Abstract
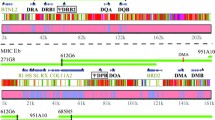
Expression of too many co-dominant major histocompatibility complex (MHC) alleles is thought to be detrimental to proper functioning of the immune system. Polyploidy of the genome will increase the number of expressed MHC genes unless they are prone to a silencing mechanism. In polyploid Xenopus species, the number of MHC class I and II genes has been physically reduced, as it does not increase with higher ploidy genomes. In the zebrafish some class IIB loci have been silenced, as only two genomically bona fide loci, DAA/DAB and DEA/DEB, have been described. Earlier studies indicated a reduction in the number of genomic and expressed class II MHC genes in a hexaploid African ‘large’ barb. This prompted us to study the number of MHC genes present in the genome of an African ‘large’ barb individual (Barbus intermedius) in relation to those expressed, adopting the following strategy. Full-length cDNA sequences were generated from mRNA and compared with partial genomic class Ia and II sequences generated by PCR using the same primer set. In addition, we performed Southern hybridizations to obtain a verification of the number of class I and IIB genes. Our study revealed three β2-microglobulin, five class Ia, four class IIA, and four class IIB genes at the genomic level, which were shown to be expressed in the hexaploid barb individual. The class Ia and class II data indicate that the ploidy status does not correlate with the presence and expression of these MHC genes.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartl S, Baish MA, Flajnik MF, Ohta Y (1997) Identification of class I genes in cartilaginous fish, the most ancient group of vertebrates displaying an adaptive immune response. J Immunol 159: 6097–6104
Betz UA, Mayer WE, Klein J (1994) Major histocompatibility complex class I genes of the coelacanth Latimeria chalumnae. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:11065–11069
Bingulac-Popovic J, Figueroa F, Sato A, Talbot WS, Johnson SL, Gates M, Postlethwait JH, Klein J (1997) Mapping of mhc class I and class II regions to different linkage groups in the zebrafish, Danio rerio. Immunogenetics 46:129–134
Bjorkman PJ, Saper MA, Samraoui B, Bennett WS, Strominger JL, Wiley DC (1987) Structure of the human class I histocompatibility antigen, HLA-A2. Nature 329:506–512
Cavender TM (1991) The fossil record of the Cyprinidae. Chapman and Hall, London
Criscitiello MF, Benedetto R, Antao A, Wilson MR, Chinchar VG, Miller NW, Clem LW, McConnell TJ (1998) Beta 2-microglobulin of ictalurid catfishes. Immunogenetics 48:339–343
Dixon B, Stet RJ, van Erp SH, Pohajdak B (1993) Characterization of beta 2-microglobulin transcripts from two teleost species. Immunogenetics 38:27–34
Dixon B, van Erp SH, Rodrigues PN, Egberts E, Stet RJ (1995) Fish major histocompatibility complex genes: an expansion. Dev Comp Immunol 19:109–133
Dixon B, Nagelkerke LA, Sibbing FA, Egberts E, Stet RJM (1996) Evolution of MHC class II beta chain-encoding genes in the Lake Tana barbel species flock (Barbus intermedius complex). Immunogenetics 44:419–431
Flajnik MF, Kasahara M, Shum BP, Salter-Cid L, Taylor E, Du Pasquier L (1993) A novel type of class I gene organization in vertebrates: a large family of non-MHC-linked class I genes is expressed at the RNA level in the amphibian Xenopus. EMBO J 12:4385–4396
Fujiki K, Booman M, Chin-Dixon E, Dixon B (2001) Cloning and characterization of cDNA clones encoding membrane-bound and potentially secreted major histocompatibility class I receptors from walleye (Stizostedion vitreum). lmmunogenetics 53:760–769
Golubtsov AS, Krysanov EY (1993) Karyological study of some cyprinid species from Ethiopia. The ploidy differences between large and small Barbus of Africa. J Fish Biol 42:445–455
Gussow D, Rein R, Ginjaar I, Hochstenbach F, Seemann G, Kottman A, Ploegh HL (1987) The human beta 2-microglobulin gene. Primary structure and definition of the transcriptional unit. J Immunol 139:3132–3138
Kasahara M, Flajnik MF, Ishibashi T, Natori T (1995) Evolution of the major histocompatibility complex: a current overview. Transpl Immunol 3:1–20
Kaufman J, Andersen R, Avila D, Engberg J, Lambris J, Salomonsen J, Welinder K, Skjodt K (1992) Different features of the MHC class I heterodimer have evolved at different rates. Chicken B-F and beta 2 microglobulin sequences reveal invariant surface residues. J lmmunol 148:1532–1546
Kaufman J, Salomonsen J, Flajnik MF (1994) Evolutionary conservation of MHC class I and class II molecules — different yet the same. Semin lmmunol 6:411–424
Klein J (1987) Origin of major histocompatibility complex polymorphism: the trans species hypothesis. Hum Immunol 19:155–162
Klein J, Figueroa F (1986) Evolution of the major histocompatibility complex. Crit Rev Immunol 6:295–386
Kruiswijk CP, Hermsen TT, Westphal AH, Savelkoul HF, Stet RJ (2002) A novel functional class I lineage in zebrafish (Danio rerio), carp (Cyprinus carpio), and large barbus (Barbus intermedius) showing an unusual conservation of the peptide binding domains. J Immunol 169:1936–1947
Kumar S, Tamura K, Jakobsen IB, Nei M (2001) MEGA2: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis software. Bioinformatics 17:1244–1245
Lawlor DA, Zemmour J, Ennis PD, Parham P (1990) Evolution of class-I MHC genes and proteins: from natural selection to thymic selection. Annu Rev Immunol 8:23–63
Li WH (1997) Molecular evolution. Sinauer, Sunderland, Massachusetts
Lundqvist ML, Appelkvist P, Hermsen T, Pilstrom L, Stet RJ (1999) Characterization of beta2-microglobulin in a primitive fish, the Siberian sturgeon (Acipenser baeri). lmmunogenetics 50:79–83
Marsh SGE, Parham P, Barber LD (2000) The HLA facts book. Academic Press, San Diego
Michalova V, Murray BW, Sultmann H, Klein J (2000) A contig map of the Mhc class I genomic region in the zebrafish reveals ancient synteny. J lmmunol 164:5296–5305
Murray BW, Nilsson P, Zaleska-Rutczynska Z, Sultmann H, Klein J (2000) Linkage relationships and haplotype variation of the major histocompatibility complex class I A genes in the cichlid fish Oreochromis niloticus. 2:437–448
Nagelkerke LAJ, Sibbing FA (2000) The large barbs (Barbus spp., Cyprinidae, Teleostei) of lake Tana (Ethiopia), with a description of a new species, Barbus osseensis. Neth J Zool 50:179–214
Nakai K, Horton P (1999) PSORT: a program for detecting sorting signals in proteins and predicting their subcellular localization. Trends Biochem Sci 24:34–36
Nelson JS (1994) Fishes of the world. Wiley, New York
Ohno J, Muramoto J, Christian L, Atkin NB (1967) Dipliod-tetrapliod relationship among old world members of the fish family Cyprinidae. Chromosoma 23:1–9
Ono H, Figueroa F, O’HUigin C, Klein J (1993a) Cloning of the beta 2 microglobulin gene in the zebrafish. lmmunogenetics 38:1–10
Ono H, O’HUigin C, Vincek V, Stet RJ, Figueroa F, Klein J (1993b) New beta chain-encoding Mhc class II genes in the carp. lmmunogenetics 38:146–149
Parnes JR, Robinson RR, Seidman JG (1983) Multiple mRNA species with distinct 3′ termini are transcribed from the beta 2-microglobulin gene. Nature 302:449–452
Persson AC, Stet RJM, Pilstrom L (1999) Characterization of MHC class l and b(2)-microglobulin sequences in Atlantic cod reveals an unusually high number of expressed class I genes. lmmunogenetics 50:49–59
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol4:406–425
Salter RD, Benjamin RJ, Wesley PK, Buxton SE, Gaffett TP, Clayberger C, Krensky AM, Norment AM, Littman DR, Parham P (1990) A binding site for the T-cell co-receptor CD8 on the alpha 3 domain of HLA-A2. Nature 345:41–46
Sammut B, Marcuz A, Du Pasquier L (2002) The fate of duplicated major histocompatibility complex class la genes in a dodecaploid amphibian, Xenopus ruwenzoriensis. Eur J lmmunol 32:2698–2709
Sato K, Flajnik MF, Du Pasquier L, Katagiri M, Kasahara M (1993) Evolution of the MHC: isolation of class II beta-chain cDNA clones from the amphibian Xenopus laevis. J Immunol 150: 831–2843
Shum BP, Avila D, Du Pasquier L, Kasahara M, Flajnik MF (1993) Isolation of a classical MHC class I cDNA from an amphibian. Evidence for only one class I locus in the Xenopus MHC. J Immunol 151: 5376–5386
Shum BP, Azurni K, Zhang S, Kehrer SR, Raison RL, Detrich HW, Parham P (1996) Unexpected beta2-microglobulin sequence diversity in individual rainbow trout. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:2779–2784
Shum BP, Guethlein L, Flodin LR, Adkison MA, Hedrick RP, Nehring RB, Stet RJ, Secombes C, Parham P (2001) Modes of salmonid MHC class I and II evolution differ from the primate paradigm. J Immunol 166:3297–3308
Shum BP, Mason PM, Magor KE, Flodin LR, Stet RJM, Parham P (2002) Structures of two major histocompatibility complex class I genes of the rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). lmmunogenetics 54:193–199
Sola L, Cataudella S, Capanna E (1981) New developments in vertebrate cytotaxonomy. III. Karyology of bony fishes: a review. Genetica 54:285–328
Stet RJM, Johnestone R, Parham P (1997) The unMHC of teleostean fish: segregation analyses in common carp and Atlantic salmon. Hereditas 127:169–170
Stet RJM, Kruiswijk CP, Saeij JP, Wiegertjes GF (1998) Major histocompatibility genes in cyprinid fishes: theory and practice. lmmunol Rev 166:301–316
Sultmann H, Mayer WE, Figueroa F, O’Huigin C, Klein J (1994) Organization of Mhc class II B genes in the zebrafish (Brachydanio rerio). Genomics 23:114
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
van Erp SH, Dixon B, Figueroa F, Egberts E, Stet RJM (1996a) Identification and characterization of a new major histocompatibility complex class I gene in carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). lmmunogenetics 44:49–61
van Erp SH, Egberts E, Stet RJM (1996b) Characterization of class II A and B genes in a gynogenetic carp clone. lmmunogenetics 44:192–202
Zardoya R, Doadrio I (1999) Molecular evidence on the evolutionary and biogeographical patterns of European cyprinids. J Mol Evol 49:227–237
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Martin de Graaf, Leo Nagelkerke and Nand Sibbing for providing tissue samples of a Lake Tana Barbus intermedius individual.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kruiswijk, C.P., Hermsen, T., Fujiki, K. et al. Analysis of genomic and expressed major histocompatibility class Ia and class II genes in a hexaploid Lake Tana African ‘large’ barb individual (Barbus intermedius). Immunogenetics 55, 770–781 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-003-0635-0
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-003-0635-0