Abstract
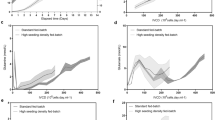
Stability and reproducibility of seeding cell performance in large-scale hybridoma cell culture has been reported by controlling only initial cell seeding density. The aim of the current study was to integrate multiple seeding cell control parameters to maintain stable and consistent cell physiological status for HAb18 cell expansion. Three parameters and their ranges were investigated, including initial cell seeding density in the range of 0.075–0.5×106 cells ml−1, “timepost” after cell passage between 8 and 36 h, and duration of subculture up to 6 months after cell revival. Cell performance was tested at the 1 L, 5 L, and 75 L scales. Desirable performance was found within the following parameter ranges: initial cell seeding density of 0.1–0.3×106 cells ml−1, “timepost” after cell passage between 14 and 22 h, and duration of subculture within 3 months of cell revival. Our results showed that cell growth rate and antibody productivity of three batches at 1 L, 5 L, and 75 L scale were found to be stably maintained within a range of 0.036–0.047 h−1 and 0.577–0.747 pg cell−1 h−1, with the positivity rate of antigen-binding activity within 97–99.75%, and the intensity of fluorescence around 200. This study may provide a simple but effective method to maintain seeding cell physiological status stable and consistent by combining seeding cell control parameters.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnes LM, Bentley CM, Dickson AJ (2003) Stability of protein production from recombinant mammalian cells. Biotechnol Bioeng 81:631–639
Briske-Anderson MJ, Finley JW, Newman SM (1997) The influence of culture time and passage number on the morphological and physiological development of Caco-2 cells. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 214:248–257
Bylund F, Castan A, Mikkola R, Veide A, Larsson G (2000) Influence of scale-up on the quality of recombinant human growth hormone. Biotechnol Bioeng 69:119–128
Harlow E, Lane D (1998) Antibodies: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Lab Press, Cold Spring Harbor Lab, NY
Hu WS, Patton R, Durand K (2003) Cell and tissue reactor engineering. http://HuGroup.cems.umn.edu
Jiang JL, Zhou Q, Yu MK, Ho LS, Chen ZN, Chan HC (2001) The involvement of HAb18G/CD147 in regulation of store-operated calcium entry and metastasis of human hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem 276:46870–46877
Jiang JL, Chan HC, Zhou Q, Yu MK, Yao XY, Lam SY, Zhu H, Ho LS, Leung KM, Chen ZN (2004) HAb18G/CD147-mediated calcium mobilization and hepatoma metastasis require both C-terminal and N-terminal domains. Cell Mol Life Sci 61:2083–2091
Leelavatcharamas V, Emery AN, Al-Rubeai M (1999) Use of cell cycle analysis to characterise growth and interferon-production in perfusion culture of CHO cells. Cytotechnology 30:59–69
Lloyd DR, Holmes P, Jackson LP, Emery AN, Al-Rubeai M (2000) Relationship between cell size, cell cycle and specific recombinant protein productivity. Cytotechnology 34:59–70
Moran EB, McGowan ST, McGuire JM, Frankland JE, Oyebade IA, Waller W, Archer LC, Morris LO, Pandya J, Nathan S, Smith L, Cadette ML, Michalowski JT (2000) A systematic approach to the validation of process parameters for monoclonal antibody production in fed-batch culture of a murine myeloma. Biotechnol Bioeng 69:242–255
Otto DD, Rudolf B (1999) Quality control and assurance from the development to the production of biopharmaceuticals. Trends Biotechnol 17:266–271
Park MT, Lee MS, Kim SH, Jo EC, Lee GM (2004) Influence of culture passages on growth kinetics and adenovirus vector production for gene therapy in monolayer and suspension cultures of HEK 293 cells. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 65:553–558
Roshni LD, Jeno MS, Murray MY (1999) Hybridoma growth and productivity: effects of conditioned medium and of inoculum size. Cytotechnology 29:1–10
Schenerman MA, Hope JN, Kletke C, Singh JK, Kimura R, Tsao EI, Folena-Wasserman G (1999) Comparability testing of a humanized monoclonal antibody (Synagis) to support cell line stability, process validation, and scale-up for manufacturing. Biologicals 27:203–215
Wang XH, Xu J, Zhang Y, Li L, Feng Q, Mi L, Chen ZN (2004) Inducible expression of Bcl-XL inhibits sodium butyrate induced apoptosis in hybridoma resulting in enhanced the antibody production. Cell Biol Int 28:185–191
Zhu H, Yang ST (2004) Long-term continuous production of monoclonal antibody by hybridoma cells immobilized in a fibrous-bed bioreactor. Cytotechnology 44:1–14
Acknowledgements
This research is supported by the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (no. 2002AA217011, no. 2002AA2Z3441). Special thanks go to Ms. Fan Peng for her careful reading and editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Mi, L., Qin, J. et al. Stability validation of seeding cell control parameters in large-scale hybridoma cell culture. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 70, 34–39 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-005-0047-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-005-0047-1