Abstract
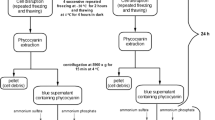
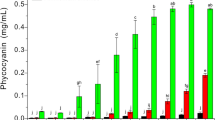
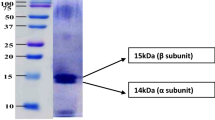
C-phycocyanin (C-PC) was extracted from fresh Spirulina platensis by deploying a species of non-pathogenic nitrogen-fixing bacteria, namely, Klebsiella pneumoniae. The algal slurry was neither washed nor centrifuged; the bacterial culture was poured into the slurry, the vessel sealed, and crude C-PC extracted after about 24 h. The extraction was clean and efficient, and the purity and concentration of C-PC proved to be of adequate quality.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abalde J, Betancourt L, Torres E, Cid A, Barwell C (1998) Purification and characterization of phycocyanin from the marine cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. IO9201. Plant Sci 136:109–120
Bermejo R, Talavera EM, Alvarez-Pez JM, Orte JC (1997) Chromatographic purification of biliproteins from Spirulina platensis high-performance liquid chromatographic separation of their α and β subunits. J Chromatogr A 778:441–450
Boussiba S, Richmond AE (1979) Isolation and characterization of phycocyanins from the blue-green algae Spirulina platensis. Arch Microbiol 120:155–159
Cohen Z (1986) Products of microalgae. In: Richmond A (ed) Handbook of microalgae mass culture. CRC Press, Boca. Raton, Florida, pp 421–454
Follows M, Hetherington PJ, Dunnill P, Lilly MD (1971) Release of protein from baker’s yeast by disruption in industrial homogeniser. Trans Inst Chem Eng 49:142–148
Furuki T, Maeda S, Imajo S, Tetsuya H, Amaya T, Hirokawa T, Ito K, Nozawa H (2003) Rapid and selective extraction of phycocyanin from Spirulina platensis with ultrasonic cell disruption. J Appl Phycol 15:319–324
Glazer AN, Stryer L (1984) Phycofluor probes. Trends Biochem Sci 9:423–447
Gottlieb RA, Adachi S (2003) Nitrogen cavitation for cell disruption to obtain mitochondria from cultured cells. Methods Enzymol 322:213–221
Harris Elizabeth H (1989) The Chlamydomonas sourcebook. p 26
Hayashi NR, Terazono K, Hasegawa N, Kodama T, Igarashi Y (1997) Identification and characterization of phycobiliprotein from a thermophilic cyanobacterium, Chroococcidiopsis sp. strain TS-821. J Ferment Bioeng 84:475–477
Herrero M, Ibanez E, Senorans J, Cifuentes A (2004) Pressurized liquid extracts from Spirulina platensis microalgae. Determination of their antioxidant activity and preliminary analysis by micellar electrokinetic chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1047:195–203
Kilpatrick KA (1985) The development of a method to measure marine cyanobacterial phycoerythrin extracted in solvents, M.S. thesis, Texas A&M University, p 12
Lin HW, Qin HC, Wu ZP, Huang WB, Liang H (1998) A new extraction and purification method for phycocyanins from Spirulina. Fine Chemicals 15:18–20
Lu C, Vonshak A (1999) Photoinhibition in outdoor Spirulina platensis cultures assessed by polyphasic chlorophyll fluorescence transients. J Appl Phycol 11:355–359
Minkova KM, Tchernov AA, Tchorbadjieva MI, Fournadjieva ST, Antova RE, Busheva MCh (2003) Purification of C-phycocyanin from Spirulina (Arthrospira) fusiformis. J Biotechnol 102:55–59
Patel A, Mishra S, Pawar R, Ghosh PK (2005) Purification and characterization of C-phycocyanin from cyanobacterial species of marine and freshwater habitat. Protein Expr Purif 40:248–255
Pulz O, Gross W (2004) Valuable products from biotechnology of microalgae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 65:635–648
Sarada R, Pillai MG, Ravishankar GA (1999) Phycocyanin from Spirulina sp.: influence of processing of biomass on phycocyanin yield, analysis of efficacy of extraction methods and stability studies on phycocyanin. Process Biochem 34:795–801
Scheer H, Kufer W (1977) Conformational studies on c-phycocyanin from spirulina platensis. Z Naturforsch 32c:513–519
Stewart DE, Farmer FH (1984) Extraction, identification and quantitation of phycobiliprotein pigments from phototrophic plankton. Limnol Oceanogr 29:392–397
Tchernov AA, Minkova KM, Houbavenska NB, Kovacheva NG (1999) Purification of phycobiliproteins from Nostoc sp. by aminohexyl-sepharose chromatography. J Biotechnol 69:69–73
Viskari PJ, Colyer CL (2003) Rapid extraction of phycobiliproteins from cultured cyanobacteria samples. Anal Biochem 319:263–271
Wyman M (1992) An in vivo method for the estimation of phycoerythrin concentration in marine cyanobacteria (Synechococcus spp.). Limnol Oceanogr 37:1300–1306
Zarrouk (1966) Contribution a letude d’une cyanophycee. Influence de divers factours physiques. et chimiques sur la croissance et la phytosynthese do Spirulina maxima. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Paris
Acknowledgements
The authors are touched by the patience and care shown by three unknown reviewers; the manuscript has benefited from their precision and good advice. Thanks are also due to our friends, Mr. Li B.X., Teng L.J. and Mrs. Qin X. Ch., for the discussions on this study. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) grant (No. 40473051) and Resource, Environment and GIS Key laboratory of Beijing City.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, Y., Chen, X.B., Wang, K.B. et al. A simple method for extracting C-phycocyanin from Spirulina platensis using Klebsiella pneumoniae . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 74, 244–248 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-006-0636-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-006-0636-7