Abstract
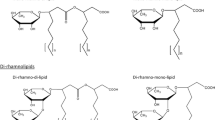
Pseudomonas aeruginosa produces glycolipidic surface-active molecules (rhamnolipids) which have potential biotechnological applications. Rhamnolipids are produced by P. aeruginosa in a concerted manner with different virulence-associated traits. Here, we review the rhamnolipids biosynthetic pathway, showing that it has metabolic links with numerous bacterial products such as alginate, lipopolysaccharide, polyhydroxyalkanoates, and 4-hydroxy-2-alkylquinolines (HAQs). We also discuss the factors controlling the production of rhamnolipids and the proposed roles this biosurfactant plays in P. aeruginosa lifestyle.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abalos A, Pinazo A, Infante MR, Casals M, Garcia F, Manresa A (2001) Physicochemical and antimicrobial properties of new rhamnolipids produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa AT10 from soybean oil refinery wastes. Langmuir 17:1367–1371
Al-Dujaili AH (1976) Toxic activity against alveolar macrophages of products of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from respiratory and non-respiratory sites. J Hyg (Lond) 77:211–220
Al-Tahhan RA, Sandrin TR, Bodour AA, Maier RM (2000) Rhamnolipid-induced removal of lipopolysaccharide from Pseudomonas aeruginosa: effect on cell surface properties and interaction with hydrophobic substrates. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:3262–3268
Arino S, Marchal R, Vandecasteele J-P (1996) Identification and production of a rhamnolipidic biosurfactant by a Pseudomonas species. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 45:162–168
Barbuzzi T et al (2004) Microbial synthesis of poly(3-hydroxyalkanoates) by Pseudomonas aeruginosa from fatty acids: identification of higher monomer units and structural characterization. Biomacromolecules 5:2469–2478
Beal R, Betts WB (2000) Role of rhamnolipid biosurfactants in the uptake and mineralization of hexadecane in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Appl Microbiol 89:158–168
Bedard M, McClure CD, Schiller NL, Francoeur C, Cantin A, Denis M (1993) Release of interleukin-8, interleukin-6, and colony-stimulating factors by upper airway epithelial cells: implication for cystic fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 9:455–462
Bredenbruch F, Nimtz M, Wray V, Morr M, Müller R, Häussler S (2005) Biosynthetic pathway of Pseudomonas aeruginosa 4-hydroxy-2-alkylquinolines. J Bacteriol 187:3630–3635
Burger MM, Glaser L, Burton RM (1966) Formation of rhamnolipids of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Methods Enzymol 8:441–445
Calfee MW, Shelton JG, McCubrey JA, Pesci EC (2005) Solubility and bioactivity of the Pseudomonas quinolone signal are increased by a Pseudomonas aeruginosa-produced surfactant. Infect Immun 73:878–882
Campos-García J, Caro AD, Nájera R, Miller-Maier RM, Al-Tahhan RA, Soberón-Chávez G (1998) The Pseudomonas aeruginosa rhlG gene encodes an NADPH-dependent β-ketoacyl reductase which is specifically involved in rhamnolipid synthesis. J Bacteriol 180:4442–4451
Chayabutra C, Wu J, Ju LK (2001) Rhamnolipid production by Pseudomonas aeruginosa under denitrification: effects of limiting nutrients and carbon substrates. Biotechnol Bioeng 72:25–33
Cosson P et al (2002) Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence analyzed in a Dictyostelium discoideum host system. J Bacteriol 184:3027–3033
Costerton JW (1980) Pseudomonas aeruginosa in nature and disease. In: Sabath CD (ed) Pseudomonas aeruginosa: the organism, diseases it causes and their treatment. Hans Huber Publishers, Bern, Switzerland pp 15–24
Coyne MJ Jr, Russell KS, Coyle CL, Goldberg JB (1994) The Pseudomonas aeruginosa algC gene encodes phosphoglucomutase, required for the synthesis of a complete lipopolysaccharide core. J Bacteriol 176:3500–3507
Davey ME, Caiazza NC, O'Toole GA (2003) Rhamnolipid surfactant production affects biofilm architecture in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. J Bacteriol 185:1027–1036
Déziel É, Paquette G, Villemur R, Lépine F, Bisaillon J-G (1996) Biosurfactant production by a soil Pseudomonas strain growing on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:1908–1912
Déziel E, Lépine F, Dennie D, Boismenu D, Mamer OA, Villemur R (1999) Liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry analysis of mixtures of rhamnolipids produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain 57RP grown on mannitol or naphthalene. Biochim Biophys Acta 1440:244–252
Déziel E, Lépine F, Milot S, Villemur R (2003) rhlA is required for the production of a novel biosurfactant promoting swarming motility in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: 3-(3-hydroxyalkanoyloxy)alkanoic acids (HAAs), the precursors of rhamnolipids. Microbiology 149:2005–2013
Déziel E et al (2004) Analysis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa 4-hydroxy-2-alkylquinolines (HAQs) reveals a role for 4-hydroxy-2-heptylquinoline in cell-to-cell communication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:1339–1344
Déziel E et al (2005) The contribution of MvfR to Pseudomonas aeruginosa pathogenesis and quorum sensing circuitry regulation: multiple quorum sensing-regulated genes are modulated without affecting lasRI, rhlRI or the production of N-acyl-L-homoserine lactones. Mol Microbiol 55:998–1014
Fujita K, Akino T, Yoshioka H (1988) Characteristics of the heat-stable extracellular hemolysin from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun 56:1385–1387
Fung DC, Somerville M, Richardson PS, Sheehan JK (1995) Mucus glycoconjugate complexes released from feline trachea by bacterial toxin. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 12:296–306
Guerra-Santos LH, Käppeli O, Fiechter A (1984) Pseudomonas aeruginosa biosurfactant production in continuous culture with glucose as carbon source. Appl Environ Microbiol 48:301–305
Guerra-Santos LH, Käppeli O, Fiechter A (1986) Dependence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa continuous culture biosurfactant production on nutritional and environmental factors. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 24:443–448
Gunther NW IV, Nunez A, Fett W, Solaiman DK (2005) Production of rhamnolipids by Pseudomonas chlororaphis, a nonpathogenic bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:2288–2293
Hastie AT, Hingley ST, Higgins ML, Kueppers F, Shryock T (1986) Rhamnolipid from Pseudomonas aeruginosa inactivates mammalian tracheal ciliary axonemes. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton 6:502–509
Häussler S, Nimtz M, Domke T, Wray V, Steinmetz I (1998) Purification and characterization of a cytotoxic exolipid of Burkholderia pseudomallei. Infect Immun 66:1588–1593
Häussler S, Rohde M, von Neuhoff N, Nimtz M, Steinmetz I (2003) Structural and functional cellular changes induced by Burkholderia pseudomallei rhamnolipid. Infect Immun 71:2970–2975
Hentzer M et al (2003) Attenuation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence by quorum sensing inhibitors. EMBO J 22:3803–3815
Hingley ST, Hastie A, Kueppers F, Higgins ML, Weinbaum G, Shryock T (1986) Effect of ciliostatic factors from Pseudomonas aeruginosa on rabbit respiratory cilia. Infect Immun 51:254–262
Itoh S, Suzuki T (1972) Effect of rhamnolipids on growth of Pseudomonas aeruginosa mutant deficient in n-paraffin-utilizing ability. Agric Biol Chem 36:2233–2235
Itoh S, Honda H, Tomita F, Suzuki T (1971) Rhamnolipids produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa grown on n-paraffin (mixture of C12, C13 and C14 fractions). J Antibiot 24:855–859
Jarvis FG, Johnson MJ (1949) A glycolipide produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Am Chem Soc 71:4124–4126
Jendrossek D, Schirmer A, Schlegel HG (1996) Biodegradation of polyhydroxyalkanoic acids. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 46:451–463
Johnson MK, Allen JH (1978) The role of hemolysin in corneal infections with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 17:480–483
Johnson MK, Boese-Marrazzo D (1980) Production and properties of heat-stable extracellular hemolysin from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun 29:1028–1033
Juhas M, Eberl L, Tummler B (2005) Quorum sensing: the power of cooperation in the world of Pseudomonas. Environ Microbiol 7:459–471
Kanthakumar K et al (1996) The effect of bacterial toxins on levels of intracellular adenosine nucleotides and human ciliary beat frequency. Pulm Pharmacol 9:223–230
Kim EJ, Sabra W, Zeng AP (2003) Iron deficiency leads to inhibition of oxygen transfer and enhanced formation of virulence factors in cultures of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Microbiology 149:2627–2634
Koch AK, Käppeli O, Fiechter A, Reiser J (1991) Hydrocarbon assimilation and biosurfactant production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa mutants. J Bacteriol 173:4212–4219
Köhler T, Curty LK, Barja F, Van Delden C, Pechère J-C (2000) Swarming of Pseudomonas aeruginosa is dependent on cell-to-cell signaling and requires flagella and pili. J Bacteriol 182:5990–5996
Kownatzki R, Tummler B, Doring G (1987) Rhamnolipid of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in sputum of cystic fibrosis patients. Lancet 1:1026–1027
Kurioka S, Liu PV (1967) Effect of the hemolysin of Pseudomonas aeruginosa on phosphatides and on phospholipase c activity. J Bacteriol 93:670–674
Lam JS (2004) Lipopolysaccharides of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. In: Ramos JL (ed) The pseudomonads. Biosynthesis of macromolecules and molecular metabolism. Kluwer/Plenum, New York, pp 3–52
Lang S, Wagner F (1993) Biological activities of biosurfactants. In: Kosaric N (ed) Biosurfactants: production, properties, applications. Dekker, New York, pp 251–268
Lang S, Wullbrandt D (1999) Rhamnose lipids—biosynthesis, microbial production and application potential. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 51:22–32
Latifi A, Foglino M, Tanaka K, Williams P, Lazdunski A (1996) A hierarchical quorum-sensing cascade in Pseudomonas aeruginosa links the transcriptional activators LasR and RhlR (VsmR) to expression of the stationary-phase sigma factor RpoS. Mol Microbiol 21:1137–1146
Lazdunski AM, Ventre I, Sturgis JN (2004) Regulatory circuits and communication in Gram-negative bacteria. Nat Rev Microbiol 2:581–592
Lépine F, Déziel E, Milot S, Villemur R (2002) Liquid chromatographic/mass spectrometric detection of the 3-(3-hydroxyalkanoyloxy)alkanoic acid precursors of rhamnolipids in Pseudomonas aeruginosa cultures. J Mass Spectrom 37:41–46
Lequette Y, Greenberg EP (2005) Timing and localization of rhamnolipid synthesis gene expression in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. J Bacteriol 187:37–44
Linhardt RJ, Bakhit R, Daniels L, Mayerl F (1989) Microbially produced rhamnolipid as a source of rhamnose. Biotechnol Bioeng 33:365–368
Lyczak JB, Cannon CL, Pier GB (2000) Establishment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection: lessons from a versatile opportunist. Microbes Infect 2:1051–1060
Madison LL, Huisman GW (1999) Metabolic engineering of poly(3-hydroxyalkanoates): from DNA to plastic. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 63:21–53
Maier RM, Soberón-Chávez G (2000) Pseudomonas aeruginosa rhamnolipids: biosynthesis and potential applications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 54:625–633
Manresa A et al (1991) Kinetic studies on surfactant production by Pseudomonas aeruginosa 44T1. J Ind Microbiol 8:133–136
McClure CD, Schiller NL (1992) Effects of Pseudomonas aeruginosa rhamnolipids on monocyte-derived macrophages. J Leukoc Biol 51:97–102
McClure CD, Schiller NL (1996) Inhibition of macrophage phagocytosis by Pseudomonas aeruginosa rhamnolipids in vitro and in vivo. Curr Microbiol 33:109–117
Medina G, Juarez K, Diaz R, Soberón-Chávez G (2003a) Transcriptional regulation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa rhlR, encoding a quorum-sensing regulatory protein. Microbiology 149:3073–3081
Medina G, Juarez K, Soberón-Chávez G (2003b) The Pseudomonas aeruginosa rhlAB operon is not expressed during the logarithmic phase of growth even in the presence of its activator RhlR and the autoinducer N-butyryl-homoserine lactone. J Bacteriol 185:377–380
Medina G, Juarez K, Valderrama B, Soberón-Chávez G (2003c) Mechanism of Pseudomonas aeruginosa RhlR transcriptional regulation of the rhlAB promoter. J Bacteriol 185:5976–5983
Mulligan CN, Gibbs BF (1989) Correlation of nitrogen metabolism with biosurfactant production by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl Environ Microbiol 55:3016–3019
Mulligan CN, Mahmourides G, Gibbs BF (1989) The influence of phosphate metabolism on biosurfactant production by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 12:199–210
Ochsner UA, Reiser J (1995) Autoinducer-mediated regulation of rhamnolipid biosurfactant synthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92:6424–6428
Ochsner UA, Fiechter A, Reiser J (1994) Isolation, characterization, and expression in Escherichia coli of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa rhlAB genes encoding a rhamnosyltransferase involved in rhamnolipid biosurfactant synthesis. J Biol Chem 269:19787–19795
Ochsner UA, Hembach T, Fiechter A (1995a) Production of rhamnolipid biosurfactants. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 53:89–118
Ochsner UA, Reiser J, Fiechter A, Witholt B (1995b) Production of Pseudomonas aeruginosa rhamnolipid biosurfactants in heterologous hosts. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:3503–3506
Olvera C, Goldberg JB, Sánchez R, Soberón-Chávez G (1999) The Pseudomonas aeruginosa algC gene product participates in rhamnolipid biosynthesis. FEMS Microbiol Lett 179:85–90
Pesci EC, Pearson JP, Seed PC, Iglewski BH (1997) Regulation of las and rhl quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 179:3127–3132
Pham TH, Webb JS, Rehm BH (2004) The role of polyhydroxyalkanoate biosynthesis by Pseudomonas aeruginosa in rhamnolipid and alginate production as well as stress tolerance and biofilm formation. Microbiology 150:3405–3413
Rahim R, Burrows LL, Monteiro MA, Perry MB, Lam JS (2000) Involvement of the rml locus in core oligosaccharide and O polysaccharide assembly in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbiology 146(Pt 11):2803–2814
Rahim R et al (2001) Cloning and functional characterization of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa rhlC gene that encodes rhamnosyltransferase 2, an enzyme responsible for di-rhamnolipid biosynthesis. Mol Microbiol 40:708–718
Read RC et al (1992) Effect of Pseudomonas aeruginosa rhamnolipids on mucociliary transport and ciliary beating. J Appl Physiol 72:2271–2277
Rehm BH, Mitsky TA, Steinbuchel A (2001) Role of fatty acid de novo biosynthesis in polyhydroxyalkanoic acid (PHA) and rhamnolipid synthesis by pseudomonads: establishment of the transacylase (PhaG)-mediated pathway for PHA biosynthesis in Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:3102–3109
Robert M et al (1989) Effect of the carbon source on biosurfactant production by Pseudomonas aeruginosa 44T1. Biotechnol Lett 11:871–874
Sabra W, Kim EJ, Zeng AP (2002) Physiological responses of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 to oxidative stress in controlled microaerobic and aerobic cultures. Microbiology 148:3195–3202
Schirmer A, Jendrossek D, Schlegel HG (1993) Degradation of poly(3-hydroxyoctanoic acid) [P(3HO)] by bacteria: purification and properties of a P(3HO) depolymerase from Pseudomonas fluorescens GK13. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:1220–1227
Schooling SR, Charaf UK, Allison DG, Gilbert P (2004) A role for rhamnolipid in biofilm dispersion. Biofilms 1:91–99
Schuster M, Lostroh CP, Ogi T, Greenberg EP (2003) Identification, timing, and signal specificity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum-controlled genes: a transcriptome analysis. J Bacteriol 185:2066–2079
Shryock TR, Silver SA, Banschbach MW, Kramer JC (1984) Effect of Pseudomonas aeruginosa rhamnolipid on human neutrophil migration. Curr Microbiol 10:323–328
Sierra G (1960) Hemolytic effect of a glycolipid produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 26:189–192
Sim L, Ward OP, Li Z-Y (1997) Production and characterization of a biosurfactant isolated from Pseudomonas aeruginosa UW-1. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 19:232–238
Smith RS, Iglewski B (2003) P. aeruginosa quorum-sensing systems and virulence. Curr Opin Microbiol 6:56–60
Soberón-Chávez G (2004) Biosynthesis of rhamnolipids. In: Ramos J-L (ed) Pseudomonas. Biosynthesis of macromolecules and molecular metabolism. Kluwer/Plenum, New York, pp 173–189
Soberón-Chávez G, Aguirre-Ramírez M, Ordóñez L (2005a) Is Pseudomonas aeruginosa only sensing quorum? Crit Rev Microbiol 131:171–182
Soberón-Chávez G, Aguirre-Ramirez M, Sanchez R (2005b) The Pseudomonas aeruginosa RhlA enzyme is involved in rhamnolipid and polyhydroxyalkanoate production. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol, in press, published on line in June 4th
Somerville M et al (1992) Release of mucus glycoconjugates by Pseudomonas aeruginosa rhamnolipid into feline trachea in vivo and human bronchus in vitro. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 6:116–122
Stanghellini ME, Miller RM (1997) Biosurfactants: their identity and potential efficacy in the biological control of zoosporic plant pathogens. Plant Dis 81:4–12
Syldatk C, Lang S, Matulovic U, Wagner F (1985a) Production of four interfacial active rhamnolipids from n-alkanes or glycerol by resting cells of Pseudomonas species DSM 2874. Z Naturforsch [C] 40:61–67
Syldatk C, Lang S, Wagner F, Wray V, Witte L (1985b) Chemical and physical characterization of four interfacial-active rhamnolipids from Pseudomonas spec. DSM 2874 grown on n-alkanes. Z Naturforsch [C] 40:51–60
Totten PA, Lara JC, Lory S (1990) The rpoN gene product of Pseudomonas aeruginosa is required for expression of diverse genes, including the flagellin gene. J Bacteriol 172:389–396
Tuleva BK, Ivanov GR, Christova NE (2002) Biosurfactant production by a new Pseudomonas putida strain. Z Naturforsch [C] 57:356–360
Van Delden C, Iglewski BH (1998) Cell-to-cell signaling and Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. Emerg Infect Dis 4:551–560
Venkata Ramana K, Karanth NG (1989) Factors affecting biosurfactant production using Pseudomonas aeruginosa CFTR-6 under submerged conditions. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 45:249–257
Wade DS, Calfee W, Rocha ER, Ling EA, Engstrom E, Coleman JP, Pesci EC (2005) J Bacteriol 187:4372–4380
Wagner VE, Bushnell D, Passador L, Brooks AI, Iglewski BH (2003) Microarray analysis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum-sensing regulons: effects of growth phase and environment. J Bacteriol 185:2080–2095
Wang X, Gong L, Liang S, Han X, Zhu C, Li Y (2005) Algicidal activity of rhamnolipid biosurfactants produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Harmful Algae 4:433–443
Whiteley M, Lee KM, Greenberg EP (1999) Identification of genes controlled by quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:13904–18909
Zhang Y, Miller RM (1994) Effect of a Pseudomonas rhamnolipid biosurfactant on cell hydrophobicity and biodegradation of octadecane. Appl Environ Microbiol 60:2101–2106
Zhang Y, Miller RM (1995) Effect of rhamnolipid (biosurfactant) structure on solubilization and biodegradation on n-alkanes. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:2247–2251
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soberón-Chávez, G., Lépine, F. & Déziel, E. Production of rhamnolipids by Pseudomonas aeruginosa . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 68, 718–725 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-005-0150-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-005-0150-3