Abstract
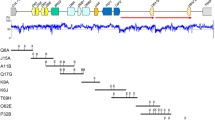
The Major Histocompatibility Complex (Mhc) genomic region of many vertebrates is known to contain at least one highly polymorphic class II gene that is homologous in sequence to one or other of the human Mhc DRB1 class II genes. The diversity of the avian Mhc class II gene sequences have been extensively studied in chickens, quails, and some songbirds, but have been largely ignored in the oceanic birds, including the flightless penguins. We have previously reported that several penguin species have a high degree of polymorphism on exon 2 of the Mhc class II DRB1-like gene. In this study, we present for the first time the complete nucleotide sequences of exon 2, intron 2, and exon 3 of the DRB1-like gene of 20 Humboldt penguins, a species that is presently vulnerable to the dangers of extinction. The Humboldt DRB1-like nucleotide and amino acid sequences reveal at least eight unique alleles. Phylogenetic analysis of all the available avian DRB-like sequences showed that, of five penguin species and nine other bird species, the sequences of the Humboldt penguins grouped most closely to the Little penguin and the mallard, respectively. The present analysis confirms that the sequence variations of the Mhc class II gene, DRB1, are useful for discriminating among individuals within the same penguin population as well those within different penguin population groups and species.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Davis LS, Darby JT (eds) (1990) Penguin biology. Academic, San Diego
del Hoyo J, Elliott A, Sargatal J (eds) (1992) Handbook of the birds of the world, vol 1, ostrich to ducks. Lynx Edicions, Barcelona
Edwards SV, Gasper J, March M (1998) Genomics and polymorphism of Agph-DAB1, an Mhc class II B gene in red-winged blackbirds (Agelaius phoeniceus). Mol Biol Evol 15:236–250
Gasper JS, Shiina T, Inoko H, Edwards SV (2001) Songbird genomics: analysis of 45 kb upstream of a polymorphic Mhc class II gene in red-winged blackbirds (Agelaius phoeniceus). Genomics 75:26–34
Hess CM, Gasper J, Hoekstra HE (2000) Mhc class II pseudogene and genomic signature of a 32-kb cosmid in the house finch (Carpodacus mexicanus). Genome Res 10:613–623
Ho CY, Prager EM, Wilson AC, Osuga DT, Feeney RE (1976) Penguin evolution: protein comparisons demonstrate phylogenetic relationship to flying aquatic birds. J Mol Evol 27:271–282
Inoko H, Ando A, Ito M, Tsuji K (1986) Southern hybridization analysis of DNA polymorphism in the HLA-D region. Hum Immunol 16:304–313
Jouventin P (ed) (1982) Visual and vocal signals in penguins, their evolution and adaptive characters. Parey, Berlin
Kaufman, J, Milne S, Gobel TW, Walker BA, Jacob JP, Auffray C, Zoorob R, Beck S (1999). The chicken B locus is a minimal essential major histocompatibility complex. Nature 401:923–925
Kulski JK, Shiina T, Anzai T, Kohara S, Inoko H (2002) Comparative genomic analysis of the Mhc: the evolution of class I duplication blocks, diversity and complexity from shark to man. Immunol Rev 190:95–122
Lambert DM, Ritchie PA, Millar CD, Holland B, Drummond AJ, Baroni C (2002) Rates of evolution in ancient DNA from Adelie penguins. Science 295:2273–2279
Marsh SG (2003) Nomenclature for factors of the HLA system 2002. Tissue Antigens 60:407–464
Marsh SGE, Parham P, Barber LD (2000) The HLA factsbook. Academic, San Diego
Pharr GT, Dodgson JB, Hunt HD, Bacon LD (1998) Class II Mhc cDNA in 15I5 B-congenic chickens. Immunogenetics 47:350–354
Reilly P (1994) Penguins of the world. Oxford University Press, UK
Ritchie PA, Lambert DM (2000) A repeat complex in the mitochondrial control region of Adelie penguins from Antarctica. Genome 43:613–618
Sato A, Figueroa F, Mayer WE, Grant PR, Grant BR, Klein J (2000) Mhc class II genes of Darwin’s finches: divergence by point mutations and reciprocal recombination. In: Kasahara M (ed) Major histocompatibility complex. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 518–541
Shiina T, Shimizu C, Oka A, Teraoka Y, Imanishi T, Gojobori T, Hanzawa K, Watanabe S, Inoko H (1999) Gene organization of the quail major histocompatibility complex (MhcCoja) class I gene region. Immunogenetics 49:384–394
Shiina T, Inoko T, Kulski JK (2004a). An update of the HLA genomic region, locus information and disease associations. Tissue Antigens (in press)
Shiina T, Shimizu S, Hosomichi K, Kohara S, Watanabe S, Hanzawa K, Beck S, Kulski JK, Inoko H (2004b). Comparative genomic analysis of two avian (quail and chicken) Mhc regions. J Immunol 172:6751–6763
Simpson GG (1976) Penguins: past and present, here and there. Yale University Press, New Haven
Sparks J, Soper T (1987) Penguins. Facts on File, New York
The MHC Sequencing Consortium (1999) Complete sequence and gene map of a human major histocompatibility complex. Nature 401:921–923
Tsuda TT, Tsuda M, Naruse T, Kawata H, Ando A, Shiina T, Fukuda M, Kurita M, LeMaho I, Kulski JK, Inoko H (2001) Phylogenetic analysis of penguin (Spheniscidae) species based on sequence variation in Mhc class II gene. Immunogenetics 53:712–716
Van Tuinen M, Butvill DB, Kirsch JA, Hedges SB (2001) Convergence and divergence in the evolution of aquatic birds. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 268:1345–1350
Vincek V, Klein D, Graser RT, Figueroa F, O’hUigin C, Klein J (1995) Molecular cloning of major histocompatibility complex class II B gene cDNA from the Bengalese finch Lonchura striata. Immunogenetics 42:262–267
Westerdahl H, Wittzell H, Schantz T (2000) Mhc diversity in two passerine birds: no evidence for a minimal essential Mhc. Immunogenetics 52:92–100
Wittzel H, Bernot A, Auffray KC, Zoorob R (1999) Concerted evolution of two Mhc class II B loci in pheasants and domestic chickens. Mol Biol Evol 16:479–490
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to JAZGA Penguin TAG (Japan Association of Zoological Gardens and Aquariums, Penguin Taxon Advisory Group), Tokyo Sea Life Park, Ueno Zoological Gardens, Port of Nagoya Public Aquarium, Kamogawa Sea World, Shima Marineland, Teradomari Aquarium, and Dr. Yasuhiko Naitou (National Institute for Polar Research) for providing with precious penguin samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The nucleotide sequence and amino acid sequence data reported in this paper have been submitted to the DDBJ database and have been assigned the accession numbers AB088371–AB088374, AB089199, AB154393–AB154399, and AB162144.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kikkawa, E.F., Tsuda, T.T., Naruse, T.K. et al. Analysis of the sequence variations in the Mhc DRB1-like gene of the endangered Humboldt penguin (Spheniscus humboldti). Immunogenetics 57, 99–107 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-005-0774-6
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-005-0774-6