Abstract
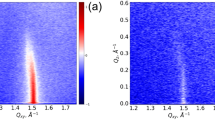
Thionins, ubiquitous plant toxins, are believed to act by lysing the membrane of pathogenic organisms. Several competing mechanisms were proposed for the lysis of phospholipid membranes by the toxins. In order to study in more detail the proposed mechanisms and possibly resolve among the competing proposals, the interactions of purothionins with a model lipid membrane in the form of a monolayer were studied. The monolayer formed at the air-water interface was studied by synchrotron X-ray reflectivity and grazing incidents diffraction methods. The model membrane was composed of 90:10 mol% DPPC:DPPS (dipylmitoyl phosphatidylcholine:dipylmitoyl phosphatidylserine). The protein interaction with the monolayer disturbs the in-plane and out-of-plane order of phospholipids, increases the amount of the liquid phase of the monolayer, and increases the average surface area per alkyl chain. The results indicate that the protein is bound only transiently, and after ~4 h most of the properties of the monolayer are reminiscent of the pure DPPC monolayer suggesting partial withdrawal of DPPS. Obtained electron density distributions perpendicular to the membrane interface do not show any significant contribution from the adsorbed proteins, further supporting the withdrawal hypothesis.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GIXD:
-
Grazing incidence X-ray diffraction
- XR:
-
X-ray reflectivity
- DPPC:
-
Dipylmitoyl phosphatidylcholine
- DPPS:
-
Dipylmitoyl phosphatidylserine
- PT:
-
Purothionin
References
Als-Nielsen J, Jacquemain D, Kjaer K, Leveiller F, Lahav M, Leiserowitz L (1994) Principles and applications of grazing incidence X-ray and neutron scattering from ordered molecular monolayers at the air-water interface. Phys Rep 246:251–313
Angerhofer CK, Shier WT, Vernon LP (1990) Phospholipase activation in the cytotoxic mechanism of thionin purified from nuts of pubera. Toxicon 28:547–557
Bohlmann H, Apel K (1991) Thionins. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 42:227–240
Broekaert WF, Cammue BPA, Debolle MFC, Thevissen K, Desamblanx GW, Osborn RW (1997) Antimicrobial peptides from plants. Crit Rev Plant Sci 16:297–323
Carrasco L, Vazquez D, Hernandez-Lucas C, Carbonero P, Garcia-Olmedo F (1981) Thionins: plant peptides that modify membrane permeability in cultured mammalian cells. Eur J Biochem 116:185–189
Castro MS, Fontes W (2005) Plant defense and antimicrobial peptides. Prot Pept Lett 12:13–18
Debreczeni JE, Girmann B, Zeeck A, Kratzner R, Sheldrick GM (2003) Structure of viscotoxin A3: disulfide location from weak SAD data. Acta Cryst D 59:2125–2132
Evans JE, Wang Y, Shaw KP, Vernon LP (1989) Cellular responses to Pyrularia thionin are mediated by Ca2+ influx and phospholipase A2 activation and are inhibited by thionin tyrosine iodination. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 86:5849–5853
Fracki WS, Li D, Owen N, Perry C, Naisbitt GH, Vernon LP (1992) Role of Tyr and Trp in membrane responses of Pyrularia thionin determined by optical and NMR spectra following Tyr iodination and Trp modification. Toxicon 30:1427–1440
Garcia-Olmedo F, Molina A, Alamillo JM, Rodriguez-Palenzuela P (1998) Plant defense peptides. Biopolymers 47:479–491
Giudici M, Pascual R, de la Canal L, Pfuller K, Pfuller U, Villalain J (2003) Interaction of viscotoxins A3 and B with membrane model systems: implications to their mechanism of action. Biophys J 85:971–981
Guinier A (1963) X-ray diffraction. Freeman, San Francisco
Hamley IW, Pedersen SJ (1994) Analysis of neutron and X-ray reflectivity data. I. Theory. J Appl Crystallogr 27:29–35
Huang W, Vernon LP, Bell JD (1994) Enhancement of adenylate cyclase activity in S49 lymphoma cell membranes by the toxin thionin from Pyrularia pubera. Toxicon 32:789–797
Hughes P, Dennis E, Whitecross M, Llewellyn D, Gage P (2000) The cytotoxic plant protein, beta-purothionin, forms ion channels in lipid membranes. J Biol Chem 275:823–827
Jensen TR, Balashev K, Bjørnholm T, Kjaer K (2001) Novel methods for studying lipids and lipases K and their mutual interaction at interfaces. Part II. Surface sensitive synchrotron X-ray scattering. Biochimie 83:399–408
Johnson KA, Kim E, Teeter MM, Suh SW, Stec B (2005) Crystal structure of alpha-hordothionin at 1.9 Angstrom resolution. FEBS Lett 579:2301–2306
Li SS, Gullbo J, Lindholm P, Larsson R, Thunberg E, Samuelsson G, Bohlin L, Claeson P (2002) Ligatoxin B, a new cytotoxic protein with a novel helix-turn-helix DNA-binding domain from the mistletoe Phoradendron liga. Biochem J 366:405–413
Llanos P, Henriquez M, Minic J, Elmorjani K, Marion D, Riquelme G, Molgo J, Benoit E (2004) Neuronal and muscular alterations caused by two wheat endosperm proteins, puroindoline-a and alpha1-purothionin, are due to ion pore formation. Eur Biophys J 33:283–287
Mansour HM, Zografi G (2007) Relationships between equilibrium spreading pressure and phase equilibria of phospholipid bilayers and monolayers at the air-water interface. Langmuir 23:3809–3819
Miller CE, Busath DD, Strongin B, Majewski J (2008a) Packing of ganglioside GT1b:DPPE and DPPC phospholipid mixtures at the air-liquid interface. An X-ray reflectivity and grazing incidence diffraction study. Biophys J 95:641–647
Miller CE, Majewski J, Watkins EB, Kuhl TL (2008b) Part I: an X-ray scattering study of cholera toxin penetration and induced phase transformations in lipid membranes. Biophys J 95:629–640
Miller CE, Majewski J, Watkins EB, Mulder DJ, Gog T, Kuhl TL (2008c) Probing the local order of single phospholipid membranes using grazing incidence X-ray diffraction. Phys Rev Lett 100:058103
Neville F, Ishitsuka Y, Hodges CS, Konovalov O, Waring AJ, Lehrer R, Lee KY, Gidalevitz D (2008) Protegrin interaction with lipid monolayers: grazing incidence X-ray diffraction and X-ray reflectivity study. Soft Matter 4:1665–1674
Oka T, Murata Y, Nakanishi T, Yoshizumi H, Hayashida H, Ohtsuki Y, Toyoshima K, Hakura A (1992) Similarity, in molecular structure and function, between the plant toxin purothionin and the mammalian pore-forming proteins. Mol Biol Evol 9:707–715
Rao U, Stec B, Teeter MM (1995) Refinement of purothionins reveals the solute particles important for the lattice formation and toxicity. Part 1: α1-purothionin revisited. Acta Cryst D51:904–913
Richard JA, Kelly I, Marion D, Pezolet M, Auger M (2002) Interaction between beta-purothionin and dimyristoylphosphatidylglycerol: a (31)P-NMR and infrared spectroscopic study. Biophys J 83:2074–2083
Richard JA, Kelly I, Marion D, Auger M, Pezolet M (2005) Structure of beta-purothionin in membranes: a two-dimensional infrared correlation spectroscopy study. Biochemistry 44:52–61
Stec B (2006) Plant thionins-the structural perspective. Cell Mol Life Sci 63:1370–1385
Stec B, Rao U, Teeter MM (1995) Refinement of purothionins reveals the solute particles important for the lattice formation and toxicity. Part 2: structure of β-purothionin at 1.7 Å resolution. Acta Cryst D51:914–924
Stec B, Markman O, Rao U, Heffron G, Henderson S, Vernon LP, Brumfeld V, Teeter MM (2004) Proposal for molecular mechanism of thionins deduced from physico-chemical studies of plant toxins. J Pept Res 64:210–224
Thevissen K, Terras FRG, Broekaert WF (1999) Permabilization of fungal membrane by plant defensins and thionins inhibits fungal growth. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:5451–5458
Vernon LP, Bell JD (1992) Membrane structure, toxins and phospholipase A2 activity. Pharmacol Ther 54:269–295
Woynarowski JM, Konopa J (1980) Interaction between DNA and viscotoxins cytotoxic basic polypeptides from Viscum album. L Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem 361:1535–1545
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by the Los Alamos National Laboratory under the auspices of the United States Department of Energy under DOE contract W7405-ENG-36, and by the DOE Office of Basic Energy Science. We thank Dr. Kristian Kjaer from the University of Copenhagen in Denmark who collaborated with us on the GIXD and XR measurements at HASYLAB, Hamburg, Germany.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Majewski, J., Stec, B. X-ray scattering studies of model lipid membrane interacting with purothionin provide support for a previously proposed mechanism of membrane lysis. Eur Biophys J 39, 1155–1165 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-009-0568-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-009-0568-0