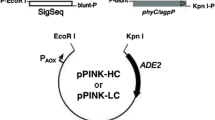
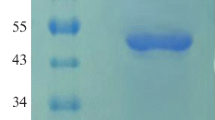
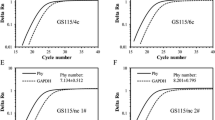
Abstract
Phytase is widespread in nature. It has been used as a cereal feed additive that can enhance the phosphorus and mineral absorption in monogastric animals to reduce the level of phosphorus output in manure. Phytase of Peniophora lycii is a 6′-phytase, which owns high specific activity. To achieve a high expression level of 6′-phytase in Pichia pastoris, the 1,230-bp phytase gene of P. lycii was synthesized and optimized for codon usage, G+C content, as well as mRNA secondary structures. The gene constructs containing wild type or modified phytase gene coding sequences under the control of the highly-inducible alcohol oxidase gene (AOX1) promoter, the synthetic signal peptide (designated MF4I), which is a codon-modified Saccharomyces cerevisiae mating factor α-prepro-leader sequence, were used to transform P. pastoris. The P. pastoris strain that expressed the modified phytase gene (phy-pl-sh) with MF4I sequence produced 12.2 g phytase per liter of fluid culture, with the phytase activity of 10,540 U ml−1. The yield of the modified phytase gene, with bias codon usage and MF4I signal, is 4.4 times higher than that of the wild type gene with MF4I signal and 13.6 times higher than that of the wild type gene with wild type S. cerevisiae signal. The recombinant phytase had one optimum pH (pH 4.5) and an optimum temperature of 50°C. The P. pastoris strain expressed the modified 6-phytase gene, with the MF4I signal peptide showing great potential as a commercial phytase production system.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bagger HL, Fuglsang CC, Westh P (2003) Preferential binding of two compatible solutes to the glycan moieties of Peniophora lycii phytase. Biochemistry 42:10295–10300
Cho J, Lee C, Kang S, Lee J, Lee H, Bok J, Woo J, Moon Y, Choi Y (2005) Molecular cloning of a phytase gene (phy M) from Pseudomonas syringae MOK1. Curr Microbiol 51:11–15
Clare JJ, Rayment FB, Ballantine SP, Sreekrishna K, Romanos MA (1991) High-level expression of tetanus toxin fragment c in Pichia pastoris strains containing multiple tandem integrations of the gene. Biotechnology 9:455–460
Cregg JM, Vedvick TS, Raschke WC (1993) Recent advances in the expression of foreign genes in Pichia pastoris. Biotechnology 11:905–910
Engelen AJ, van der Heeft FC, Randsdorp PH, Smit EL (1994) Simple and rapid determination of phytase activity. J AOAC Int 77:760–764
Gellissen G (2000) Heterologous protein production in methylotrophic yeasts. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 54:741–750
Graf E (1983) Calcium binding to phytic acid. J Agric Food Chem 31:851–855
Greiner R, Konietzny U, Jany KD (1993) Purification and characterization of two phytases from Escherichia coli. Arch Biochem Biophys 303:107–113
Ha NC, Oh BC, Shin S, Kim HJ, Oh TK, Kim YO, Choi KY, Oh BH (2000) Crystal structures of a novel, thermostable phytase in partially and fully calcium-loaded states. Nat Struct Biol 7:147–153
Haefner S, Knietsch A, Scholten E, Braun J, Lohscheidt M, Zelder O (2005) Biotechnological production and applications of phytases. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 23:1–10
Han Y, Lei XG (1999) Role of glycosylation in the functional expression of an Aspergillus niger phytase gene (phyA) in Pichia pastoris. Arch Biochem Biophys 36:483–490
Hurrell RF (2004) Phytic acid degradation as a means of improving iron absorption. Int J Vitam Nutr Res 74:445–452
Jendza JA, Dilger RN, Adedokun SA, Sands JS, Adeola O (2005) Escherichia coli phytase improves growth performance of starter, grower, and finisher pigs fed phosphorus-deficient diets. J Anim Sci 83:1882–1889
Kjeldsen T, Pettersson AF, Hach M (1999) Secretory expression and characterization of insulin in Pichia pastoris. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 29:79–86
Lassen SF, Breinholt J, Ostergaard PR, Brugger R, Bischoff A, Wyss M, Fuglsang CC (2001) Expression, gene cloning, and characterization of five novel phytases from four basidiomycete fungi: Peniophora lycii, Agrocybe pediades, a Ceriporia sp., and Trametes pubescens. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:4701–4707
Lee S, Kim T, Stahl CH, Lei XG (2005) Expression of Escherichia coli AppA2 phytase in four yeast systems. Biotechnol Lett 27:327–334
Lei XG, Stahl CH (2001) Biotechnological development of effective phytases for mineral nutrition and environmental protection. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 57:474–481
Lei XG, Porres JM (2003) Phytase enzymology, applications, and biotechnology. Biotechnol Lett 25:1787–1794
Lei X, Pao K, Elwyn RM, Ullrey DE, Yokoyama MT (1993) Supplemental microbial phytase improves bioavailability of dietary zinc to weanling pigs. J Nutr 123:1117–1123
Mitchell DB, Vogel K, Weimann B, Pasamontes L, Loon APGM (1997) The phytase subfamily of histidine acid phosphatases: isolation of genes for two novel phytases from the fungi Aspergillus terreus and Myceliophthora thermophola. Microbiology 143:245–252
Mullaney EJ, Ullah AH (1998) Identification of a histidine acid phosphatase (phyA)-like gene in Arabidopsis thaliana. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 251:252–255
Mullaney EJ, Daly CB, Sethumadhavan K, Rodriquez E, Lei XG, Ullah AH (2000) Phytase activity in Aspergillus fumigatus isolates. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 275:759–763
Pasamontes L, Haiker M, Henriquez-Huecas M, Mitchell DB, Loon AP (1997a) Cloning of the phytases from Emericella nidulans and the thermophilic fungus Talaromyces thermophilus. Biochim Biophys Acta 1353:217–223
Pasamontes L, Haiker M, Wyss M, Tessier M, van Loon AP (1997b) Gene cloning, purification, and characterization of a heat-stable phytase from the fungus Aspergillus fumigatus. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:1696–1700
Peng RH, Xiong AS, Li X, Fan HQ, Yao QH, Guo MJ, Zhang SL (2002) High expression of a heat-stable phytase in Pichia pastoris. Sheng Wu Hua Xue Yu Sheng Wu Wu Li Xue Bao (Shanghai) 34:725–730
Peng R, Xiong A, Li X, Fuan H, Yao Q (2003) A delta-endotoxin encoded in Pseudomonas fluorescens displays a high degree of insecticidal activity. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 63:300–306
Reddy NR, Sathe SK, Salunkhe DK (1982) Phytates in legumes and cereals. Adv Food Res 28:1–92
Rodriguez E, Han Y, Lei XG (1999) Cloning, sequencing, and expression of an Escherichia coli acid phosphatase/phytase gene (appA2) isolated from pig colon. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 257:117–123
Sagt CM, Kleizen B, Verwaal R, de Jong MD, Muller WH, Smits A, Visser C, Boonstra J, Verkleij AJ, Verrips CT (2000) Introduction of an N-glycosylation site increases secretion of heterologous proteins in yeasts. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:4940–4944
Sambrook J, Frisch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
Scorer CA, Clare JJ, McCombie WR, Romanos MA, Sreekrishna K (1994) Rapid selection using G418 of high copy number transformants of Pichia pastoris for high-level foreign gene expression. Biotechnology 12:181–184
Sharp PM, Tuohy TMF, Mosurski KR (1986) Codon usage in yeast: cluster analysis clearly differentiates highly and lowly expression genes. Nucleic Acids Res 14:5125–5143
Sreekrishna K, Brankamp RG, Kropp KE, Blankenship DT, Tsay JT, Smith PL, Wierschke JD, Subramaniam A, Birkenberger LA (1997) Strategies for optimal synthesis and secretion of heterologous proteins in the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris. Gene 190:55–62
Stahl CH, Roneker KR, Thorntonm JR, Lei XG (2000) A new phytase expressed in yeast effectively improves the bioavailability of phytate phosphorus to weanling pigs. J Anim Sci 78:668–674
Stemmer WP, Crameri A, Ha KD, Brennan TM, Heyneker HL (1995) Single-step assembly of a gene and entire plasmid from large numbers of oligonucleotides. Gene 164:49–53
Ullah AHJ, Gibson DM (1987) Extracelluar phytase (E.C.3.1.3.8) from Aspergillus ficuum NRRL 3135: purification and characterization. Prep Biochem 17:63–91
Ullah AHJ, Phillippy BQ (1994) Substrate selectivity in Aspergillus ficuum phytase and acid phosphatases using myo-inositol phosphates. J Agric Food Chem 42:277–283
Ullah AH, Sethumadhavan K (2003) PhyA gene product of Aspergillus ficuum and Peniophora lycii produces dissimilar phytases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 303:463–468
Vohra A, Satyanarayana T (2003) Phytases: microbial sources, production, purification, and potential biotechnological applications. Crit Rev Biotechnol 23:29–60
Waterham HR, Russell KA, Vries Y, Cregg JM (1997) Peroxisomal targeting, import, and assembly of alcohol oxidase in Pichia pastoris. J Cell Biol 139:1419–1431
Wodzinski RJ, Ullah AH (1996) Phytase. Adv Appl Microbiol 42:263–302
Wyss M, Pasamontes L, Remy R, Kohler J, Kusznir E, Gadient M, Muller F, van Loon APGM (1998) Comparison of the thermostability properties of three acid phosphatases from molds: Aspergillus fumigatus phytase, A. niger phytase, and A. niger PH 2.5 acid phosphatase. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:4446–4451
Wyss M, Brugger R, Kronenberger A, Remy R, Fimbel R, Oesterhelt G, Lehmann M, van Loon AP (1999a) Biochemical characterization of fungal phytases (myo-inositol hexakisphosphate phosphohydrolases): catalytic properties. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:367–373
Wyss M, Pasamontes L, Friedlein A, Remy R, Tessier M, Kronenberger A, Middendorf A, Lehmann M, Schnoebelen L, Rothlisberger U, Kusznir E, Wahl G, Muller F, Lahm HW, Vogel K, van Loon AP (1999b) Biophysical characterization of fungal phytases (myo-inositol hexakisphosphate phosphohydrolases): molecular size, glycosylation pattern, and engineering of proteolytic resistance. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:359–366
Xiong AS, Peng RH, Li X, Fan HQ, Yao QH, Guo MJ, Zhang SL (2003) The study of signal peptide sequence affecting expression of heterologous protein in Pichia pastoris. Sheng Wu Hua Xue Yu Sheng Wu Wu Li Xue Bao (Shanghai) 35:154–160
Xiong AS, Yao QH, Peng RH, Li X, Fan HQ, Guo MJ, Zhang SL (2004a) Isolation, characterization, molecular cloning of the cDNA encoding a novel phytase from Aspergillus niger 113 and high expression in Pichia pastoris. J Biochem Mol Biol 37:282–291
Xiong AS, Yao HQ, Peng RH, Li X, Fan HQ, Li Y, Cheng ZM (2004b) A simple, rapid, high fidelity and cost-effective PCR-based two-step DNA synthesis (PTDS) method for long gene sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 32:e98
Xiong AS, Yao QH, Peng RH, Han PL, Cheng ZM, Li Y (2005) High level expression of a recombinant acid phytase gene in Pichia pastoris. J Appl Microbiol 98:418–428
Zhao X, Huo KK, Li YY (2000) Synonymous codon usage in Pichia pastoris. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao 16:308–311
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Dr. Jian Zhang, Dr. Wen-Jin Yu (University of Guelph, Canada) and Prof. Zong-Ming Cheng (University of Tennessee, USA) for their careful reading and valuable comments on the manuscript. This research was supported by the Fund of National Natural Science Foundation of China (30471258), Shanghai Natural Science Foundation (04ZR14116), Shanghai Rising-Star Program (05QMX1445), Key Project of Science and Technology Commission Foundation of Shanghai (993913002). We thank Shanghai YongYe Bio-engineering for providing some instruments and technical help.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiong, AS., Yao, QH., Peng, RH. et al. High level expression of a synthetic gene encoding Peniophora lycii phytase in methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 72, 1039–1047 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-006-0384-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-006-0384-8