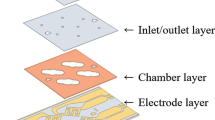
Abstract
Recently, it was shown that electrical DNA-chips in connection with a magnetic bead-based sandwich-hybridization assay can be a suitable alternative for the analysis of gene expression by monitoring the respective mRNA levels. In this study, we established an improved assay which allowed for a significantly shortened but sensitive detection of specific mRNAs. These improvements include the change to a solution-based sandwich-hybridization and the rearrangement of the used oligonucleotide probes. The introduction of a second labeled detection probe further increased the hybridization signals and, in turn, leads to a substantial time reduction of the detection protocol. The presented solution-based sandwich-hybridization protocol for the electrochemical detection of specific mRNAs requires about 60 min and the whole procedure, including sampling, cell disruption, and RNA isolation, approx. 80 min. The assay of this study was verified by nutrient-limited growth experiments and the analysis of selected starvation marker genes of the industrial host Bacillus licheniformis. The expression profiles determined with the electrical chip and the optimized protocol were, in most cases, comparable with the profiles determined by real-time RT-PCR measurements.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barken KB, Gabig-Ciminska M, Holmgren A, Molin S (2004) Effect of unlabeled helper probes on detection of an RNA target by bead-based sandwich hybridization. Biotechniques 36:124–132
Büttgenbach S, Michalzik M, Wilke R (2006) New approaches to online bioprocess monitoring. Eng Life Sci 6:449–454
DeLisa MP, Li J, Rao G, Weigand WA, Bentley WE (1999) Monitoring GFP-operon fusion protein expression during high cell density cultivation of Escherichia coli using an on-line optical sensor. Biotechnol Bioeng 65:54–64
Dulieu C, Poncelet D (1999) Spectrophotometric assay of a-acetolactate decarboxylase. Enzyme MicrobTechnol 25:537–542
Elsholz B, Wörl R, Blohm L, Albers J, Feucht H, Grunwald T, Jürgen B, Schweder T, Hintsche R (2006) Automated detection and quantitation of bacterial RNA by using electrical microarrays. Anal Chem 78:4794–4802
Gabig-Ciminska M, Holmgren A, Andresen H, Barken KB, Wümpelmann M, Albers J, Hintsche R, Breitenstein A, Neubauer P, Los M, Czyz A, Wegrzyn G, Silfversparre G, Jürgen B, Schweder T, Enfors SO (2004) Electric chips for rapid detection and quantification of nucleic acids. Biosens Bioelectron 19:537–546
Harms P, Kostov Y, Rao G (2002) Bioprocess monitoring. Curr Opin Biotechnol 13:124–127
Hoi LT, Voigt B, Jürgen B, Ehrenreich A, Gottschalk G, Evers S, Feesche J, Maurer KH, Hecker M, Schweder T (2006) The phosphate-starvation response of Bacillus licheniformis. Proteomics 6:3582–3601
Jürgen B, Tobisch S, Wümpelmann M, Gördes D, Koch A, Thurow K, Albrecht D, Hecker M, Schweder T (2005a) Global expression profiling of Bacillus subtilis cells during industrial-close fed-batch fermentations with different nitrogen sources. Biotechnol Bioeng 92:277–298
Jürgen B, Barken KB, Tobisch S, Pioch D, Wümpelmann M, Hecker M, Schweder T (2005b) Application of an electric DNA-chip for the expression analysis of bioprocess-relevant marker genes of Bacillus subtilis. Biotechnol Bioeng 92:299–307
Kotler LE, Zevin-Sonkin D, Sobolev IA, Beskin AD, Ulanovsky LE (1993) DNA sequencing: modular primers assembled from a library of hexamers or pentamers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 90:4241–4245
Kraft M, Knüpfer U, Wenderoth R, Pietschmann P, Hock B, Horn U (2007) An online monitoring system based on a synthetic sigma32-dependent tandem promoter for visualization of insoluble proteins in the cytoplasm of Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 75:397–406
Kyaw A, Maung-U K, Toe T (1985) Determination of inorganic phosphate with molybdate and Triton X-100 without reduction. Anal Biochem 145:230–234
Lane M, Paner T, Kashin I, Faldasz B, Li B, Gallo F, Benight A (1997) The thermodynamic advantage of DNA oligonucleotide ‘stacking hybridization’ reactions: energetics of a DNA nick. Nucleic Acids Res 25:611–617
Leskelä T, Tilsala-Timisjärvi A, Kusnetsov J, Neubauer P, Breitenstein A (2005) Sensitive genus-specific detection of Legionella by a 16S rRNA based sandwich hybridization assay. J Microbiol Methods 62:167–179
O’Meara D, Nilsson P, Nygren PA, Uhlén M, Lundeberg J (1998a) Capture of single-stranded DNA assisted by oligonucleotide modules. Anal Biochem 255:195–203
O’Meara D, Yun Z, Sönnerborg A, Lundeberg J (1998b) Cooperative oligonucleotides mediating direct capture of hepatitis C virus RNA from serum. J Clin Microbiol 36:2454–2549
Pioch D, Jürgen B, Evers S, Maurer K-H, Hecker M, Schweder T (2007) At-line monitoring of bioprocess-relevant marker genes. Eng Life Sci 7:373–379
Reischer H, Schotola I, Striedner G, Pötschacher F, Bayer K (2004) Evaluation of the GFP signal and its aptitude for novel on-line monitoring strategies of recombinant fermentation processes. J Biotechnol 108:115–125
Rey MW, Ramaiya P, Nelson BA, Brody-Karpin SD, Zaretsky EJ, Tang M, de Leon AL, Xiang H, Gusti V, Clausen IG, Olsen PB, Rasmussen MD, Andersen JT, Jørgensen PL, Larsen TS, Sorokin A, Bolotin A, Lapidus A, Galleron N, Ehrlich SD, Berka RM (2004) Complete genome sequence of the industrial bacterium Bacillus licheniformis and comparisons with closely related Bacillus species. Genome Biol 5:R77
Schuster K (2000) Monitoring the physiological status in bioprocesses on the cellular level. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 66:185–208
Schweder T, Hecker M (2004) Monitoring of stress responses. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 89:47–71
Veith B, Herzberg C, Steckel S, Feesche J, Maurer KH, Ehrenreich P, Bäumer S, Henne A, Liesegang H, Merkl R, Ehrenreich A, Gottschalk G (2004) The complete genome sequence of Bacillus licheniformis DSM13, an organism with great industrial potential. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 7:204–211
Voigt B, Hoi LT, Jürgen B, Albrecht D, Ehrenreich A, Veith B, Evers S, Maurer KH, Hecker M, Schweder T (2007) The glucose and nitrogen starvation response of Bacillus licheniformis. Proteomics 7:413–423
Wende K, Krenn L, Unterrieder I, Lindequist U (2004) Red clover extracts stimulate differentiation of human osteoblastic osteosarcoma HOS58 cells. Planta Med 70:1003–1005
Westerfeld WW (1945) A colorimetric determination of blood acetoin. J Biol Chem 161:495–502
Yakovchuk P, Protozanova E, Frank-Kamenetskii MD (2006) Base-stacking and base-pairing contributions into thermal stability of the DNA double helix. Nucleic Acids Res 34:564–574
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF: 0312707 and 0313751) and by the Ministry of Education, Science and Culture of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern (1400/0052 1401). We thank Stefanie Leja for excellent technical assistance and support during the fermentations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pioch, D., Jürgen, B., Evers, S. et al. Improved sandwich-hybridization assay for an electrical DNA-chip-based monitoring of bioprocess-relevant marker genes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 78, 719–728 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1347-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1347-z