Abstract
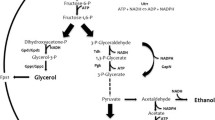
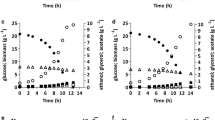
The two homologous genes GPD1 and GPD2, encoding two isoenzymes of NAD+-dependent glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase in industrial yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae CICIMY0086, had been deleted. The obtained two kinds of mutants gpd1Δ and gpd2Δ were studied under alcoholic fermentation conditions. gpd1Δ mutants exhibited a 4.29% (relative to the amount of substrate consumed) decrease in glycerol production and 6.83% (relative to the amount of substrate consumed) increased ethanol yield while gpd2Δ mutants exhibited a 7.95% (relative to the amount of substrate consumed) decrease in glycerol production and 7.41% (relative to the amount of substrate consumed) increased ethanol yield compared with the parental strain. The growth rate of the two mutants were slightly lower than that of the wild type under the exponential phase whereas ANG1 (gpd1Δ) and the decrease in glycerol production was not accompanied by any decline in the protein content of the strain ANG1 (gpd1Δ) but a slight decrease in the strain ANG2 (gpd2Δ). Meanwhile, dramatic decrease of acetate acid formation was observed in strain ANG1 (gpd1Δ) and ANG2 (gpd2Δ) compared to the parental strain. Therefore, it is possible to improve the ethanol yield by interruption of glycerol pathway in industrial alcoholic yeast.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albers E, Larsson C, Lidén G, Niklasson C, Gustafsson L (1996) Influence of the nitrogen source on Saccharomyces cerevisiae anaerobic growth and product formation. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:3187–3195
André L, Hemming A, Adler L (1991) Osmoregulation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Studies on the osmotic induction of glycerol production and glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (NAD+). FEBS Lett 286:13–17
Ansell R, Granath K, Hohmann S, Thevelein JM, Adler L (1997) The two isoenzymes for yeast NAD+-dependent glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogenase encoded by GPD1 and GPD2 have distinct roles in c and redox regulation. EMBO J 16:2179–2187
Björkqvist S, Ansell R, Adler L, Lidén G (1997) Physiological response to anaerobicity of glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:128–132
De Vries S, van Witzenburg R, Grivell LA, Marres CAM (1992) Primary structure and import pathway of the rotenone-insensitive NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase of mitochondria from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur J Biochem 203:587–592
Eriksson P, André L, Ansell R, Blomberg A, Adler L (1995) Cloning and characterisation of GPD2, a second gene encoding sn-glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (NAD+) in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, and its comparison with GPD1. Mol Microbiol 17:95–107
Larsson K, Ansell R, Eriksson P, Adler L (1993) A gene encoding sn-glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (NAD+) complements an osmosensitive mutant of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Microbiol 10:1101–1111
Nissen TL, Schulze U, Nielsen J, Villadsen J (1997) Flux distributions in anaerobic, glucose-limited continuous cultivations of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiology 143:203–218
Nissen TL, Hamann CW, Kielland-Brandt MC, Nielsen J, Villadsen J (2000) Anaerobic and aerobic batch cultivations of Saccharomyces cerevisiae mutants impaired in glycerol synthesis. Yeast 16:463–474
Remize F, Barnavon L, Dequin S (2001) Glycerol export and glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, but not glycerol phosphatase, are rate limiting for glycerol production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Metab Eng 3:301–312
Valadi H, Larsson C, Gustafsson L (1998) Improved ethanol production by glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 4:434–439
Verduyn C, Stouthamer AH, Scheffers WA, van Dijken JP (1991) A theoretical evaluation of growth yields of yeasts. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 59:49–63
Acknowledgements
This work was financial supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (20706024), the “863” Program(2006AA020101, 2007AA10Z359), the Open Project Program of the Key Laboratory of Industrial Biotechnology, Ministry of Education, China (KLIB-KF200701) and Technology Development Programme for institute of Yunnan Province (No.2006KFZX-10).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, Zp., Zhang, L., Ding, Zy. et al. Interruption of glycerol pathway in industrial alcoholic yeasts to improve the ethanol production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 82, 287–292 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1777-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1777-7