Abstract
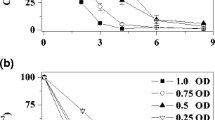
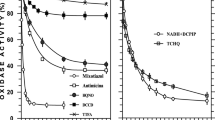
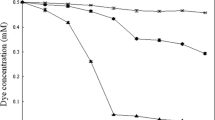
Shewanella decolorationis S12 was able to reduce various azo dyes in a defined medium with formate, lactate, and pyruvate or H2 as electron donors under anaerobic conditions. Purified membranous, periplasmic, and cytoplasmic fractions from strain S12 analyzed, respectively, only membranous fraction was capable of reducing azo dye in the presence of electron donor, indicating that the enzyme system for anaerobic azoreduction was located on cellular membrane. Respiratory inhibitor Cu2+, dicumarol, stigmatellin, and metyrapone inhibited anaerobic azoreduction by purified membrane fraction, suggesting that the bacterial anaerobic azoreduction by strain S12 was a biochemical process that oxidizes the electron donors and transfers the electrons to the acceptors through a multicompound system related to electron transport chain. Dehydrogenases, cytochromes, and menaquinones were essential electron transport components for the azoreduction. The electron transport process for azoreduction was almost fully inhibited by O2, 6 mM of \({\text{NO}}^{ - }_{3} \), and 0.9 mM of \({\text{NO}}^{ - }_{2} \), but not by 10 mM of Fe3+. The inhibition may be a result from the competition for electrons from electron donors. These findings impact on the understanding of the mechanism of bacterial anaerobic azoreduction and have implication for improving treatment methods of wastewater contaminated by azo dyes.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnold RG, DiChristina TJ, Hoffmann MR (1986) Inhibitor studies of dissimilative Fe(III) reduction by Pseudomonas sp. strain 200 (“Pseudomonas ferrireductans”). Appl Environ Microbiol 52:281–289
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Bragger JL, Lloyd AW, Soozandehfar SH, Bloomfield SF, Marriott C, Martin GP (1997) Investigations into the azo reducing activity of a common colonic microorganism. Int J Pharm 157:61–71
Brown JP (1981) Reduction of polymeric azo and nitro dyes by intestinal bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 41:1283–1286
Brown MA, DeVito SC (1993) Predicting azo dye toxicity. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 23:249–324
Bumpus JA (1995) Microbial degradation of azo dyes. Prog Ind Microbiol 32:157–176
Chang JS, Lin YC (2000) Fed-batch bioreactor strategies for microbial decolorization of azo dye using a Pseudomonas luteola strain. Biotechnol Prog 16:979–985
Chung KT, Cerniglia CE (1992) Mutagenicity of azo dyes: structure-activity relationships. Mutat Res 77:201–220
Chung KT, Fulk GE, Egan M (1978) Reduction of azo dyes by intestinal anaerobes. Appl Environ Microbiol 35:558–562
Chung KT, Stevens SEJ, Cerniglia CE (1992) The reduction of azo dyes by the intestinal microflora. Crit Rev Microbiol 18:175–197
Dubin P, Wright KL (1975) Reduction of azo food dyes in cultures of Proteus vulgaris. Xenobiotica 5:563–571
Fernandez VM, Rua ML, Reyes P, Cammack R, Hatchikian EC (1989) Inhibition of Desulfovibrio gigas hydrogenase with copper salts and other metal ions. Eur J Biochem 185:449–454
Gerencsér L, Rinyu L, Kálmán L, Takahashi E, Wraight CA, Maróti P (2004) Competitive binding of quinone and antibiotic stigmatellin to reaction centers of photosynthetic bacteria. Acta Biologica Szegediensis 48:25–33
Ghiorse WC, Ehrlich HL (1976) Electron transport components of the MnO2 reductase system and the location of the terminal reductase in a marine Bacillus. Appl Environ Microbiol 31:977–985
Haug W, Schmidt A, Nortemann B, Hempel DC, Stolz A, Knackmuss HJ (1991) Mineralization of the sulfonated azo dye mordant yellow 3 by a 6-aminonaphthalene-2-sulfonate-degrading bacterial consortium. Appl Environ Microbiol 57:3144–3149
He Q, Sanford RA (2003) Characterization of Fe(III) reduction by chlororespiring Anaeromxyobacter dehalogenans. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:2712–2718
Hu TL (1994) Decolourization of reactive azo dyes by transformation with Pseudomonas luteola. Bioresour Technol 49:47–51
Jan G, Oliver D, Geert K, Mischa K, Luit PW, Roger H, Matthew DC, Jan CG (1999) Influence of different electron donors and acceptors on dehalorespiration of tetrachloroethene by Desulfitobacterium frappieri TCE1. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:5212–5221
Keck A, Klein J, Kudlich M, Stolz A, Knackmuss HJ, Mattes R (1997) Reduction of azo dyes by redox mediators originating in the naphthalenesulfonic acid degradation of Sphingomonas sp. strain BN6. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:3684–3690
Kudlich M, Keck A, Klein J, Stolz A (1997) Localization of the enzyme system involved in the anaerobic degradation of azo dyes by Sphingomonas sp. BN6 and effect of artificial redox mediators on the rate of azo reduction. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:3691–3694
Louie TM, Mohn WW (1999) Evidence for a chemiosmotic model of dehalorespiration in Desulfomonile tiedjei. DCB-1. J Bacteriol 181:41–46
Lovley DR, Phillips EJP (1988) Novel mode of microbial energy metabolism: organic carbon oxidation coupled to dissimilatory reduction of iron or manganese. Appl Environ Microbiol 54:1472–1480
Maguire RJ (1992) Occurrence and persistence of dyes in a Canadian river. Water Sci Technol 25:265–270
Miller TL, Wolin ML (1974) A serum bottle modification of the Hungate technique for cultivating obligate anaerobes. Appl Microbiol 27:985–987
Osborn MJ, Munson R (1974) Separation of the inner (cytoplasmic) and outer membranes of gram-negative bacteria. Methods Enzymol 31:642–653
Ouchane S, Agalidis I, Astier C (2002) Natural resistance to inhibitors of the ubiquinol cytochrome c oxidoreductase of Rubrivivax gelatinosus: sequence and functional analysis of the cytochrome bc1 complex. J Bacteriol 184:3815–3822
Pearce CI, Lloyd JR, Guthrie JT (2003) The removal of colour from textile wastewater using whole bacterial cells: a review. Dyes Pigm 58:179–196
Rafii F, Franklin W, Cerniglia CE (1990) Azoreductase activity of anaerobic bacteria isolated from human intestinal microflora. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:2146–2151
Rau J, Stolz A (2003) Oxygen-insensitive nitroreductases NfsA and NfsB of Escherichia coli function under anaerobic conditions as lawsone-dependent azo reductases. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:3448–3455
Rau J, Knackmuss H-J, Stolz A (2002) Effects of different quinoide redox mediators on the anaerobic reduction of azo dyes by bacteria. Environ Sci Technol 36:1497–1504
Satoh T (1984) Inhibition of electron transfer through the cytochrome b-c 1 complex by nitric oxide in a photodenitrifer, Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides forma sp. denitrificans. Arch Microbiol 139:179–183
Scheline RR, Nygaard RT, Longberg B (1970) Enzymatic reduction of the azo dye, acid yellow, by extracts of Streptococcus faecalis, isolated from rat intestine. Food Cosmet Toxicol 8:55–58
Seshadri S, Bishop PL, Agha AM (1994) Anaerobic/aerobic treatment of selected azo dyes in wastewater. Waste Manag 14:127–137
Selvam K, Swaminathan K, Keo-Sang C (2003) Microbial decolorization of azo dyes and dye industry effluent by Fomes lividus. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 19:591–593
Stolz A (2001) Basic and applied aspects in the microbial degradation of azo dyes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 56:69–80
Van der Zee FP, Lettinga G, Field JA (2001) Azo dye decolourisation anaerobic granular sludge. Chemosphere 44:1169–1176
Williams PA, Cosme J, Vinkovic DM, Ward A, Angove HC, Day PJ, Vonrhein C, Tickle IJ, Jhoti H (2004) Crystal structures of human cytochrome P450 3A4 bound to metyrapone and progesterone. Science 305:683–686
Wolin EA, Wolin MJ, Wolfe RS (1963) Formation of methane by bacterial extracts. J Biol Chem 238:2882–2886
Xu M, Guo J, Cen Y, Zhong X, Cao W, Sun G (2005) Shewanella decolorationis sp. nov., a dye-decolorizing bacterium isolated from an activated-sludge of wastewater treatment plant. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:363–368
Zollinger H (1991) Color chemistry: syntheses, properties and applications of organic dyes and pigments, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Zumft WG (1993) The biological role of nitric oxide in bacteria. Arch Microbiol 160:253–264
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Chinese National Programs for High Technology Research and Development (2003AA214040), Guangdong Provincial Programs for Natural Science Foundation Group (015017), and Guangdong Provincial key Programs for Science and Technology Development (05100365).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, Y., Chen, X., Guo, J. et al. Effects of electron donors and acceptors on anaerobic reduction of azo dyes by Shewanella decolorationis S12. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 74, 230–238 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-006-0657-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-006-0657-2