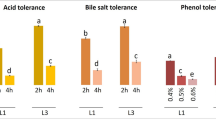
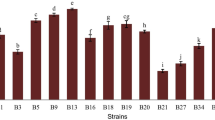
Abstract
Reutericyclin is an inhibitory compound produced by sourdough isolates of Lactobacillus reuteri that is structurally but not functionally related to naturally occurring tetramic acids. It is bacteriostatic or bactericidal to gram-positive bacteria based on its activity as a proton-ionophore, and a broad range of food-related spoilage organisms and pathogens is inhibited by reutericyclin. Gram-negative bacteria are resistant to reutericyclin because of the barrier properties of their outer membrane, and resistance of beer-spoiling lactobacilli towards hop bitter acids provides cross-protection to reutericyclin. Remarkably, reutericyclin-producing strains were shown to persist for a period of 10 years in an industrial sourdough fermentation, and reutericyclin was shown to be produced in concentrations active against competitors during growth of L. reuteri in sourdough. Based on the known properties of reutericyclin and L. reuteri, reutericyclin-producing strains may have applications in the biopreservation of foods. Furthermore, these strains were shown to colonize reconstituted lactobacilli-free mice at high levels. Therefore, they could serve as a suitable model system to evaluate a possible impact of antimicrobial compounds on the intestinal microflora of humans and animals.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alakomi HL, Skyttä E, Saarela M, Mattila-Sandholm T, Latva-Kala K, Helander K (2000) Lactic acid permeabilizes gram-negative bacteria by disrupting the outer membrane. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:2001–2005
Axelsson LT, Chung TC, Dobrogosz WJ, Lindgren SE (1989) Production of a broad spectrum antimicrobial substance by Lactobacillus reuteri. Microbial. Ecol. Health Disease 2:131–136
Bateup JM, McConnell MA, Jenkinson HF, Tannock GW (1995) Comparison of Lactobacillus strains with respect to bile salt hydrolase activity, colonization of the gastrointestinal tract, and growth rate of the murine host. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:1147–1149
Bennik MHJ, Verheul A, Abee T, Naaktgeboren-Stoffels G, Gorris LGM, Smid EJ (1997) Interactions of nisin and pediocin PA-1 with closely related lactic acid bacteria that manifest over 100-fold differences in bacteriocin sensitivity. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:3628–3639
De Vuyst L, Vandamme EJ (1994) Antimicrobial potential of lactic acid bacteria. In: de Vuyst L, Vandamme EJ (eds) Bacteriocins of lactic acid bacteria. Chapman and Hall, London, pp 91–142
Eijsink VGH, Axelsson L, Diep DB, Havarstein LS, Holo H, Nes IF (2002) Production of class II bacteriocins by lactic acid bacteria: an example of biological warfare and communication. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 81:639–654
Gänzle MG, Vogel RF (2002) Contribution of reutericyclin production to the stable persistence of Lactobacillus reuteri in an industrial sourdough fermentation. Int J Food Microbiol 80:31–45
Gänzle MG, Vogel RF (2003) Studies on the mode of action of reutericyclin. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:1305–1307
Gänzle MG, Hertel C, Hammes WP (1995) Antimicrobial activity in lactobacilli from sourdough. In: Scheffers WA, van Dijken JP (eds) Beijerinck Centennial. Microbiol physiology and gene regulation: Emerging principles and applications. Delft University Press, Delft, pp 380–381
Gänzle MG, Hertel C, Hammes WP (1999) Resistance of Escherichia coli and Salmonella against nisin and curvacin A. Int J Food Microbiol 48:37–50
Gänzle MG, Höltzel A, Walter J, Jung G, Hammes WP (2000) Characterization of reutericyclin produced by Lactobacillus reuteri LTH2584. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:4325–4333
Gänzle MG, Ulmer HM, Vogel RF (2001) High pressure inactivation of Lactobacillus plantarum in a model beer system. J Food Sci 66:1174–1181
Gänzle MG, Korakli M, Vogel RF (2002) Reutericyclin production during sourdough fermentation. In: 7th meeting on lactic acid bacteria, September 2002, Egmond aan Zee
Gao Y, van Belkum MJ, Stiles ME (1999) The outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria inhibits antibacterial activity of brochocin-C. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:4329–4333
Gitterman CO (1965) Antitumor, cytotoxic, and antibacterial activities of tenuazonic acid and congeneric tetramic acids. J Med Chem 8:483–486
Hayashi N, Ito M, Horiike S, Taguchi H (2001) Molecular cloning of a putative divalent-cation transporter gene as a new genetic marker for the identification of Lactobacillus brevis strains capable of growing in beer. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 55:596–603
Helander IM, Mattila-Sandholm T (2000) Permeability barrier of the Gram-negative bacterial outer membrane with special reference to nisin. Int J Food Microbiol 60:153–161
Heng NCK, Bateup JM, Loach DM, Wu X, Jenkinson HF, Morrison M, Tannock GW (1999) Influence of different functional elements of plasmid pGT232 on maintenance of recombinant plasmids in Lactobacillus reuteri populations in vitro and in vivo. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:5378–5385
Höltzel A, Ganzle MG, Nicholson GJ, Hammes WP, Jung G (2000) The first low molecular weight antibiotic from lactic acid bacteria: reutericyclin, a new tetramic acid. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 39:2766–2768
Hugas M (1998) Bacteriocinogenic lactic acid bacteria for the biopreservation of meat and meat products. Meat Sci. 49:S139-S150
Kabuki T, Saito T, Kawai Y, Uemura J, Itoh T (1997) Production, purification and characterization of reutericin 6, a bacteriocin with lytic activity produced by Lactobacillus reuteri LA6. Int J Food Microbiol 34:145–156
Kalchayanand N, Sikes A, Dunne CP, Ray B (1998) Factors influencing death and injury of foodborne pathogens by hydrostatic pressure-pasteurization. Food Microbiol 15:207–214
Katla T, Naterstad K, Vancanneyt M, Swings J, Axelsson L (2003) Differences in susceptibility of Listeria monocytogenes strains to sakacin P, sakacin A, pediocin PA-1, and nisin. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:4431–4437
Konings WN (2002) The cell membrane and the struggle for life of lactic acid bacteria. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 82:3–27
Lebrun MH, Nicolas L, Boutar M, Gaudemer F, Ranomenjanahary S, Gaudemer A (1988) Relationships between the structure and the phytotoxicity of the fungal toxin tenuazonic acid. Phytochemistry 27:77–84
Leroy F, de Vuyst L (2000) Sakacins. In: Naidu AS (ed) Natural food antimicrobial systems. CRC , Boca Raton, Florida, pp 589–610
Leser TD, Amenuvor JZ, Jensen TK, Lindecrona RH, Boye M, Moeller K (2002) Culture-independent analysis of gut bacteria: the pig gastrointestinal tract microbiota revisited. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:673–690
Lindgren SE, Dobrogosz WJ (1990) Antagonistic activities of lactic acid bacteria in food and feed fermentations. FEMS Microbiol Rev 7:149–163
Luthi-Peng Q, Dileme FB, Puhan Z (2002) Effect of glucose on glycerol bioconversion by Lactobacillus reuteri. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 59:289–296
Marfori EC, Bamba T, Kajiyama S, Fukusaki E, Kobayashi A (2002) Biosynthetic studies of the tetramic acid antibiotic trichosetin. Tetrahedron 58:6655–6658
Marquardt U, Schmid D, Jung G (2000) Racemic synthesis of the new antibiotic tetramic acid reutericyclin. Syn Lett 8:1131–1132
McAuliffe O, Ross RP, Hill C (2001) Lantibiotics: structure, biosynthesis, and mode of action. FEMS Microbiol Rev 25:285–308
Nikaido H (1994) Prevention of drug access to bacterial targets: permeability barriers and active efflux. Science 264:382–387
Nikaido H (1996) Molecular architecture and assembly of cell parts. Outer membrane. In: Neidhardt FC (ed) Escherichia coli and Salmonella. ASM Press, Washington DC, pp 29–47
Röcken W, Spicher G (1993) Fadenziehende Bakterien—Vorkommen, Bedeutung, Gegenmaßnahmen. Getreide Mehl Brot 47:30–35
Rodriguez E, Arques JL, Rodriguez R, Nunez M, Medina M (2003) Reuterin production by lactobacilli isolated from pig faeces and evaluation of probiotic traits. Lett Appl Microbiol 37:259–263
Rosenkvist H, Hansen A (1995) Contamination profiles and characterisation of Bacillus species in wheat bread and raw materials for bread production. Int J Food Microbiol 26:353–363
Rosenquist H, Hansen A (1998) The antimicrobial effect of organic acids, sour dough and nisin against Bacillus subtilis and B. licheniformis isolated from wheat bread. J Appl Microbiol 85:621–631
Ross RP, Morgan S, Hill C (2002) Preservation and fermentation: past, present and future. Int J Food Microbiol 79:3–16
Royles BJL (1995) Naturally occurring tetramic acids: structure, isolation, and synthesis. Chem Rev 95:1981–2001
Sakamoto K, Margolles A, van Veen HW, Konings WN (2001) Hop resistance in the beer spoilage bacterium Lactobacillus brevis is mediated by the ATP-binding cassette multidrug transporter HorA. J Bacteriol 183:5371–5375
Sakamoto K, van Veen HW, Saito H, Kobayashi H, Konings WN (2002) Membrane-bound ATPase contributes to hop resistance of Lactobacillus brevis. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:5374–5378
Sami M, Suzuki K, Sakamoto K, Kadokura H, Kitamoto K, Yoda K (1998) A plasmid pRH45 of Lactobacillus brevis confers hop resistance. J Gen Appl Microbiol 44:361–363
Simpson WJ (1993) Studies on the sensitivity of lactic acid bacteria to hop bitter acids. J Inst Brew 99:405–411
Schillinger U, Geisen R, Holzapfel WH (1996) Potential of antagonistic microorganisms and bacteriocins for the biological preservation of foods. Trends Food Sci Technol 7:158–164
Stickings CE, Townsend RJ (1961) Metabolites of Alternaria tenuis auct.: the biosynthesis of tenuazonic acid. Biochem J 78:412–418
Stiles ME (1996) Biopreservation by lactic acid bacteria. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 70:331–345
Suzuki K, Sami M, Kadokura H, Nakajima H, Kitamoto K (2002) Biochemical characterization of horA-independent hop resistance mechanisms in Lactobacillus brevis. Int J Food Microbiol 76:223–230
Tagg JR, Dajani AS, Wannamaker LW (1976) Bacteriocins of gram-positive bacteria. Bacteriol. Rev. 40:722–756
Talarico TL, Dobrogosz WJ (1989) Chemical characterization of an antimicrobial substance produced by Lactobacillus reuteri. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 33:674–679
Tannock GW, Chrichton C, Welling GW, Koopman JP, Midtvedt T (1988) Reconstitution of the gastrointestinal microflora of lactibacillus-free mice. Appl Environ Microbiol 54:2971–2975
Toba T, Samant SK, Yoshioka E, Ito T (1991) Reutericin 6, a new bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus reuteri LA6. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 13:281–286
Tungjaroenchai W, Drake MA, White CH (2001) Influence of adjunct cultures on ripening of reduced fat Edam cheeses. J Dairy Sci 84:2117–2124
Vaara M (1993) Antibiotic-supersusceptible mutants of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 47:2255–2260
Vogel RF, Ehrmann MA, Gänzle MG (2002) Development and potential of starter lactobacilli resulting from exploration of the sourdough ecosystem. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 81:631–638
Walter J, Hertel C, Tannock GW, Lis CM, Munro K, Hammes WP (2001) Detection of Lactobacillus, Pediococcus, Leuconostoc, and Weissella species in human feces by using group-specific PCR primers and denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:2578–2585
Walter J, Heng NCK, Hammes WP, Loach DM, Tannock GW, Hertel C (2003) Identification of Lactobacillus reuteri genes specifically induced in the mouse gastrointestinal tract. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:2044–2051
Weiß A, Molnar P, Wolf G, Hammes WP (2001) Maßnahmen zur Reduzierung des hygienischen Risikos bei Keimlingen. In: Symposium Schnellmethoden und Automatisierung in der Lebensmittelmikrobiologie, Lemgo, July 2001
Weiß A, Wolf G, Hammes WP (2002) Verbesserung der hygienischen Sicherheit von roh zu verzehrenden Keimlingen mit Hilfe von Schutzkulturen. In: 4. Fachsymposium der Fachgruppe Lebensmittelmikrobiologie, Karlsruhe March 2002
Acknowledgements
Clarissa Schwab is acknowledged for her careful revision of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gänzle, M.G. Reutericyclin: biological activity, mode of action, and potential applications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 64, 326–332 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-003-1536-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-003-1536-8