Abstract
A ribosome is an enzyme that catalyzes translation of the genetic information encoded in messenger RNA (mRNA) into proteins. Besides translation through the single-stranded mRNA, the ribosome is also able to translate through the duplex region of mRNA via unwinding the duplex. Here, based on our proposed ribosome translation model, we study analytically the dynamics of Escherichia coli ribosome translation through the duplex region of mRNA, and compare with the available single molecule experimental data. It is shown that the ribosome uses only one active mechanism (mechanical unwinding), rather than two active mechanisms (open-state stabilization and mechanical unwinding), as proposed before, to unwind the duplex. The reduced rate of translation through the duplex region is due to the occurrence of futile transitions, which are induced by the energy barrier from the duplex unwinding to the forward translocation along the single-stranded mRNA. Moreover, we also present predicted results of the average translation rate versus the external force acting on the ribosome translating through the duplex region and through the single-stranded region of mRNA, which can be easily tested by future experiments.




Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
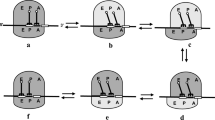
Since the mRNA channel in the 30S subunit is tight now, the mRNA–tRNA complex is fixed to the 30S subunit during relative rotations between the two ribosomal subunits (Fig. 1b, 1b′). Thus, the relative ribosomal rotations can only induce the two tRNAs moving from 50S A and P sites to 50S P and E sites (from Fig. 1b to 1b′) and from 50S P and E sites to 50S A and P sites (from Fig. 1b′ to 1b).
Since the locking of the ribosome prohibits the binding of EF-G.GTP, only aminoacyl-tRNA.EF-Tu.GTP complex can now bind to the ribosome.
In this paper, the spontaneous opening of mRNA base pairs refers to the mRNA unwinding that is induced by the thermal noise and/or the external pulling force to destabilize the mRNA duplex, i.e., it refers to the mRNA unwinding that is not induced by the ribosome translocation along the mRNA.
References
Abel K, Yoder MD, Hilgenfeld R, Jurnak F (1996) An α to β conformational switch in EF-Tu. Structure 4:1153–1159
Blanchard SC, Kim HD, Gonzalez RL Jr, Puglisi JD, Chu S (2004) tRNA dynamics on the ribosome during translation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:12893–12898
Buhot A, Halperin A (2004) Effects of stacking on the configurations and elasticity of single-stranded nucleic acids. Phys Rev E 70:020902
Cui S, Yu Y, Lin Z (2009) Modeling single chain elasticity of single-stranded DNA: a comparison of three models. Polymer 50:930–935
Dell VA, Miller DL, Johnson AE (1990) Effects of nucleotide and aurodox-induced changes in elongation factor Tu conformation upon its interactions with aminoacyl transfer RNA. A fluorescence study. Biochemistry 29:1757–1763
Feinberg JS, Joseph S (2001) Identification of molecular interactions between P-site tRNA and the ribosome essential for translocation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:11120–11125
Fischer N, Konevega AL, Wintermeyer W, Rodnina MV, Stark H (2010) Ribosome dynamics and tRNA movement by time-resolved electron cryomicroscopy. Nature 466:329–333
Frank J, Agrawal RK (2000) A ratchet-like inter-subunit reorganization of the ribosome during translocation. Nature 406:318–322
Frank J, Gao H, Sengupta J, Gao N, Taylor DJ (2007) The process of mRNA–tRNA translocation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:19671–19678
Freier SM, Kierzek R, Jaeger JA, Sugimoto N, Caruthers MH, Neilson T, Tuener DH (1986) Improved free-energy parameters for predictions of RNA duplex stability. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:9373–9377
Green R, Noller HF (1997) Ribosomes and translation. Annu Rev Biochem 66:679–716
Lill R, Robertson JM, Wintermeyer W (1989) Binding of the 30-terminus of tRNA to 23S rRNA in the ribosomal exit site actively promotes translocation. EMBO J 8:3933–3938
Lionnet T, Spiering MM, Benkovic SJ, Bensimon D, Croquette V (2007) Real-time observation of bacteriophage T4 gp41 helicase reveals an unwinding mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:19790–19795
Moazed D, Noller HF (1989) Intermediate states in the movement of transfer RNA in the ribosome. Nature 342:142–148
Noller HF, Yusupov MM, Yusupova GZ, Baucom A, Cate JHD (2002) Translocation of tRNA during protein synthesis. FEBS Lett 514:11–16
Petrov A, Kornberg G, O’Leary S, Tsai A, Uemura S, Puglisi JD (2011) Dynamics of the translational machinery. Curr Opin Struct Biol 21:137–145
Polekhina G, Thirup S, Kjeldgaard M, Nissen P, Lippmann C, Nyborg J (1996) Helix unwinding in the effector region of elongation factor EF-Tu–GDP. Structure 4:1141–1151
Qu X, Wen J-D, Lancaster L, Noller HF, Bustamante C, Tinoco I Jr (2011) The ribosome uses two active mechanisms to unwind messenger RNA during translation. Nature 475:118–121
Rodnina MV, Fricke R, Kuhn L, Wintermeyer W (1995) Codon dependent conformational change of elongation factor Tu preceding GTP hydrolysis on the ribosome. EMBO J 14:2613–2619
Savelsbergh A, Katunin VI, Mohr D, Peske F, Rodnina MV, Wintermeyer W (2003) An elongation factor G-induced ribosome rearrangement precedes tRNA-mRNA translocation. Mol Cell 11:1517–1523
Schuwirth BS, Borovinskaya MA, Hau CW, Zhang W, Vila-Sanjurjo A, Holton JM, Cate JHD (2005) Structures of the bacterial ribosome at 3.5 Å resolution. Science 310:827–834
Smith S, Cui Y, Bustamante C (1996) Overstretching B-DNA: the elastic response of individual double-stranded and single-stranded DNA molecules. Science 271:795–799
Takyar S, Hickerson RP, Noller HF (2005) mRNA helicase activity of the ribosome. Cell 120:49–58
Taylor DJ, Nilsson J, Merrill AR, Andersen GM, Nissen P, Frank J (2007) Structures of modified eEF2.80S ribosome complexes reveal the role of GTP hydrolysis in translocation. EMBO J 26:2421–2431
Thomen P, Lopez PJ, Heslot F (2005) Unravelling the mechanism of RNA-polymerase forward motion by using mechanical force. Phys Rev Lett 94:128102
Uemura S, Aitken CE, Korlach J, Flusberg BA, Turner SW, Puglisi JD (2010) Real-time tRNA transit on single translating ribosomes at codon resolution. Nature 464:1012–1017
Valle M (2011) Almost lost in translation. Cryo-EM of a dynamic macromolecular complex: the ribosome. Eur Biophys J 40:589–597
Valle M, Zavialov A, Sengupta J, Rawat U, Ehrenberg M, Frank J (2003) Locking and unlocking of ribosomal motions. Cell 114:123–134
Wintermeyer W, Peske F, Beringer M, Gromadski KB, Savelsbergh A, Rodnina MV (2004) Mechanisms of elongation on the ribosome: dynamics of a macromolecular machine. Biochem Soc Trans 32:733–737
Xie P (2007) On translocation mechanism of ring-shaped helicase along single-stranded DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta 1774:737–748
Xie P (2013) Dynamics of tRNA occupancy and dissociation during translation by the ribosome. J Theor Biol 316:49–60
Yusupova GZ, Yusupov MM, Cate JHD, Noller HF (2001) The path of messenger RNA through the ribosome. Cell 106:233–241
Zavialov AV, Ehrenberg M (2003) Peptidyl-tRNA regulates the GTPase activity of translation factors. Cell 224:113–122
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 10974248).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, P. Model of ribosome translation and mRNA unwinding. Eur Biophys J 42, 347–354 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-012-0879-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-012-0879-4