Abstract.
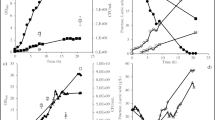
3-Hydroxypropionaldehyde (3-HPA) is considered as a potent antimicrobial substance. Exploration of its application as a food preservative or as a therapeutic auxiliary agent has been documented in the literature. In the present work, factors that may impact on 3-HPA accumulation by Lactobacillus reuteri and on the stability of 3-HPA were investigated. Three media – H2O, milk and MRS broth – were chosen as test systems. Data indicated that 3-HPA accumulation in resting cells of L. reuteri in a two-step fermentation is greatly affected by temperature, pH, cell age and biomass as well as components in the test system. Within 2 h of incubation, 170 mM 3-HPA could be produced with a cell dry weight of 30 g/l, representing 85% of the glycerol supplied (200 mM) in H2O. The presence of glycerol during cell growth increased the productivity of 3-HPA by resting cells. In general, 3-HPA is much more stable in H2O than in milk and MRS. Factors that enhanced accumulation of 3-HPA did not simply show the same positive impact on the stability of 3-HPA. Thus, for defined applications, factors affecting production and stability of 3-HPA should be evaluated separately.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lüthi-Peng, .Q., Schärer, .S. & Puhan, .Z. Production and stability of 3-hydroxypropionaldehyde in Lactobacillus reuteri . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 60, 73–80 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-002-1099-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-002-1099-0