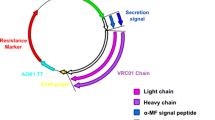
Abstract
The administration of antibodies against the cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen-4 (CTLA-4) is a promising approach in the upregulation of immune responses in many cancers and infectious diseases. The single-chain variable fragment of antibody against CTLA4 is also useful in developing immunotoxins that might be used in the treatment of cancer, transplant rejection, and autoimmune diseases. Here, we report the production of a soluble and functional scFv antibody against CTLA4 by using Pichia pastoris as the expression system. The gene encoding scFv hS83 with an additional 6His-tag at the 5’-end was inserted into the expression vector pPIC9K. Then, the transformants were double-screened on plates containing 0.25 mg/mL and 1.5 mg/mL of neomycin G418 and many clones with different levels of G418-resistance were selected for further studies on expression. After induction by the addition of methanol, various levels of hS83 were detected in the supernatant of P. pastoris containing pPIC9K-hS83. Clones with low G418-resistance produced more hS83 than those with higher G418-resistance. Under the optimized conditions (initial inoculum, 40 A600nm AU/mL; pH 6.0; methanol concentration, 3.0%; induction time, 72 h), approximately 16–20 mg protein could be recovered from 1 L of the culture. The purified hS83 had a stronger binding ability towards CTLA4-positive Raji cells than CTLA4-negative ECV304 cells. This finding indicates that the antibody produced by P. pastoris is functional and may be used in immunotherapy for cancer, infection, transplant rejection, and autoimmune diseases.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alegre ML, Fallarino F (2006) Mechanism of CTLA4-Ig in tolerance induction. Curr Pharm Des 12:149–160
Amoura Z, Piette JC (2006) New therapies for autoimmune diseases. Rev Neurol (Paris) 162(1):3S7–3S11
Chen LH, Huang Q, Wan L, Zeng LY, Li SF, Li YP, Lu XF, Cheng JQ (2006) Expression, purification, and in vitro refolding of a humanized single-chain Fv antibody against human CTLA4 (CD152). Protein Expr Purif 46:495–502
Clare JJ, Rayment FB, Ballantyne SP, Sreerkrishna K, Romanos MA (1991) High-level expression of tetanus toxin fragment C in Pichia pastoris strains containing multiple tandem integrations of the gene. Bio/Technology 9:455–460
Clarkson MR, Sayegh MH (2005) T-cell costimulatory pathways in allograft rejection and tolerance. Transplantation 80(5):555–63
Cranmer LD, Hersh E (2007) The role of the CTLA4 blockade in the treatment of malignant melanoma. Cancer Invest 25:613–631
Cregg JM, Lin-Cereghino J, Shi J, Higgins DR (2000) Recombinant protein expression in Pichia pastoris. Mol Biotechnol 16:23–52
Emberson LM, Trivett AJ, Blower PJ, Nicholls PJ (2005) Expression of an anti-CD33 single-chain antibody by Pichia pastoris. J Immunol Methods 305(2):135–51
Frederick M (1995) Short Protocols in Molecular Biology, 3rd edn. Wiley, New York
Hohenblum H, Gasser B, Maurer M, Borth N, Mattanovich D (2004) Effects of gene dosage, promoters, and substrates on unfolded protein stress of recombinant Pichia pastoris. Biotechnol Bioeng 85:367–375
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Martins GA, Tadokoro CE, Silva RB, Silva JS, Rizzo LV (2004) CTLA-4 blockage increases resistance to infection with the intracellular protozoan Trypanosoma cruzi. J Immunol 172(8):4893–901
McCoy K, Camberis M, Gros GL (1997) Protective immunity to nematode infection is induced by CTLA-4 blockade. J Exp Med 186:183–187
McGrew JT, Leiske D, Dell B, Klinke R, Krasts D, Wee SF, Abbott N, Armitage R, Harrington K (1997) Expression of trimeric CD40 ligand in Pichia pastoris: use of a rapid method to detect high-level expressing transformants. Gene 187:193–200
Romanos MA, Scorer CA, Clare JJ (1992) Foreign gene expression in yeast: a review. Yeast 8:423–488
Miller KD, Weaver-Feldhaus J, Gray SA, Siegel RW, Feldhaus MJ (2005) Production, purification, and characterization of human scFv antibodies expressed in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Pichia pastoris, and Escherichia coli. Protein Expr Purif 42(2):255–67
Murphy ML, Cotterell SE, Gorak PM, Engwerda CR, Kaye PM (1998) Blockade of CTLA-4 enhances host resistance to the intracellular pathogen, Leishmania donovani. J Immunol 161(8):4153–60
O’Day SJ, Hamid O, Urba WJ (2007) Targeting Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte Antigen-4 (CTLA-4), a novel strategy for the treatment of melanoma and other malignancies. Cancer 110(12):2614–2627
Peggs KS, Quezada SA, Korman AJ, Allison JP (2006) Principles and use of anti-CTLA4 antibody in human cancer immunotherapy. Curr Opin Immunol 18:206–213
Pistillo MP, Tazzari PL, Ellis JH, Ferrara GB (2000) Molecular characterization and applications of recombinant scFv antibodies to CD152 co-stimulatory molecule. Tissue Antigens 55:229–238
Pistillo MP, Tazzari PL, Palmisano GL (2003) CTLA-4 is not restricted to the lymphoid cell lineage and can function as a target molecule for apoptosis induction of leukemic cells. Blood 101(1):202–209
Tazzari PL, Polito L, Bolognesi A, Pistillo MP, Capanni P, Palmisano GL, Lemoli RM, Curti A, Biancone L, Camussi G, Conte R, Ferrara GB, Stirpe F (2001) Immunotoxins containing recombinant anti-CTLA-4 single-chain fragment variable antibodies and saporin: in vitro results and in vivo effects in an acute rejection model. J Immunol 167:4222–4229
Vassileva A, Chugh DA, Swaminathan S, Khanna N (2001) Expression of hepatitis B surface antigen in the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris using the GAP promoter. J Biotechnol 88:21–35
Wan L, Zeng LY, Chen LH, Huang Q, Li SF, Lu YR, Li YP, Cheng JQ, Lu XF (2006) Expression, purification, and refolding of a novel immunotoxin containing humanized single-chain fragment variable antibody against CTLA4 and the N-terminal fragment of human perforin. Protein Express Purif 48:307–313
Watanabe K, Murakami K, Sato R, Okimoto T, Maeda K, Nasu M (2004) CTLA-4 blockade inhibits induction of Helicobacter pyloriassociated gastritis in mice. Clin Exp Immunol 135(1):29–34
Woo JH, Liu YY, Stavrou S, Neville DM (2004) Increasing secretion of a bivalent anti-T-cell immunotoxin by Pichia pastoris. Appl Environ Microbiol 70(6):3370–3376
Xin L, Zhang L (2001) Expression of human angiostatin in Pichia pastoris and the detection of Its anti-angiogenic activity. Acta Biochim Biophys 33(3):291–295
Zhong RK, Loken M, Lane TA, Ball ED (2006) CTLA-4 blockade by a human MAb enhances the capacity of AML-derived DC to induce T-cell responses against AML cells in an autologous culture system. Cytotherapy 8(1):3–12
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by National Basic Research Program of China (2009CB522401), Natural Science Fund of China (30572273), Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (NCET-06–0790) and Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Huawei Cai and Lihong Chen contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, H., Chen, L., Wan, L. et al. High-level expression of a functional humanized anti-CTLA4 single-chain variable fragment antibody in Pichia pastoris . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 82, 41–48 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1744-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1744-3