Abstract
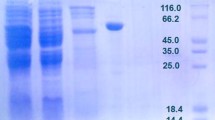
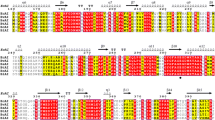
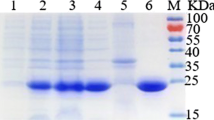
Based on analysis of the genome sequence of Bacillus licheniformis ATCC 14580, an isomerase-encoding gene (araA) was proposed as an l-arabinose isomerase (L-AI). The identified araA gene was cloned from B. licheniformis and overexpressed in Escherichia coli. DNA sequence analysis revealed an open reading frame of 1,422 bp, capable of encoding a polypeptide of 474 amino acid residues with a calculated isoelectric point of pH 4.8 and a molecular mass of 53,500 Da. The gene was overexpressed in E. coli, and the protein was purified as an active soluble form using Ni–NTA chromatography. The molecular mass of the purified enzyme was estimated to be ~53 kDa by sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and 113 kDa by gel filtration chromatography, suggesting that the enzyme is a homodimer. The enzyme required a divalent metal ion, either Mn2+or Co2+, for enzymatic activity. The enzyme had an optimal pH and temperature of 7.5 and 50°C, respectively, with a k cat of 12,455 min−1 and a k cat/K m of 34 min−1 mM−1 for l-arabinose, respectively. Although L-AIs have been characterized from several other sources, B. licheniformis L-AI is distinguished from other L-AIs by its wide pH range, high substrate specificity, and catalytic efficiency for l-arabinose, making B. licheniformis L-AI the ideal choice for industrial applications, including enzymatic synthesis of l-ribulose. This work describes one of the most catalytically efficient L-AIs characterized thus far.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Chakravarthy S, Varadarajan R (2000) Elucidation of determinants of protein stability through gene sequence analysis. FEBS Lett 470:65–69
Chouayekh H, Bejar W, Rhimi M, Jelleli K, Mseddi M, Bejar S (2007) Characterization of an l-arabinose isomerase from the Lactobacillus plantarum NC8 strain showing pronounced stability at acidic pH. FEMS Microbiol Lett 277:260–267
Dische Z, Borenfreund E (1951) A new spectrophotometric method for the detection and determination of keto sugars and trioses. J Biol Chem 192:583–587
Izumori K (2002) Bioproduction strategies for rare hexose sugars. Naturwissenschaften 89:120–124
Jorgensen F, Hansen OC, Stougaard P (2004) Enzymatic conversion of d-galactose to d-tagatose: heterologous expression and characterisation of a thermostable l-arabinose isomerase from Thermoanaerobacter mathranii. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 64:816–822
Kim P (2004) Current studies on biological tagatose production using l-arabinose isomerase: a review and future perspective. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 65:243–249
Kim HJ, Oh DK (2005) Purification and characterization of an l-arabinose isomerase from an isolated strain of Geobacillus thermodenitrificans producing d-tagatose. J Biotechnol 120:162–173
Kim BC, Lee YH, Lee HS, Lee DW, Choe EA, Pyun YR (2002) Cloning, expression and characterization of l-arabinose isomerase from Thermotoga neapolitana: bioconversion of d-galactose to d-tagatose using the enzyme. FEMS Microbiol Lett 212:121–126
Kim HJ, Kim JH, Oh HJ, Oh DK (2006) Characterization of a mutated Geobacillus stearothermophilusl-arabinose isomerase that increases the production rate of d-tagatose. J Appl Microbiol 101:213–221
Lee DW, Jang HJ, Choe EA, Kim BC, Lee SJ, Kim SB, Hong YH, Pyun YR (2004) Characterization of a thermostable l-arabinose (d-galactose) isomerase from the hyperthermophilic eubacterium Thermotoga maritima. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:1397–1404
Lee SJ, Lee DW, Choe EA, Hong YH, Kim SB, Kim BC, Pyun YR (2005) Characterization of a thermoacidophilic l-arabinose isomerase from Alicyclobacillus acidocaldarius: role of Lys-269 in pH optimum. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:7888–7896
Lee DW, Hong YH, Choe EA, Lee SJ, Kim SB, Lee HS, Oh JW, Shin HH, Pyun YR (2005a) A thermodynamic study of mesophilic, thermophilic, and hyperthermophilic l-arabinose isomerases: the effects of divalent metal ions on protein stability at elevated temperatures. FEBS Lett 579:1261–1266
Lee DW, Choe EA, Kim SB, Eom SH, Hong YH, Lee SJ, Lee HS, Lee DY, Pyun YR (2005b) Distinct metal dependence for catalytic and structural functions in the l-arabinose isomerases from the mesophilic Bacillus halodurans and the thermophilic Geobacillus stearothermophilus. Arch Biochem Biophys 434:333–343
Liu SY, Wiegel J, Gherardini FC (1996) Purification and cloning of a thermostable xylose (glucose) isomerase with an acidic pH optimum from Thermoanaerobacterium strain. JW/SL-YS 489. J Bacteriol 178:5938–5945
Manjasetty BA, Chance MR (2006) Crystal structure of Escherichia colil-arabinose isomerase (ECAI), the putative target of biological tagatose production. J Mol Biol 360(2):297–309
Patrick JW, Lee N (1968) Purification and properties of an l-arabinose isomerase from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 243:4312–4318
Rhimi M, Bejar S (2006) Cloning, purification and biochemical characterization of metallic-ions independent and thermoactive l-arabinose isomerase from the Bacillus stearothermophilus US100 strain. Biochim Biophys Acta 1760:191–199
Roh HJ, Kim P, Park YC, Choi JH (2000) Bioconversion of d-galactose into d-tagatose by expression of l-arabinose isomerase. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 31:1–4
Seemann JE, Schulz GE (1997) Structure and mechanism of l-fucose isomerase from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol 273:256–268
Sterner R, Liebl W (2001) Thermophilic adaptation of proteins. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 36:39–106
Veith B, Herzberg C, Steckel S, Feesche J, Maurer KH, Ehrenreich P, Baumer S, Henne A, Liesegang H, Merkl R, Ehrenreich A, Gottschalk G (2004) The complete genome sequence of Bacillus licheniformis DSM13, an organism with great industrial potential. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 7:204–211
Yamanaka K (1975) l-Arabinose isomerase from Lactobacillus gayonii. Methods Enzymol 41:458–461
Yoon SH, Kim P, Oh DK (2003) Properties of l-arabinose isomerase from Escherichia coli as biocatalyst for tagatose production. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 19:47–51
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by a grant (code 20070301034024) from Biogreen 21 Program, Rural Development Administration, Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prabhu, P., Kumar Tiwari, M., Jeya, M. et al. Cloning and characterization of a novel l-arabinose isomerase from Bacillus licheniformis . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 81, 283–290 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1652-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1652-6