Abstract
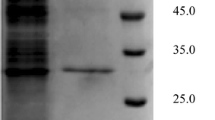
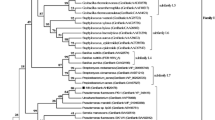
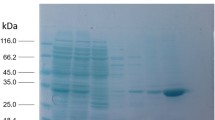
A lipase-producing bacterium strain B68 screened from soil samples of China was identified as Pseudomonas fluorescens. With GenomeWalker, the open reading frame of lipase gene lipB68, encoding 476 amino acids, was cloned and expressed in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3). By affinity chromatography, the recombinant LipB68 protein was purified to the purity of 95%. As a member of lipase subfamily I.3, LipB68 has a unique optimum temperature of 20 °C, which was the lowest in this subfamily. In chiral resolution, LipB68 effectively catalyzed the transesterification of both α-phenylethanol and α-phenylpropanol at 20 °C, achieving E values greater than 100 and 60 after 120 h, respectively. Among all the known catalysts in biodiesel production, LipB68 produced biodiesel with a yield of 92% after 12 h, at the lowest temperature of 20 °C, and is the first one of the I.3 lipase subfamily reported to be capable of catalyzing the transesterification reaction of biodiesel production. Since lipase-mediated biodiesel production is normally carried out at 35–50 °C, the availability of a highly active lipase with a low optimal temperature can provide substantial savings in energy consumption. Thus, this novel psychrophilic lipase (LipB68) may represent a highly competitive energy-saving biocatalyst.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn JH, Pan JG, Rhee JS (1999) Identification of the tliDEF ABC Transporter Specific for Lipase in Pseudomonas fluorescens SIK W1. J Bacteriol 181:1847–1852
Amada K, Haruki M, Imanaka T, Morikawa M, Kanaya S (2000) Overproduction in Escherichia coli, purification and characterization of a family I.3 lipase from Pseudomonas sp. MIS38. Biochim Biophys Acta 1478:201–210
Andersson RE (1980) Microbial lipolysis at low temperatures. Appl Environ Microbiol 39:36–40
Binet R, Letoffe S, Ghigo JM, Delepelaire P, Wandersman C (1997) Protein secretion by Gram-negative bacterial ABC exporters—a review. Gene 192:7–11
Feller G, Narinx E, Arpigny JL, Aittaleb M, Baise E, Genicot S, Gerday C (1996) Enzymes from psychrophilic organisms. FEMS Microbiol Rev 18:189–202
Gao XG, Zhang K Ch, Cao Sh G (1998) Isolation of a lipase-producing pseudomonas strain and optimization of its fermentation conditions. Acta Microbiol Sin 38:313–317
Iso M, Chen B, Eguchi M, T Kudo T, Shresth S (2001) Production of biodiesel fuel from triglycerides and alcohol using immobilized lipase. J Mol Catal B Enzym 16:53–58
Jaeger KE, Ransac S, Dijkstra BW, Colson C, van Heuvel M, Misset O (1994) Bacterial lipases. FEMS Microbiol Rev 15:29–63
Lee YP, Chung GH, Rhee JS (1993) Purification and characterization of Pseudomonas fluorescens SIK W1 lipase expressed in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta 1169:156–164
Ley SV, Parra M, Redgrave AJ, Sternfeld F (1990) Microbial oxidation in synthesis: preparation of myoinositol phosphates and related cyclitol derivatives from benzene. Tetrahedron 46:4995–5026
Liu AMF, Somers NA, Kazlauskas RJ, Brush TS, Zocher F, Enzelberger MM, Bornscheuer UT, Horsman GP, Mezzetti A, Schmidt-Dannert C, Schmid RD (2001) Mapping the substrate selectivity of new hydrolases using colorimetric screening: lipases from Bacillus thermocatenulatus and Ophiostoma piliferum, esterases from Pseudomonas fluorescens and Streptomyces diastatochromogenes. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 12:545–556
Mohamed MS, Uwe TB (2003) Improvement in lipase-catalyzed synthesis of fatty acid methyl esters from sunflower oil. Enzyme Microb Technol 33:97–103
Mori K, Akao H (1980) Synthesis of optically active alkenyl alcohols and α-hydroxyl esters by microbial asymmetric hydrolysis by the corresponding acetates. Tetrahedron 36:91–96
Morris DD, Gibbs MD, Chin CW, Koh MH, Wong RW, Allison RW, Nelson PJ, Bergquist PL (1998) Cloning of the xynB gene from Dictyoglomus thermophilum Rt46B.1 and action of the gene product on kraft pulp. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:1759–1765
Rajmohan S, Dodd CER, Waites WM (2002) Enzymes from isolates of Pseudomonas fluorescens involved in food spoilage. J Appl Microbiol 93:205–213
Rashid N, Shimada Y, Ezaki S, Atomi H, Imanaka T (2001) Low-temperature lipase from psychrotrophic Pseudomonas sp. strain KB700A. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:4064–4069
Rosenau F, Jaeger KE (2000) Bacterial lipases from Pseudomonas: regulation of gene expression and mechanisms of secretion. Biochimie 82:1023–1032
Soumanou MM, Uwe TB (2003) Lipase-catalyzed alcoholysis of vegetable oils. Eur J Lipid Sci Technol 105:656–660
Sugihara A, Tani T, Tominaga Y (1991) Purification and characterization of a novel thermostable lipase from Bacillus sp. J Biochem (Tokyo) 109:211–216
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the grant from the Ministry of Science and Technology, Basic Research project No.: 2002CCA400, and Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University, project No.: NCET-04-0411. Furthermore, we thank Drs. Yusen Liu and Charles V. Smith of the Ohio State University for editing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, Y., Zheng, Y., Jiang, Z. et al. A novel psychrophilic lipase from Pseudomonas fluorescens with unique property in chiral resolution and biodiesel production via transesterification. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 73, 349–355 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-006-0478-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-006-0478-3