Abstract
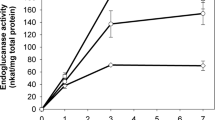
The Aspergillus aculeatus β-glucosidase 1 (bgl1) gene was expressed in a lactic-acid-producing Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain to enable lactic fermentation with cellobiose. The recombinant β-glucosidase enzyme was expressed on the yeast cell surface by fusing the mature protein to the C-terminal half region of the α-agglutinin. The β-glucosidase expression plasmids were integrated into the genome. Three strong promoters of S. cerevisiae, the TDH3, PGK1, and PDC1 promoters, were used for β-glucosidase expression. The specific β-glucosidase activity varied with the promoter used and the copy number of the bgl1 gene. The highest activity was obtained with strain PB2 that possessed two copies of the bgl1 gene driven by the PDC1 promoter. PB2 could grow on cellobiose and glucose minimal medium at the same rate. Fermentation experiments were conducted in non-selective-rich media containing 95 g l−1 cellobiose or 100 g l−1 glucose as a carbon source under microaerobic conditions. The maximum rate of l-lactate production by PB2 on cellobiose (2.8 g l−1 h−1) was similar to that on glucose (3.0 g l−1 h−1). This indicates that efficient fermentation of cellobiose to l-lactate can be accomplished using a yeast strain expressing β-glucosidase from a mitotically stable genomic integration plasmid.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adachi E, Torigoe M, Sugiyama M, Nikawa J, Shimizu K (1998) Modification of metabolic pathways of Saccharomyces cerevisiae by the expression of lactate dehydrogenase and deletion of pyruvate decarboxylase genes for the lactic acid fermentation at low pH value. J Ferment Bioeng 86:284–289
Adam AC, Polaina J (1991) Construction of a Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain able to ferment cellobiose. Curr Genet 20:5–8
Adam AC, Rubio-Texeira M, Polaina J (1995) Induced expression of bacterial b-glucosidase activity in Saccharomyces. Yeast 11:395–406
Beguin P, Aubert JP (1994) The biological degradation of cellulose. FEMS Microbiol Rev 13:25–58
Bianchi MM, Brambilla L, Protani F, Liu CL, Lievense J, Porro D (2001) Efficient homolactic fermentation by Kluyveromyces lactis strains defective in pyruvate utilization and transformed with the heterologous LDH gene. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:5621–5625
Cho KM, Yoo YJ, Kang HS (1999) d-Integration of endo/exo-glucanase and b-glucosidase genes into the yeast chromosomes for direct conversion of cellulose to ethanol. Enzyme Microb Technol 25:23–30
Dequin S, Barre P (1994) Mixed lactic acid-alcoholic fermentation by Saccharomyces cerevisiae expressing the Lactobacillus caseil(+)-LDH. Biotechnology (N Y) 12:173–177
Eberhardt I, Cederberg H, Li H, König S, Jordan F, Hohmann S (1999) Autoregulation of yeast pyruvate decarboxylase gene expression requires the enzyme but not its catalytic activity. Eur J Biochem 262:191–201
Fujita Y, Takahashi S, Ueda M, Tanaka A, Okada H, Morikawa Y, Kawaguchi T, Arai M, Fukuda H, Kondo A (2002) Direct and efficient production of ethanol from cellulosic material with a yeast strain displaying cellulolytic enzymes. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:5136–5141
Fujita Y, Ito J, Ueda M, Fukuda H, Kondo A (2004) Synergistic saccharification, and direct fermentation to ethanol, of amorphous cellulose by use of an engineered yeast strain codisplaying three types of cellulolytic enzyme. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:1207–1212
Haber JE, Garvik B (1977) A new gene affecting the efficiency of mating-type interconversions in homothallic strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 87:33–50
Henrissat B, Driguez H, Viet C, Schülein M (1985) Synergism of cellulases from Trichoderma reesei in the degradation of cellulose. Biotechnology 3:722–726
Holtzapple M, Cognata M, Shu Y, Hendrickson C (1990) Inhibition of Trichoderma reesei cellulase by sugars and solvents. Biotechnol Bioeng 36:275–287
Ishida N, Saitoh S, Tokuhiro K, Nagamori E, Matsuyama T, Kitamoto K, Takahashi H (2005) Efficient production of l-lactic acid by metabolically engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae with a genome-integrated l-lactate dehydrogenase gene. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:1964–1970
Kawaguchi T, Enoki T, Tsurumaki S, Sumitani J, Ueda M, Ooi T, Arai M (1996) Cloning and sequencing of the cDNA encoding b-glucosidase 1 from Aspergillus aculeatus. Gene 173:287–288
Kruus K, Andreacchi A, Wang WK, Wu JH (1995) Product inhibition of the recombinant CelS, an exoglucanase component of the Clostridium thermocellum cellulosome. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 44:399–404
Lynd LR, Weimer PJ, van Zyl WH, Pretorius IS (2002) Microbial cellulose utilization: fundamentals and biotechnology. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 66:506–577
Lynd LR, van Zyl WH, McBride JE, Laser M (2005) Consolidated bioprocessing of cellulosic biomass: an update. Curr Opin Biotechnol 16(5):577–583
McBride JE, Zietsman JJ, Van Zyl WH, Lynd LR (2005) Utilization of cellobiose by recombinant b-glucosidase-expressing strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: characterization and evaluation of the sufficiency of expression. Enzyme Microb Technol 37:93–101
Medve J, Karlsson J, Lee D, Tjerneld F (1998) Hydrolysis of microcrystalline cellulose by cellobiohydrolase I and endoglucanase II from Trichoderma reesei: adsorption, sugar production pattern, and synergism of the enzymes. Biotechnol Bioeng 59:621–634
Murai T, Ueda M, Kawaguchi T, Arai M, Tanaka A (1998) Assimilation of cellooligosaccharides by a cell surface-engineered yeast expressing b-glucosidase and carboxymethylcellulase from Aspergillus aculeatus. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:4857–4861
Nagamori E, Tokuhiro K, Ishida N, Takahashi H, Saitoh S, Saotome O (2006) Method for producing lactic acid. Japanese patent application JP2006-020602A
Saitoh S, Ishida N, Onishi T, Tokuhiro K, Nagamori E, Kitamoto K, Takahashi H (2005) Genetically engineered wine yeast produces a high concentration of l-lactic acid of extremely high optical purity. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:2789–2792
Skory CD (2003) Lactic acid production by Saccharomyces cerevisiae expressing a Rhizopus oryzae lactate dehydrogenase gene. J Ind Microbiol Biotech 30:22–27
Tuka K, Zverlov VV, Velikodvorskaya GA (1992) Synergism between Clostridium thermocellum cellulases cloned in Escherichia coli. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 37:201–207
van Rensburg P, van Zyl WH, Pretorius IS (1998) Engineering yeast for efficient cellulose degradation. Yeast 14:67–76
van Rooyen R, Hahn-Hägerdal B, La Grange DC, van Zyl WH (2005) Construction of cellobiose-growing and fermenting Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains. J Biotechnol 120:284–295
Wee YJ, Kim JN, Ryu HW (2006) Biotechnological production of lactic acid and its recent applications. Food Tech Biotechnol 44:163–172
Acknowledgments
We thank Keiko Uemura for the technical assistance. This work was supported by a Bioprocess Development Project (Focus 21) grant from the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tokuhiro, K., Ishida, N., Kondo, A. et al. Lactic fermentation of cellobiose by a yeast strain displaying β-glucosidase on the cell surface. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 79, 481–488 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1454-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1454-x