Abstract
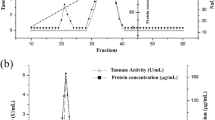
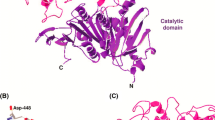
An extracellular tannase (tannin acyl hydrolase) was isolated from Paecilomyces variotii and purified from cell-free culture filtrate using ammonium sulfate precipitation followed by ion exchange and gel filtration chromatography. Fractional precipitation of the culture filtrate with ammonium sulfate yielded 78.7% with 13.6-folds purification, and diethylaminoethyl–cellulose column chromatography and gel filtration showed 19.4-folds and 30.5-folds purifications, respectively. Molecular mass of tannase was found 149.8 kDa through native polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) analysis. Sodium dodecyl sulphate–PAGE revealed that the purified tannase was a monomeric enzyme with a molecular mass of 45 kDa. Temperature of 30 to 50°C and pH of 5.0 to 7.0 were optimum for tannase activity and stability. Tannase immobilized on alginate beads could hydrolyze tannic acid even after extensive reuse and retained about 85% of the initial activity. Thin layer chromatography, high performance liquid chromatography, and 1H-nuclear magnetic resonance spectral analysis confirmed that gallic acid was formed as a byproduct during hydrolysis of tannic acid.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajay Kumar R, Gunasekaran P, Lakshmanan M (1999) Biodegradation of tannic acid by Citrobacter freundii isolated from a tannery effluent. J Basic Microbiol 39:161–169
Aoki K, Shinke R, Nishira H (1976) Purification and some properties of yeast tannase. Agric Biol Chem 40:79–85
Aoki K, Tanaka T, Shinke RL, Nishira H (1979) Detection of tannase in polyacrylamide gels. J Chromatogr 170:446–448
Ascencion RCM, Gustavo VG, Darvill A, Augur C (2003) A novel tannase from Aspergillus niger with β-glucosidase activity. Microbiology 149:2941–2946
Barthomeuf C, Regerat F, Pourrat H (1994) Production, purification and characterization of a tannase from A. niger LCF 8. J Ferment Bioeng 77:320–323
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Dhar SC, Bose SM (1964) Purification, crystallization and physio-chemical properties of tannase of Aspergillus niger. Leather Sci 11:27–38
Farias GM, Gorbea C, Elkins JR, Griffin GJ (1994) Purification, characterization and substrate relationships of the tannase from Chryphonectria parasitica. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 44:51–63
Hadi TA, Banerjee R, Bhattacharyya BC (1994) Optimisation of tannase biosynthesis by a newly isolated Rhizopus oryzae. Bioprocess Eng 11:239
Hatamoto O, Watarai T, Kikuchi M, Misusawa K, Sekine H (1996) Cloning and sequencing of the gene encoding tannase and structural study of the tannase subunit from Aspergillus oryzae. Gene 175:215–221
Kar B, Banerjee R (2000) Biosynthesis of tannin acyl hydrolase from tannin-rich forest residue under different fermentation conditions. J Ind Microbiol Biotech 25:29–38
Knezevic X, Bobic S, Milutinovic A, Obradovic B, Mojovic L, Bugarski B (2002) Alginate-immobilized lipase by electrostatic extrusion for the purpose of palm oil hydrolysis in lecithin/isooctane system. Process Biochem 38:313–318
Laemmli UK (1971) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–684
Lekha PK, Lonsane BK (1997) Production and application of tannin-acyl hydrolase—state of the art. Adv Appl Microbiol 44:215–260
Lewis JA, Starkey RL (1969) Decomposition of plant tannins by some soil microorganisms. Soil Sci 107:235–241
Mahendran B (2002) Investigations on the role of tannase and microbial consortium in tannery effluent treatment. Ph.D. thesis, University of Madras, Chennai, India
Misro SK, Kumar MR, Banerjee R, Bhattachrayya BC (1997) Production of gallic acid by immobilization of Rhizopus oryzae. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 16:257–260
Mondal KC, Pati BR (2000) Studies on the extracellular tannase from newly isolated Bacillus licheniformis KBR 6. J Basic Microbiol 40:223–232
Nelson KE, Pell AN, Schofiel P, Zinder S (1995) Isolation and characterization of an anaerobic ruminal bacterium capable of degrading hydrolyzable tannins. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:3293–3298
Rajkumar SG, Nandy SC (1983) Isolation, purification and some properties of Penicillium chrysogenum tannase. Appl Environ Microbiol 46:525–527
Reischwitz A, Reh DK, Buchholz K (1995) Unconventional immobilization of dextransucrase with alginate. Enzyme Microb Technol 17:457–461
Sharma S, Bhat TK, Dawra RK (2000) A spectrophotometric method for assay of tannase using rhodanine. Anal Biochem 279:85–89
Weetal HH (1985) Enzymatic gallic acid estrification. Biotechnol Bioeng 27:124–127
Yamada H, Adachi O, Watanabe M, Sato N (1968) Studies of fungal tannase. Part-I. Formation, purification and catalytic properties of tannase of Aspergillus flavus. Agric Biol Chem 32:1070–1078
Acknowledgements
The senior research fellowship from the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), New Delhi, India, to first author is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mahendran, B., Raman, N. & Kim, DJ. Purification and characterization of tannase from Paecilomyces variotii: hydrolysis of tannic acid using immobilized tannase. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 70, 444–450 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-005-0082-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-005-0082-y