Abstract
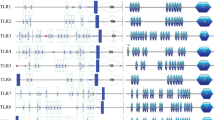
Phylogenetic analyses supported the hypothesis that the vertebrate toll-like receptors (TLRs) include two very ancient groups that arose by gene duplication prior to the divergence of protostomes and deuterostomes: (1) the TLR1 family (including mammalian TLR1, TLR2, TLR6, and TLR10); and (2) a clade including the remainder of mammalian TLRs. Correlating data on ligand type, subcellular localization, and gene expression in leukocytes and other tissues with the phylogeny provided evidence that certain major functional specializations within the TLRs occurred after ancient gene duplication events and that these traits have been retained through further events of gene duplication. For example, the recognition of bacterial lipoproteins appears to have arisen in the ancestor of the TLR1 family and continues to characterize members of that family whose ligands are known. Likewise, expression on the endosomal membrane and the recognition of nucleic acids appears to have been arisen in the ancestor of the TLR7 family and some related TLRs. On the other hand, gene expression patterns across tissues appear to have been much more volatile over the evolution of the vertebrate TLRs, since genes may show expression profiles similar to those of distantly related genes but dissimilar to those of closely related genes. Thus, the vertebrate TLRs provide an example of a multi-gene family in which gene duplication has been followed by extensive changes in certain aspects of gene function, while others have been conserved throughout vertebrate history.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aderem A, Ulevitch RJ (2000) Toll-like receptors in the induction of the innate immune response. Nature 406:782–787
Albiger B, Dahlberg S, Henriques-Normark B, Normark S (2007) Role of the innate immune system in host defence against bacterial infections: focus on the Toll-like receptors. J Int Med 261:511–528
Bell MP, Svingen PA, Rahman MK, Xiong Y, Faubion WA Jr (2007) FOXP3 regulates TLR10 expression in human T regulatory cells. J Immunol 179:1893–1900
Beutler B, Rehli M (2002) Evolution of the TIR, tolls, and TLRs: functional inferences from computational biology. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 270:1–21
Carpenter S, O’Neill LA (2007) How important are Toll-like receptors for antimicrobial responses. Cell Microbiol 9:1891–1901
Dopazo J (1994) Estimating errors and confidence intervals for branch lengths in phylogenetic trees by a bootstrap approach. J Mol Evol 38:300–304
Dunne A, O’Neill LA (2005) Adaptor usage and toll-like receptor signaling specificity. FEBS Lett 579:3330–3335
Friedman R, Hughes AL (2002) Molecular evolution of the NFkB signaling system. Immunogenetics 53:964–974
Hasan U, Chaffois C, Gaillard C, Saulnier V, Merck E, Tancredi S, Guiet C, Brière F, Vlach J, Lebecqu S, Trinchieri G, Bates EEM (2005) Human TLR10 is a functional receptor, expressed by B cells and plasmacytoid dendritic cells, which activates gene transcription through MyD88. J Immunol 174:2942–2950
Huelsenbeck JP, Ronquist F (2001) MRBAYES: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics 17:754–755
Hughes AL (1994) The evolution of functionally novel proteins after gene duplication. Proc R Soc Lond B 256:119–124
Hughes AL (1999) Adaptive evolution of genes and genomes. New York, Oxford University Press
Hughes AL (2005) Gene duplication and the origin of novel proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:8791–8792
Ishii KJ, Coban C, Akira S (2005) Manifold mechanisms of toll-like receptor-ligand recognition. J Clin Immunol 25:511–521
Ishii A, Matsuo A, Sawa H, Tsujita T, Shida K, Matsumoto M, Seya T (2007) Lamprey TLRs with properties distinct from those of the variable lymphocyte receptors. J Immunol 178:397–406
Jeffrey KL, Brummer T, Rolph MS, Liu SM, Callejas NA, Grumont RJ, Gillieron C, Mackay F, Grey S, Camps M, Rommel C, Gerondakis SD, Mackay CR (2006) Positive regulation of immune cell function and inflammatory responses by phosphate PAC-1. Nature Immunol 7:274–283
Jones DT, Taylor WR, Thornton JM (1992) The rapid generation of mutation data matrices from protein sequences. Comput Appl Biosci 8:275–282
Kagan JC, Medzhitov R (2006) Phosphoinositide-mediated adaptor recruitment controls toll-like receptor signaling. Cell 125:943–955
Krishnan J, Selvarajoo K, Tsuchiya M, Lee G, Choi S (2007) Toll-like receptor signal transduction. Exp Mol Med 39:421–438
Kruithof EK, Satta N, Liu JW, Dunoyer-Geindre S, Fish RJ (2007) Gene conversion limits the divergence of mammalian TLR1 and TLR6. BMC Evol Biol 7:148
Lynch M (2007) The origins of genome architecture. Sinauer, Sunderland, MA
Matsushima N, Tanaka T, Enkhbayar P, Mikami T, Taga M, Yamade K, Kuroki Y (2007) Comparative sequence analysis of leucine-rich repeats (LRRs) within vertebrate toll-like receptors. BMC Genomics 8:14
Nei M (1969) Gene duplication and nucleotide substitution in evolution. Nature 221:40–42
Nei M, Gojobori T (1986) Simple methods for estimating the numbers of synonymous and nonsynonymous nucleotide substitutions. Mol Biol Evol 3:418–426
Nishimura M, Naito S (2005) Tissue-specific mRNA expression profiles of human toll-like receptors and related genes. Biol Pharm Bull 28:886–892
Ohno S (1970) Evolution by gene duplication. Springer, Berlin
Opsal MA, Våge DI, Hayes B, Berget I, Lien S (2006) Genomic organization and transcript profiling of the bovine toll-like receptor gene cluster TLR6-TLR1-TLR10. Gene 384:45–50
Piatigorsky J (2007) Gene sharing an evolution: the diversity of protein functions. Harvard University Press, Cambridge, MA
Pichlmair A, Reis e Sousa C (2007) Innate recognition of viruses. Immunity 27:370–383
Roach JC, Glusman G, Rowen L, Kaur A, Purcell MK, Smith KD, Hood LE, Adaerem A (2005) The evolution of vertebrate Toll-like receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:9577–9582
Rodriguez F, Oliver JF, Marí A, Medina JR (1990) The general stochastic model of nucleotide substitution. J Theor Biol 142:485–501
Rzhetsky A, Nei M (1992) A simple method for estimating and testing minimum-evolution trees. J Mol Evol 35:367–375
Sanghavi SK, Shankarappa R, Reinhart TA (2004) Genetic analysis of Toll/interleukin-1 receptor (TIR) domain sequences from rhesus macaque Toll-like receptors (TLRs) 1–10 reveals high homology to human TLR/TIR sequences. Immunogenetics 56:667–674
Schmidt HA, Strimmer K, Vingron M, von Haeseler A (2002) TREE-PUZZLE: maximum likelihood phylogenetic analysis using quartets and parallel computing. Bioinformatics 18:502–504
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Tanji T, Ip YT (2005) Regulators of the toll and imd pathways in the Drosophila innate immune response. Trends Immunol 26:193–198
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Diggins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Watters TM, Kenny EF, O’Neill LAJ (2007) Structure, function and regulation of the Toll/IL-1 receptor adaptor proteins. Immunol Cell Biol 85:411–419
Wheeler DL, Barrett T, Benson DA, Bryant SH, Canese K, Chetvernin V, Church DM, DiCuccio M, Edgar R, Federhen S, Geer LY, Helmberg W, Kapustin Y, Kenton DL, Khovayko O, Lipman DJ, Madden TL, Maglott DR, Ostell J, Pruitt KD, Schuler GD, Schrimi LM, Sequeira E, Sherry ST, Sirotkin K, Souvorov A, Starchenko G, Suzek TO, Tatusov R, Tatusova TA, Wagner L, Yaschenko E (2006) Database resources of the national center for biotechnology information. Nucleic Acids Res 34:D173–D180
Wiens M, Korzhev M, Perović-Ottstadt S, Lthringer B, Brandt D, Klein S, Műller WE (2007) Toll-like receptors are part of the innate immune defense system of sponges (Desmospongiae: Porifera). Mol Biol Evol 24:792–804
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by grant GM43940 from the National Institutes of Health to A.L.H. and by the Research Council of Kent State University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hughes, A.L., Piontkivska, H. Functional diversification of the toll-like receptor gene family. Immunogenetics 60, 249–256 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-008-0283-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-008-0283-5