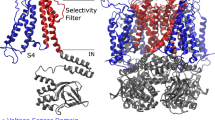
Abstract
The unique gating kinetics of hERG K+ channels are critical for normal cardiac repolarization, and patients with mutations in hERG have a markedly increased risk of cardiac arrhythmias and sudden cardiac arrest. HERG K+ channels are also remarkably promiscuous with respect to drug binding, which has been a very significant problem for the pharmaceutical industry. Here, we review the progress that has been made in understanding the structure and function of hERG K+ channels with a particular focus on nuclear magnetic resonance studies of the domains of the hERG K+ channel.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhavan A, Atanasiu R, Shrier A (2003) Identification of a COOH-terminal segment involved in maturation and stability of human ether-a-go–go-related gene potassium channels. J Biol Chem 278:40105–40112
Akhavan A, Atanasiu R, Noguchi T, Han W, Holder N, Shrier A (2005) Identification of the cyclic-nucleotide-binding domain as a conserved determinant of ion-channel cell-surface localization. J Cell Sci 118:2803–2812
Apponyi MA, Ozawa K, Dixon NE, Otting G (2008) Cell-free protein synthesis for analysis by NMR spectroscopy. Methods Mol Biol 426:257–268
Aydar E, Palmer C (2001) Functional characterization of the C-terminus of the human ether-a-go–go-related gene K(+) channel (HERG). J Physiol 534:1–14
Brelidze TI, Carlson AE, Zagotta WN (2009) Absence of direct cyclic nucleotide modulation of mEAG1 and hERG1 channels revealed with fluorescence and electrophysiological methods. J Biol Chem 284:27989–27997
Brelidze TI, Carlson AE, Sankaran B, Zagotta WN (2012) Structure of the carboxy-terminal region of a KCNH channel. Nature 481:530–533
Curran ME, Splawski I, Timothy KW, Vincent GM, Green ED, Keating MT (1995) A molecular basis for cardiac arrhythmia: HERG mutations cause long QT syndrome. Cell 80:795–803
Doyle DA, Morais Cabral J, Pfuetzner RA, Kuo A, Gulbis JM, Cohen SL, Chait BT, MacKinnon R (1998) The structure of the potassium channel: molecular basis of K+ conduction and selectivity. Science 280:69–77
Farrelly AM, Ro S, Callaghan BP, Khoyi MA, Fleming N, Horowitz B, Sanders KM, Keef KD (2003) Expression and function of KCNH2 (HERG) in the human jejunum. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 284:G883–G895
Fernandez-Trillo J, Barros F, Machin A, Carretero L, Dominguez P, de la Pena P (2011) Molecular determinants of interactions between the N-terminal domain and the transmembrane core that modulate hERG K+ channel gating. PLoS ONE 6:e24674
Gayen S, Li Q, Kang C (2012) The solution structure of the S4–S5 linker of the hERG potassium channel. J Pept Sci 18:140–145
Gong Q, Anderson CL, January CT, Zhou Z (2002) Role of glycosylation in cell surface expression and stability of HERG potassium channels. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 283:H77–H84
Gong Q, Keeney DR, Robinson JC, Zhou Z (2004) Defective assembly and trafficking of mutant HERG channels with C-terminal truncations in long QT syndrome. J Mol Cell Cardiol 37:1225–1233
Goujon M, McWilliam H, Li W, Valentin F, Squizzato S, Paern J, Lopez R (2010) A new bioinformatics analysis tools framework at EMBL-EBI. Nucleic Acids Res 38:W695–W699
Gustina AS, Trudeau MC (2009) A recombinant N-terminal domain fully restores deactivation gating in N-truncated and long QT syndrome mutant hERG potassium channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:13082–13087
Gustina AS, Trudeau MC (2011) hERG potassium channel gating is mediated by N- and C-terminal region interactions. J Gen Physiol 137:315–325
Jiang Y, Lee A, Chen J, Ruta V, Cadene M, Chait BT, MacKinnon R (2003) X-ray structure of a voltage-dependent K+ channel. Nature 423:33–41
Jiang M, Zhang M, Maslennikov IV, Liu J, Wu DM, Korolkova YV, Arseniev AS, Grishin EV, Tseng GN (2005) Dynamic conformational changes of extracellular S5–P linkers in the hERG channel. J Physiol 569:75–89
Ju P, Pages G, Riek RP, Chen PC, Torres AM, Bansal PS, Kuyucak S, Kuchel PW, Vandenberg JI (2009) The pore domain outer helix contributes to both activation and inactivation of the HERG K+ channel. J Biol Chem 284:1000–1008
Kannankeril P, Roden DM, Darbar D (2010) Drug-induced long QT syndrome. Pharmacol Rev 62:760–781
Klammt C, Schwarz D, Dotsch V, Bernhard F (2007) Cell-free production of integral membrane proteins on a preparative scale. Methods Mol Biol 375:57–78
Kutteh R, Vandenberg JI, Kuyucak S (2007) Molecular dynamics and continuum electrostatics studies of inactivation in the HERG potassium channel. J Phys Chem B 111:1090–1098
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, Valentin F, Wallace IM, Wilm A, Lopez R, Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Higgins DG (2007) Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23:2947–2948
Lee SY, Lee A, Chen J, MacKinnon R (2005) Structure of the KvAP voltage-dependent K+ channel and its dependence on the lipid membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:15441–15446
Li Q, Gayen S, Chen AS, Huang Q, Raida M, Kang C (2010) NMR solution structure of the N-terminal domain of hERG and its interaction with the S4–S5 linker. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 403:126–132
Liu J, Zhang M, Jiang M, Tseng GN (2002) Structural and functional role of the extracellular S5–P linker in the HERG potassium channel. J Gen Physiol 120:723–737
Long SB, Campbell EB, MacKinnon R (2005) Crystal structure of a mammalian voltage-dependent Shaker family K+ channel. Science 309:897–903
Long SB, Tao X, Campbell EB, MacKinnon R (2007) Atomic structure of a voltage-dependent K+ channel in a lipid membrane-like environment. Nature 450:376–382
Morais Cabral JH, Lee A, Cohen S, Chait B, Li M, Mackinnon R (1998) Crystal structure and functional analysis of the HERG potassium channel N terminus: a eukaryotic PAS domain. Cell 95:649–655
Muskett FW, Thouta S, Thomson SJ, Bowen A, Stansfeld PJ, Mitcheson JS (2011) Mechanistic insight into human ether-a-go–go-related gene (hERG) K+ channel deactivation gating from the solution structure of the EAG domain. J Biol Chem 286:6184–6191
Ng CA, Hunter MJ, Perry MD, Mobli M, Ke Y, Kuchel PW, King GF, Stock D, Vandenberg JI (2011) The N-terminal tail of hERG contains an amphipathic alpha-helix that regulates channel deactivation. PLoS ONE 6:e16191
Ng CA, Perry MD, Tan PS, Hill AP, Kuchel PW, Vandenberg JI (2012) The S4–S5 linker acts as a signal integrator for hERG K+ channel activation and deactivation gating. PLoS ONE 7:e31640
Pages G, Torres AM, Ju P, Bansal PS, Alewood PF, Kuchel PW, Vandenberg JI (2009) Structure of the pore-helix of the hERG K(+) channel. Eur Biophys J 39:111–120
Perrin MJ, Subbiah RN, Vandenberg JI, Hill AP (2008) Human ether-a-go–go related gene (hERG) K+ channels: function and dysfunction. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 98:137–148
Petrecca K, Atanasiu R, Akhavan A, Shrier A (1999) N-linked glycosylation sites determine HERG channel surface membrane expression. J Physiol 515(Pt 1):41–48
Sanguinetti MC, Tristani-Firouzi M (2006) hERG potassium channels and cardiac arrhythmia. Nature 440:463–469
Sanguinetti MC, Jiang C, Curran ME, Keating MT (1995) A mechanistic link between an inherited and an acquired cardiac arrhythmia: HERG encodes the IKr potassium channel. Cell 81:299–307
Schonherr R, Heinemann SH (1996) Molecular determinants for activation and inactivation of HERG, a human inward rectifier potassium channel. J Physiol 493(Pt 3):635–642
Schwarz D, Junge F, Durst F, Frolich N, Schneider B, Reckel S, Sobhanifar S, Dotsch V, Bernhard F (2007) Preparative scale expression of membrane proteins in Escherichia coli-based continuous exchange cell-free systems. Nat Protoc 2:2945–2957
Subbotina J, Yarov-Yarovoy V, Lees-Miller J, Durdagi S, Guo J, Duff HJ, Noskov SY (2010) Structural refinement of the hERG1 pore and voltage-sensing domains with ROSETTA-membrane and molecular dynamics simulations. Proteins 78:2922–2934
Torres AM, Bansal PS, Sunde M, Clarke CE, Bursill JA, Smith DJ, Bauskin A, Breit SN, Campbell TJ, Alewood PF, Kuchel PW, Vandenberg JI (2003) Structure of the HERG K+ channel S5P extracellular linker: role of an amphipathic alpha-helix in C-type inactivation. J Biol Chem 278:42136–42148
Trudeau MC, Warmke JW, Ganetzky B, Robertson GA (1995) HERG, a human inward rectifier in the voltage-gated potassium channel family. Science 269:92–95
Tseng GN, Sonawane KD, Korolkova YV, Zhang M, Liu J, Grishin EV, Guy HR (2007) Probing the outer mouth structure of the HERG channel with peptide toxin footprinting and molecular modeling. Biophys J 92:3524–3540
Vandenberg JI, Torres A, Campbell T, Kuchel PW (2004) The HERG K+ channel: progress in understanding the molecular basis of its unusual gating kinetics. Eur Biophys J 33:89–97
Wang J, Trudeau MC, Zappia AM, Robertson GA (1998) Regulation of deactivation by an amino terminal domain in human ether-à-go–go-related gene potassium channels. J Gen Physiol 112:637–647
Wang J, Myers CD, Robertson GA (2000) Dynamic control of deactivation gating by a soluble amino-terminal domain in HERG K+ channels. J Gen Physiol 115:749–758
Warmke JW, Ganetzky B (1994) A family of potassium channel genes related to eag in Drosophila and mammals. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:3438–3442
Acknowledgments
Research in the authors’ laboratories is supported by the National Health and Medical Research Council (JIV; 459401, 1019693), National Heart Foundation of Australia (JIV; G09S-450, G11S-5829) and the Australian Research Council (JIV, PWK; DP0986316).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Special Issue: From kinetics to imaging: An NMR odyssey.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ng, C.A., Torres, A.M., Pagès, G. et al. Insights into hERG K+ channel structure and function from NMR studies. Eur Biophys J 42, 71–79 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-012-0808-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-012-0808-6