Abstract.
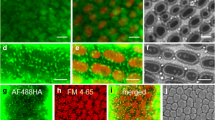
In ciliated protozoa, most nutrients are internalized via phagocytosis by food vacuole formation at the posterior end of the buccal cavity. The uptake of small-sized molecules and external fluid through the plasma membrane is a localized process. That is because most of the cell surface is internally covered by an alveolar system and a fibrous epiplasm, so that only defined areas of the cell surface are potential substance uptake sites. The purpose of this study is to analyze, by fluorescence confocal laser scanning microscopy, the relationship between WGA (Triticum vulgaris agglutinin) and dextran internalization in Paramecium primaurelia cells blocked in the phagocytic process, so that markers could not be internalized via food vacuole formation. WGA, which binds to surface constituents of fixed and living cells, was used as a marker for membrane transport and dextran as a marker for fluid phase endocytosis. After 3 min incubation, WGA-FITC is found on plasma membrane and cilia, and successively within small cytoplasmic vesicles. After a 10–15 min chase in unlabeled medium, the marked vesicles decrease in number, increase in size and fuse with food vacuoles. This fusion was evidenced by labeling food vacuoles with BSA-Texas red. Dextran enters the cell via endocytic vesicles which first localize in the cortical region, under the plasma membrane, and then migrate in the cytoplasm and fuse with other endocytic vesicles and food vacuoles. When cells are fed with WGA-FITC and dextran-Texas red at the same time, two differently labeled vesicle populations are found. Cytosol acidification and incubation in sucrose medium or in chlorpromazine showed that WGA is internalized via clathrin vesicles, whereas fluid phase endocytosis is a clathrin-independent process.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Revised version: 24 April 2001
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramoino, .P., Fronte, .P., Fato, .M. et al. Fluid phase and receptor-mediated endocytosis in Paramecium primaurelia by fluorescence confocal laser scanning microscopy. Eur Biophys J 30, 305–312 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002490100166
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002490100166