PC-3-7 and the other uidA transformants with the same amounts of protein in SDS-PAGE gels. This observation was further analyzed by measuring mRNA levels of cellulase and xylanase genes in the disruptants using quantitative real-time PCR. In the Pcbh1-gus, mRNA levels for cbh2 and egl1 genes were higher than those in native T. reesei PC-3-7 and all other disruptant strains. The cbh2 disruptant strain had the highest amount of cbh1 mRNA among the strains tested. Homologous integration of uidA at the egl1, egl3, and xyn3 loci was also found to cause a slight increased level of cbh1 mRNA, whereas mRNA levels for egl1, egl3, and xyn3 in all the disruptants were similar to those of T. reesei PC-3-7.




Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Eto H, Michiki H, Ishibashi H, Ado Y, Murata Y, Ogoshi T, Furuichi M, Morikawa Y, Hirotani T (1988) Fuel ethanol production from cellulosic biomass in Proceedings of VII International Symposium on Alcohol Fuels. New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organizatoin, Kawasaki, pp 155–160
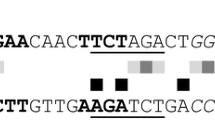
Furukawa T, Shida Y, Kitagami N, Ota Y, Adachi M, Nakagawa S, Shimada R, Kato M, Kobayashi T, Okada H, Ogasawara W, Morikawa Y (2008) Identification of the cis-acting elements involved in regulation of xylanase III gene expression in Trichoderma reesei PC-3-7. Fungal Genet Biol 45:1094–1102
Ghose TK (1987) Measurement of cellulase activities. Pure and Appl Chem 59:257–268
Harkki A, Mäntylä A, Penttilä M, Muttilainen S, Bühler R, Suominen P, Knowles J, Nevalainen H (1991) Genetic engineering of Trichoderma to produce strains with novel cellulase profiles. Enzyme Microb Technol 13:227–233
Henrique-Silva F, El-Gogary S, Carle-Urioste JC, Matheucci E Jr, Crivellaro O, El-Dorry H (1996) Two regulatory regions controlling basal and cellulose-induced expression of the gene encoding cellobiohydrolase I of Trichoderma reesei are adjacent to its TATA box. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 228:229–237
Hynes MJ, Corrick CM, King JA (1983) Isolation of genomic clones containing the amdS gene of Aspergillus nidulans and their use in the analysis of structural and regulatory mutations. Mol Cell Biol 3:1430–1439
Ilmén M, Saloheimo A, Onnela ML, Penttilä M (1997) Regulation of cellulase gene expression in the filamentous fungus Trichoderma reesei. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:1298–1306
Ilmén M, Onnela ML, Klemsdal S, Keränen S, Penttilä M (1998) Functional analysis of the cellobiohydrolase I promoter of the filamentous fungus Trichoderma reesei. Mol Gen Genet 253:303–314
Jefferson RA (1987) Assaying chimeric genes in plants: the GUS gene fusion system. Plant Mol Biol Rep 5:387–405
Kawamori M, Morikawa Y, Takasawa S (1985) Inductive formation of cellulases by l-sorbose in Trichoderma reesei. Appl Microbiol Biothechnol 22:235–236
Kawamori M, Morikawa Y, Takasawa S (1986) Induction and production of cellulases by l-sorbose in Trichoderma reesei. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 24:449–453
Keränen S, Penttilä M (1995) Production of recombinant proteins in the filamentous fungus Trichoderma reesei. Curr Opin Biotechnol 6:534–537
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Mäntylä A, Paloheimo M, Hakola S, Lindberg E, Leskinen S, Kallio J, Vehmaanperä J, Lantto R, Suominen P (2007) Production in Trichoderma reesei of three xylanases from Chaetomium thermophilum: a recombinant thermoxylanase for biobleaching of kraft pulp. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 76:377–386
Miettinen-Oinonen A, Suominen P (2002) Enhanced production of Trichoderma reesei endoglucanse and use of the new cellulase preparations in producing the stonewash effect on denim febric. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:3956–3964
Miettinen-Oinonen A, Paloheimo M, Lantto R, Suominen P (2004) Enhanced production of cellobiohydrolase in Trichoderma reesei and evaluation of the new preparations in biofinishing of cotton. J Biotechnol 116:305–317
Nevalainen H, Suominen P, Taimisto K (1994) On the safety of Trichoderma reesei. J Biotechnol 37:193–200
Nogawa M, Goto M, Okada H, Morikawa Y (2001) l-Sorbose induces cellulase gene transcription in the cellulolytic fungus Trichoderma reesei. Curr Genet 38:329–334
Ogasawara W, Yosuke S, Furukawa T, Shimada R, Nakagawa S, Kawamura M, Yagyu T, Kosuge A, Xu J, Nogawa M, Okada H, Morikawa Y (2006) Cloning, functional expression and promoter analysis of xylanase III gene from Trichoderma reesei. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 72:995–1003
Okada H, Tada K, Sekiya T, Yokoyama K, Takahashi A, Tohda H, Kumagai H, Morikawa Y (1998) Molecular characterization and heterologous expression of the gene encoding a low-molecular-mass endoglucanase from Trichoderma reesei QM9414. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:555–563
Paloheimo M, Mäntylä A, Kallio J, Puranen T, Suominen P (2007) Increased production of Xylanase by expression of a truncated version of the xyn11A gene from Nonomuraea flexuosa in Trichoderma reesei. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:3215–3224
Penttilä M (1998) Heterologous protein production in the Trichoderma. In: Harman GE, Kubicek CP (eds) Trichoderma and Gliocladium. Taylor and Francis, London, pp 365–382
Penttilä M, Nevalainen H, Rättö M, Salminen E, Knowels JKC (1987) A versatile transformation system for the cellulolytic filamentous fungus Trichoderma reesei. Gene 61:155–164
Sambrook J, Russel DW (2001) Molecular cloning, 3rd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor
Seiboth B, Hartl L, Pail M, Fekete E, Karaffa L, Kubicek CP (2004) The galactokinase of Hypocrea jecorina is essential for cellulase induction by lactose but dispensable for growth on d-galactose. Mol Microbiol 51:1015–1025
Shida Y, Furukawa T, Ogasawara W, Kato M, Kobayashi T, Okada H, Morikawa Y (2008) Functional analysis of the egl3 upstream region in the filamentous fungus Trichoderma reesei. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 78:515–524
Somogyi M (1952) Notes on sugar determination. J Biol Chem 195:19–23
Stangl H, Gruber F, Kubicek CP (1993) Characterization of the Trichoderma reesei cbh2 promoter. Curr Genet 23:115–122
Stricker AR, Grosstessner-Hain K, Würleitner E, Mach RL (2006) Xyr1 (xylanase regulator 1) regulates both the hydrolytic enzyme system and d-xylose metabolism in Hypocrea jecorina. Eucaryotic Cell 5:2128–2137
Wang TH, Liu T, Wu ZH, Liu SL, Lu Y, Qu YB (2004) Novel cellulase profile of Trichoderma reesei strains constructed by cbh1 gene replacement with eg3 gene expression cassette. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 36:667–672
Würleitner E, Pera L, Wacenovsky C, Cziferszky A, Zeilinger S, Kubicek CP, Mach RL (2003) Transcriptional regulation of xyn2 in Hypocrea jecorina. Eukaryotic Cell 2:150–158
Xu J, Nogawa M, Okada H, Morikawa Y (1998) Xylanase induction by l-sorbose in Trichoderma reesei PC-3-7. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 62:1555–1559
Xu J, Nogawa M, Okada H, Morikawa Y (2000) Regulation of xyn3 gene expression in a fungus, Trichoderma reesei PC-3-7. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 54:370–375
Zeilinger S, Mach RL, Schindler M, Herzog P, Kubicek CP (1996) Different inducibility of expression of the two xylanase genes xyn1 and xyn2 in Trichoderma reesei. J Biol Chem 271:25624–25629
Zeilinger S, Mach RL, Kubicek CP (1998) Two adjacent protein binding motifs in the cbh2 (cellobiohydrolase II-encoding) promoter of the fungus Hypocrea jecorina (Trichoderma reesei) cooperate in the induction by cellulose. J Biol Chem 273:34463–34471
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by a grant (Project ID:06A43502c, to W. Ogasawara) from the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO) project of the Ministry of Industry and Technology of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rahman, Z., Shida, Y., Furukawa, T. et al. Evaluation and characterization of Trichoderma reesei cellulase and xylanase promoters. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 82, 899–908 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1841-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1841-3