Abstract
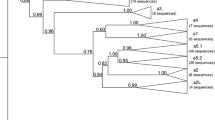
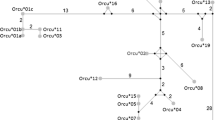
In domestic rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus), three serological types have been distinguished at the variable domain of the antibody H chain, the so-called V H a allotypes a1, a2, and a3. They correspond to highly divergent allelic lineages of the V H 1 gene, which is the gene rabbit utilizes in more than 80% of VDJ rearrangements. The sharing of serological V H a markers between rabbit and snowshoe hare (Lepus americanus) has suggested that the large genetic distances between rabbit V H 1 alleles (9–14% nucleotide differences) can be explained by unusually long lineage persistence times (transspecies polymorphism). Because this interpretation of the serological data is uncertain, we have determined the nucleotide sequences of V H genes expressed in specimens of Lepus species. Two sequence groups were distinguished, one of which occurred only in hare specimen displaying serological motifs of the rabbit V H a-a2 allotype. Sequences of this group are part of a monophyletic cluster containing the V H 1 sequences of the rabbit a2 allotype. The fact that this “transspecies a2 cluster” did not include genes of other rabbit V H a allotypes (a1, a3, and a4) is incompatible with the existence of a common V H a ancestor gene within the species, and suggests that the divergence of the V H a lineages preceded the Lepus vs Oryctolagus split. The sequence data are furthermore compatible with the hypothesis that the V H a polymorphism can be two times older than the divergence time between the Lepus and Oryctolagus lineages, which was estimated at 16–24 million years.




Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Callou C (1995) Modifications de l'aire de répartition du Lapin (Oryctolagus cuniculus) en France et en Espagne, du Pléistocène à l'époque actuelle. État de la question. Anthropozoologica 21:95–114
Cazenave PA, Bennamar A, Sogn JA, Kindt TJ (1987) Immunoglobulin genes in the feral rabbit. In: Dubiski S (ed) The rabbit in contemporary immunological research. Longman, New York, pp 148–160
Cooper MD, Perey DY, Gabrielsen AE, Sutherland DE, McKneally MF, Good RA (1968) Production of an antibody deficiency syndrome in rabbits by neonatal removal of organized intestinal lymphoid tissues. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol 33:65–88
Dray SG, Young O, Nisonoff A (1963) Distribution of allotypic specificities among rabbit immunoglobulin γ-globulin molecules genetically defined at two loci. Nature 199:52
Esteves PJ, Lanning D, Zhai SK, Ferrand N, Knight KL, van der Loo W (2004) Allelic variation at the VHa locus in natural populations of rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus, L.). J Immunol 172:1044–1053
Fan WM, Kasahara M, Gutknecht J, Klein D, Mayer WE, Jonker M, Klein J (1989) Shared class II MHC polymorphisms between humans and chimpanzees. Hum Immunol 26:107–121
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791
Friedman ML, Tunyaplin C, Zhai SK, Knight KL (1994) Neonatal V H , D, and JH gene usage in rabbit B lineage cells. J Immunol 152:632–641
Glazko GV, Nei M (2003) Estimation of divergence times for major lineages of primate species. Mol Biol Evol 20:424–434
Halanych KM, Robinson TJ (1999) Multiple substitutions affect the phylogenetic utility of cytochrome b and 12S rDNA data: examining a rapid radiation in leporid (Lagomorpha) evolution. J Mol Evol 48:369–379
Herd ZL, Edmonds JW (1977) Population genetics of Aa and Ab immunoglobulin allotypes in wild rabbits of south-eastern Australia. I. Allotype frequencies. J Immunogenet 4:315–323
Horng WJ, Papagiannes E, Dray S, Rodkey LS (1980) Expression of cross-reacting determinants of the immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region a3 allotype in Oryctolagus and Lepus. Mol Immunol 17:111–117
Kabat EA, Wu TT, Perry HM, Gottsman KS, Foeller C (1991) Sequences of proteins of immunologic interest, 5th edn. US Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD
Kim BS, Dray S (1973) Expression of the a, x, and y variable region genes of heavy chains among IgG, IgM, and IgA molecules of normal and a locus allotype-suppressed rabbits. J Immunol 111:750–760
Klein J, Satta Y, Takahata N, O'hUigin C (1993) Trans-specific Mhc polymorphism and the origin of species in primates. J Med Primatol 22:57–64
Knight KL, Becker RS (1990) Molecular basis of the allelic inheritance of rabbit immunoglobulin V H allotypes: implications for the generation of antibody diversity. Cell 60:963–970
Krug MS, Berger SL (1987) First strand cDNA synthesis primed with oligo (dT). Methods Enzymol 152:316
Kumar S, Tamura K, Nei M (2004) MEGA3: integrated software for molecular evolutionary genetics analysis and sequence alignment. Brief Bioinform 5:150–163
Lanning D, Sethupathi P, Rhee KJ, Zhai SK, Knight KL (2000a) Intestinal microflora and diversification of the rabbit antibody repertoire. J Immunol 165:2012–2019
Lanning D, Zhu X, Zhai SK, Knight KL (2000b) Development of the antibody repertoire in rabbit: gut-associated lymphoid tissue, microbes, and selection. Immunol Rev 175:214–228
Lawlor DA, Ward FE, Ennis PD, Jackson AP, Parham P (1988) HLA-A and B polymorphisms predate the divergence of humans and chimpanzees. Nature 335:268–271
Lefranc MP, Giudicelli V, Kaas Q, Duprat E, Jabado-Michaloud J, Scaviner D, Ginestoux C, Clement O, Chaume D, Lefranc G (2005) IMGT, the international ImMunoGeneTics information system. Nucleic Acids Res 33(Database Issue):D593–D597
Lopez-Martinez N (1989) Revision sistematica y biostratigrafica de los lagomorphos (Mammalia) del Terciario y Cuaternario de España. Memorias del Museo Paleontologico de la Universidad de Zaragoza, n°3. Diputacion General de Aragon
Mage RG, Bernstein KE, McCartney-Francis N, Alexander CB, Young-Cooper GO, Padlan EA, Cohen GH (1984) The structural and genetic basis for expression of normal and latent V H a allotypes of the rabbit. Mol Immunol 21:1067–1081
Mayer WE, O'hUigin C, Zaleska-Rutczynska Z, Klein J (1992) Trans-species origin of Mhc-DRB polymorphism in the chimpanzee. Immunogenetics 37:12–23
Nei M, Kumar S (2000) Molecular evolution and phylogenetics. Oxford University Press, New York
Nei M, Gu X, Sitnikova T (1997) Evolution by the birth-and-death process in multigene families of the vertebrate immune system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94:7799–7806
Ota T, Nei M (1994) Divergent evolution and evolution by the birth-and-death process in the immunoglobulin V H gene family. Mol Biol Evol 11:469–482
Oudin J (1960) Allotype of rabbit serum proteins. I. Immunochemical analysis leading to the individualization of seven main allotypes. J Exp Med 112:107–124
Ros F, Puels J, Reichenberger N, van Schoten W, Buelow R, Platzer J (2004) Sequence analysis of 0.5 Mb of the rabbit germline immunoglobulin heavy chain locus. Gene 330:49–59
Roux KH (1981) A fourth heavy chain variable region subgroup, w, with 2 variants defined by an induced auto-antiserum in the rabbit. J Immunol 127:626–632
Rzhetsky A, Nei M (1992) Statistical properties of the ordinary least-squares, generalized least-squares, and minimum-evolution methods of phylogenetic inference. J Mol Evol 35:367–675
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Sehgal D, Obiakor H, Mage RG (2002) Distinct clonal Ig diversification patterns in young appendix compared to antigen-specific splenic clones. J Immunol 168:5424–5433
Short JA, Sethupathi P, Zhai SK, Knight KL (1991) VDJ genes in VHa2 allotype-suppressed rabbits. Limited germline VH gene usage and accumulation of somatic mutations in D regions. J Immunol 147:4014–4018
Sitnikova T (1996) Bootstrap method of interior-branch test for phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 13:605–611
Sitnikova T, Su C (1998) Coevolution of immunoglobulin heavy- and light-chain variable-region gene families. Mol Biol Evol 15:617–625
Su C, Nei M (1999) Fifty-million-year-old polymorphism at an immunoglobulin variable region gene locus in the rabbit evolutionary lineage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:9710–9715
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
van der Loo W (1987) Studies on the adaptive significance of the immunoglobulin alleles (ig allotypes) in wild rabbit. In: Dubiski S (ed) The rabbit in contemporary immunological research. Longman, New York, pp 164–190
van der Loo W (1993) Variance analysis of immunoglobulin alleles in natural populations of rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus): the extensive interallelic divergence at the b locus could be the outcome of overdominance-type selection. Genetics 135:171–187
van der Loo W, De Baetselier P, Hamers-Casterman C, Hamers R (1977) Evidence for quasi-silent germline genes coding for phylogenetically ancient determinants of the rabbit a locus allotypes. Eur J Immunol 7:15–22
van der Loo W, Mougel F, Sanchez MS, Bouton C, Castien E, Fonseca A, Ferrand N, Soriguer R, Monnerot M (1999) Cytonuclear disequilibria in wild populations of rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus L.) suggest unequal allele turnover rates at the b locus (IGKC1). Immunogenetics 49:629–643
Xia X, Xie Z (2001) DAMBE: software package for data analysis in molecular biology and evolution. J Heredity 92:371–373
Yamada F, Takaki M, Suzuki H (2002) Molecular phylogeny of Japanese Leporidae, the Amami rabbit Pentalagus furnessi, the Japanese hare Lepus brachyurus, and the mountain hare Lepus timidus, inferred from mitochondrial DNA sequences. Genes Genet Syst 77:107–116
Zhu X, Boonthum A, Zhai SK, Knight KL (1999) B lymphocyte selection and age-related changes in VH gene usage in mutant Alicia rabbits. J Immunol 163:3313–3320
Acknowledgements
We thank Paulo Celio Alves for all the help in collecting tissue samples of Oryctolagus and Lg, and Franz Suchentrunk for providing us with tissue samples of Le. This work was partially supported by Direcção Geral de Florestas, by a grant of the Foundation for Science and Technology-Portugal (Praxis XXI/BPD/14551/2003) to P.E., by the National Institutes of Health grants AI50260 and AI49458 to K.L.K. and D.L., and by a grant of the Belgian Fonds voor Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek Vlaanderen (Krediet 1.5579.98-FWOKN35) to W.vdL.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Esteves, P.J., Lanning, D., Ferrand, N. et al. The evolution of the immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region (IgV H ) in Leporids: an unusual case of transspecies polymorphism. Immunogenetics 57, 874–882 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-005-0022-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-005-0022-0