Abstract.
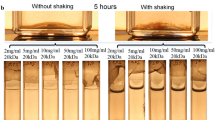
Significant decreases in the apparent viscosity of a bacterial biofilm suspension were measured following addition of sodium, potassium, magnesium, or calcium salts, whereas iron salts increased the viscosity. Electrostatic interactions contribute to biofilm cohesion and iron cations are potent crosslinkers of the biofilm matrix.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, X., Stewart, P.S. Role of electrostatic interactions in cohesion of bacterial biofilms. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 59, 718–720 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-002-1044-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-002-1044-2