Abstract
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is one of the most prevalent autoimmune diseases, which involves the central nervous system. In this illness, Treg/Th17 cell imbalance causes the defect. Several studies revealed that T helper 17 (Th17) cells play a crucial role in pathogenesis, inflammation, and autoimmunity of several autoimmune diseases such as MS. In the present study, we assessed transcript levels of miR-27a and miR-214, in purified CD4+ T cells of MS patients, during relapsing and remitting phases in inducing differentiation of T naïve cells to Th17 cells. Forty RR-MS patient samples including those in relapsing (n = 20) and remitting (n = 20) phases were participated in this study. In addition, transcript levels of IL-17A, RORγt, IL-23R, Foxp3, and TGF-β in purified CD4+ T cells of patients in relapsing and remitting phases of RRMS patients were compared to healthy controls. Expression levels of miR-27a and miR-214 were measured by RT-qPCR and compared to healthy control group (n = 10). Data indicated upregulation of miR27a in relapsing phase of multiple sclerosis compared to remitting phase and healthy volunteers while miR-214 downregulated in relapsing phase of MS compared to remitting phase and healthy volunteers. In silico studies demonstrated pathways which miR-27a and miR-214 could effect on CD4+ T cell lineage fate including TGF-β and mTOR signaling, respectively. Our data suggest that miR-27a may probably inhibit negative regulators of Th17 cell differentiation, thus promoting its differentiation while miR-214 has an adverse effect.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartel DP (2009) MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 136(2):215–233. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.002
Bendszus M, Storch-Hagenlocher B (2013) Multiple sclerosis and other demyelinating diseases. inflammatory diseases of the brain. Springer, pp 3–18
Bettelli E, Carrier Y, Gao W, Korn T, Strom TB, Oukka M, Weiner HL, Kuchroo VK (2006) Reciprocal developmental pathways for the generation of pathogenic effector TH17 and regulatory T cells. Nature 441(7090):235–238. doi:10.1038/nature04753
Brucklacher-Waldert V, Stuerner K, Kolster M, Wolthausen J, Tolosa E (2009) Phenotypical and functional characterization of T helper 17 cells in multiple sclerosis. Brain 132(Pt 12):3329–3341. doi:10.1093/brain/awp289
Calabresi PA (2004) Diagnosis and management of multiple sclerosis. Am Fam Physician 70(10):1935–1944
Carthew RW, Sontheimer EJ (2009) Origins and mechanisms of miRNAs and siRNAs. Cell 136(4):642–655. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.035
Chen W, Jin W, Hardegen N, Lei KJ, Li L, Marinos N, McGrady G, Wahl SM (2003) Conversion of peripheral CD4+CD25− naive T cells to CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells by TGF-beta induction of transcription factor Foxp3. J Exp Med 198(12):1875–1886. doi:10.1084/jem.20030152
Chen L, Shen Z, Wang G, Fan P, Liu Y (2008) Dynamic frequency of CD4+ CD25+ Foxp3+ Treg cells in psoriasis vulgaris. J Dermatol Sci 51(3):200–203. doi:10.1016/j.jdermsci
Chhabra R, Dubey R, Saini N (2010) Cooperative and individualistic functions of the microRNAs in the miR-23a ∼ 27a ∼ 24-2 cluster and its implicationin human diseases. Mol Cancer 3(9):232. doi:10.1186/1476-4598-9-232
da Huang W, Sherman BT, Lempicki RA (2009) Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc 4(1):44–57. doi:10.1038/nprot.2008.211
Davidson TS, DiPaolo RJ, Andersson J, Shevach EM (2007) Cutting edge: IL-2 is essential for TGF-β-mediated induction of Foxp3+ T regulatory cells. J Immunol 178(7):4022–4026. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.178.7.4022
Delgoffe GM, Kole TP, Zheng Y, Zarek PE, Matthews KL, Xiao B, Worley PF, Kozma SC, Powell JD (2009) The mTOR kinase differentially regulates effector and regulatory T cell lineage commitment. Immunity 30(6):832–844. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2009.04.014
Dong C (2008) TH17 cells in development: an updated view of their molecular identity and genetic programming. Nat Rev Immunol 8(5):337–348. doi:10.1038/nri2295
Du C, Liu C, Kang J, Zhao G, Ye Z, Huang S, Li Z, Wu Z, Pei G (2009) MicroRNA miR-326 regulates TH-17 differentiation and is associated with the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis. Nat Immunol 10(12):1252–1259. doi:10.1038/ni.1798
Duerr RH, Taylor KD, Brant SR, Rioux JD, Silverberg MS, Daly MJ, Steinhart AH, Abraham C, Regueiro M, Griffiths A, Dassopoulos T, Bitton A, Yang H, Targan S, Datta LW, Kistner EO, Schumm LP, Lee AT, Gregersen PK, Barmada MM, Rotter JI, Nicolae DL, Cho JH (2006) A genome-wide association study identifies IL23R as an inflammatory bowel disease gene. Science 314(5804):1461–1463. doi:10.1126/science.1135245
Fernandez D, Perl A (2010) mTOR signaling: a central pathway to pathogenesis in systemic lupus erythematosus? Discov Med 9(46):173–178
Fernandez D, Bonilla E, Mirza N, Niland B, Perl A (2006) Rapamycin reduces disease activity and normalizes T cell activation induced calcium fluxing in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 54(9):2983–2988. doi:10.1002/art.22085
Fugger L, Friese MA, Bell JI (2009) From genes to function: the next challenge to understanding multiple sclerosis. Nat Rev Immunol 9(6):408–417. doi:10.1038/nri2554
Fujishima S, Watanabe H, Kawaguchi M, Suzuki T, Matsukura S, Homma T, Howell BG, Hizawa N, Mitsuya T, Huang SK, Iijima M (2010) Involvement of IL-17F via the induction of IL-6 in psoriasis. Arch Dermatol Res 302(7):499–505. doi:10.1007/s00403-010-1033-8
Guerau-de-Arellano M, Smith KM, Godlewski J, Liu Y, Winger R, Lawler SE, Whitacre CC, Racke MK, Lovett-Racke AE (2011) MicroRNA dysregulation in multiple sclerosis favours pro-inflammatory T-cell-mediated autoimmunity. Brain 134(Pt 12):3578–3589. doi:10.1093/brain/awr262
Harrington LE, Hatton RD, Mangan PR, Turner H, Murphy TL, Murphy KM, Weaver CT (2005) Interleukin 17-producing CD4+ effector T cells develop via a lineage distinct from the T helper type 1 and 2 lineages. Nat Immunol 6(11):1123–1132. doi:10.1038/ni1254
Honardoost MA, Kiani-Esfahani A, Ghaedi K, Etemadifar M, Salehi M (2014) miR-326 and miR-26a, two potential markers for diagnosis of relapse and remission phases in patient with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Gene 544(2):128–133. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2014.04.069
Ivanov II, McKenzie BS, Zhou L, Tadokoro CE, Lepelley A, Lafaille JJ, Cua DJ, Littman DR (2006) The orphan nuclear receptor RORgammat directs the differentiation program of proinflammatory IL-17 T helper cells. Cell 126(6):1121–1133. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.07.035
Jacobs JP, Wu HJ, Benoist C, Mathis (2009) D IL-17-producing T cells can augment autoantibody-induced arthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106(51):21789–21794. doi:10.1073/pnas.0912152106
Jadidi-Niaragh F, Mirshafiey A (2011) Th17 cell, the new player of neuroinflammatory process in multiple sclerosis. Scand J Immunol 74(1):1–13. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3083.2011.02536.x, Review
Junker A, Krumbholz M, Eisele S, Mohan H, Augstein F, Bittner R, Lassmann H, Wekerle H, Hohlfeld R, Meinl E (2009) MicroRNA profiling of multiple sclerosis lesions identifies modulators of the regulatory protein CD47. Brain 132(Pt 12):3342–3352. doi:10.1093/brain/awp300
Korn T, Oukka M, Kuchroo V, Bettelli E (2007) Th17 cells: effector T cells with inflammatory properties. Semin Immunol 19(6):362–371. doi:10.1016/j.smim.2007.10.007, Review
Korn T, Bettelli E, Oukka M, Kuchroo VK (2009) IL-17 and Th17 Cells. Annu Rev Immunol 27:485–517. doi:10.1146/annurev.immunol.021908.132710
Lassmann H, Brück W, Lucchinetti C (2001) Heterogeneity of multiple sclerosis pathogenesis: implications for diagnosis and therapy. Trends Mol Med 7(3):115–121. doi:10.1016/S1471-4914(00)01909-2
McFarland HF, Martin R (2007) Multiple sclerosis: a complicated picture of autoimmunity. Nat Immunol 8(9):913–919, Review
McGeachy MJ, Bak-Jensen KS, Chen Y, Tato CM, Blumenschein W, McClanahan T, Cua DJ (2007) TGF-beta and IL-6 drive the production of IL-17 and IL-10 by T cells and restrain TH-17 cell-mediated pathology. Nat Immunol 8(12):1390–1397. doi:10.1038/ni1539
McGeachy MJ, Chen Y, Tato CM, Laurence A, Joyce-Shaikh B, Blumenschein WM, McClanahan TK, O’Shea JJ, Cua DJ (2009) The interleukin 23 receptor is essential for the terminal differentiation of interleukin 17-producing effector T helper cells in vivo. Nat Immunol 10(3):314–324. doi:10.1038/ni.1698
Miyara M, Yoshioka Y, Kitoh A, Shima T, Wing K, Niwa A, Parizot C, Taflin C, Heike T, Valeyre D, Mathian A, Nakahata T, Yamaguchi T, Nomura T, Ono M, Amoura Z, Gorochov G, Sakaguchi S (2009) Functional delineation and differentiation dynamics of human CD4+ T cells expressing the FoxP3 transcription factor. Immunity 30(6):899–911. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2009.03.019
Muranski P, Restifo NP (2013) Essentials of Th17 cell commitment and plasticity. Blood 121(13):2402–2414. doi:10.1182/blood-2012-09-378653
Naghavian R, Ghaedi K, Kiani-Esfahani A, Ganjalikhani-Hakemi M, Etemadifar M, Nasr-Esfahani MH (2015) miR-141 and miR-200a, Revelation of new possible players in modulation of Th17/Treg differentiation and pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis. PLoS One 10(5), e0124555. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0124555
Oppmann B, Lesley R, Blom B, Timans JC, Xu Y, Hunte B, Vega F, Yu N, Wang J, Singh K, Zonin F, Vaisberg E, Churakova T, Liu M, Gorman D, Wagner J, Zurawski S, Liu Y, Abrams JS, Moore KW, Rennick D, de Waal-Malefyt R, Hannum C, Bazan JF, Kastelein RA (2000) Novel p19 protein engages IL-12p40 to form a cytokine, IL-23, with biological activities similar as well as distinct from IL-12. Immunity 13(5):715–725. doi:10.1016/S1074-7613(00)00070-4
Park H, Li Z, Yang XO, Chang SH, Nurieva R, Wang YH, Wang Y, Hood L, Zhu Z, Tian Q, Dong C (2005) A distinct lineage of CD4 T cells regulates tissue inflammation by producing interleukin 17. Nat Immunol 6(11):1133–1141. doi:10.1038/ni1254
Penna E, Orso F, Taverna D (2015) miR-214 as a key hub that controls cancer networks: small player, multiple functions. J Invest Dermatol 135(4):960–969. doi:10.1038/jid.2014.479
Pierrot-Deseilligny C, Souberbielle JC (2013) Contribution of vitamin D insufficiency to the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis. Ther Adv Neurol Disord 6(2):81–116. doi:10.1177/1756285612473513
Rogler CE, Levoci L, Ader T, Massimi A, Tchaikovskaya T, Norel R, Rogler LE (2009) MicroRNA-23b cluster microRNAs regulate transforming growth factorbeta/bone morphogenetic protein signaling and liver stem cell differentiation by targeting Smads. Hepatology 50(2):575–584. doi:10.1002/hep.22982
Samson M, Audia S, Janikashvili N, Ciudad M, Trad M, Fraszczak J, Ornetti P, Maillefert JF, Miossec P, Bonnotte B (2012) Inhibition of interleukin-6 function corrects Th17/Treg cell imbalance in patients with rheumatoid. Arthritis Rheum 64(8):2499–2503. doi:10.1002/art.34477
Shevach EM (2011) Biological functions of regulatory T cells. Adv Immunol 112:137–176. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-387827-4.00004-8, Review
Tritt M, Sgouroudis E, d’Hennezel E, Albanese A, Piccirillo CA (2008) Functional waning of naturally occurring CD4+ regulatory T-cells contributes to the onset of autoimmune diabetes. Diabetes 57(1):113–123. doi:10.2337/db06-1700
Tzartos JS, Friese MA, Craner MJ, Palace J, Newcombe J, Esiri MM, Fugger L (2008) Interleukin-17 production in central nervous system-infiltrating T cells and glial cells is associated with active disease in multiple sclerosis. Am J Pathol 172(1):146–155. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2008.070690
Veldhoen M, Hocking RJ, Atkins CJ, Locksley RM, Stockinger B (2006) TGFβ in the context of an inflammatory cytokine milieu supports de novo differentiation of IL-17-producing T cells. Immunity 24(2):179–189. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2006.01.001
Weichhart T, Säemann MD (2009) The multiple facets of mTOR in immunity. Trends Immunol 30(5):218–226. doi:10.1016/j.it.2009.02.002
Yang XO, Panopoulos AD, Nurieva R, Chang SH, Wang D, Watowich SS, Dong C (2007) STAT3 regulates cytokine-mediated generation of inflammatory helper T cells. J Biol Chem 282(13):9358–9363. doi:10.1074/jbc.C600321200
Yang L, Anderson DE, Baecher-Allan C, Hastings WD, Bettelli E, Oukka M, Kuchroo VK, Hafler DA (2008) IL-21 and TGF-beta are required for differentiation of human T (H)17 cells. Nature 454(7202):350–352. doi:10.1038/nature07021
Yang J, Chu Y, Yang X, Gao D, Zhu L, Yang X, Wan L, Li M (2009) Th17 and natural Treg cell population dynamics in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 60:1472–1483. doi:10.1002/art.24499
Zhang F, Meng G, Strober W (2008) Interactions among the transcription factors Runx1, RORgammat and Foxp3 regulate the differentiation of interleukin 17-producing T cells. Nat Immunol 9(11):1297–1306. doi:10.1038/ni.1663
Zheng SG, Wang J, Wang P, Gray JD, Horwitz DA (2007) IL-2 is essential for TGF-beta to convert naive CD4+CD25− cells to CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells and for expansion of these cells. J Immunol 178(4):2018–2027. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.178.4.2018
Zhou L, Lopes JE, Chong MM, Ivanov II, Min R, Victora GD, Shen Y, Du J, Rubtsov YP, Rudensky AY, Ziegler SF, Littman DR (2008) TGF-beta-induced Foxp3 inhibits TH17 cell differentiation by antagonizing RORgammat function. Nature 453(7192):236–240. doi:10.1038/nature06878
Zhu J, Paul WE (2008) CD4 T cells: fates, functions, and faults. Blood 112(5):1557–1569. doi:10.1182/blood-2008-05-078154
Acknowledgments
We thank the blood donors, Al-Zahra Hospital staffs, and our colleagues especially the MS research team in Royan Institute for their helpful participation and comments. All authors support submission to this journal.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Fig. S1
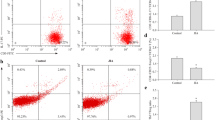
Real-time PCR profiles and gel electrophoresis patterns. a. b. c Real-time PCR profiles for miR-27a, miR-214, and RNU48. d Real-time PCR products for miR-27a, miR-214, and RNU48 were run on 12 % polyacrylamide gel to evaluate the specificity of primers used (M 50 bp) (GIF 60 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmadian-Elmi, M., Bidmeshki Pour, A., Naghavian, R. et al. miR-27a and miR-214 exert opposite regulatory roles in Th17 differentiation via mediating different signaling pathways in peripheral blood CD4+ T lymphocytes of patients with relapsing–remitting multiple sclerosis. Immunogenetics 68, 43–54 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-015-0881-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-015-0881-y