Abstract
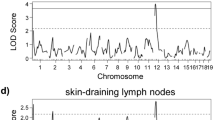
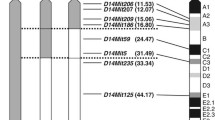
Type 1 diabetes is a multigenic autoimmune disease, the genetic basis for which is perhaps best characterized in the nonobese diabetic (NOD) mouse model. We previously located a NOD diabetes susceptibility locus, designated Idd11, on mouse Chromosome (Chr) 4 by analyzing diabetic backcross mice produced after crossing NOD/Lt with the nondiabetic resistant strain C57BL/6 (B6) strain. In order to confirm Idd11 and further refine its location, three NOD congenic mouse strains with different B6 derived intervals within Chr 4 were generated. Two of the congenic strains had a significant decrease in the cumulative incidence of diabetes compared with NOD/Lt control mice. The third NOD congenic strain, containing a B6 interval surrounding the Slc9a1 locus, was not protected against diabetes. These results define a new distal boundary for Idd11 and eliminate the Slc9a1 gene as a candidate. The Idd11 locus has now been definitively mapped to a 13cM interval on mouse Chr 4.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 15 May 1999 / Revised: 25 September 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brodnicki, T., McClive, P., Couper, S. et al. Localization of Idd11 using NOD congenic mouse strains: elimination of Slc9a1 as a candidate gene. Immunogenetics 51, 37–41 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002510050006
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002510050006