Abstract
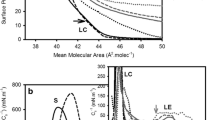
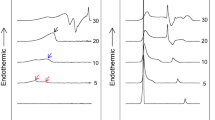
Ceramides are precursors of major sphingolipids and can be important cellular effectors. The biological effects of ceramides have been suggested to stem from their biophysical effects on membrane structure affecting the lateral and transbilayer organization of other membrane components. In this study we investigated the effect of acyl chain composition in ceramides (C4-C24:1) on their miscibility with N-palmitoyl-sphingomyelin (PSM) using differential scanning calorimetry. We found that short-chain (C4 and C8) ceramides induced phase separation and lowered the T m and enthalpy of the PSM endotherm. We conclude that short-chain ceramides were more miscible in the fluid-phase than in the gel-phase PSM bilayers. Long-chain ceramides induced apparent heterogeneity in the bilayers. The main PSM endotherm decreased in cooperativity and enthalpy with increasing ceramide concentration. New ceramide-enriched components could be seen in the thermograms at all ceramide concentrations above X Cer = 0.05. These broad components had higher T m values than pure PSM. C24:1 ceramide exhibited complex behavior in the PSM bilayers. The miscibility of C24:1 ceramide with PSM at low (X Cer = 0.05–0.10) concentrations was exceptionally good according to the cooperativity of the transition. At higher concentrations, multiple components were detected, which might have arisen from interdigitated gel-phases formed by this very asymmetric ceramide. The results of this study indicate that short-chain and long-chain ceramides have very different effects on the sphingomyelin bilayers. There also seems to be a correlation between their miscibility in binary systems and the effect of ceramides of different hydrophobic length on sphingomyelin-rich domains in multicomponent membranes.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alanko SM, Halling KK, Maunula S, Slotte JP, Ramstedt B (2005) Displacement of sterols from sterol/sphingomyelin domains in fluid bilayer membranes by competing molecules. Biochim Biophys Acta 1715:111–121
Bar LK, Barenholz Y, Thompson TE (1997) Effect of sphingomyelin composition on the phase structure of phosphatidylcholine-sphingomyelin bilayers. Biochemistry 36:2507–2516
Björkqvist YJE, Nyholm TKM, Slotte JP, Ramstedt B (2005) Domain formation and stability in complex lipid bilayers as reported by cholestatrienol. Biophys J 88:4054–4063
Carrer DC, Maggio B (1999) Phase behavior and molecular interactions in mixtures of ceramide with dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine. J Lipid Res 40:1978–1989
Carrer DC, Hartel S, Monaco HL, Maggio B (2003) Ceramide modulates the lipid membrane organization at molecular and supramolecular levels. Chem.Phys.Lipids 122:147–152
Carrer DC, Schreier S, Patrito M, Maggio B (2006) Effects of a short-chain ceramide on bilayer domain formation, thickness, and chain mobililty: DMPC and asymmetric ceramide mixtures. Biophys J 90:2394–2403
Castro BM, de Almeida RF, Silva LC, Fedorov A, Prieto M (2007) Formation of ceramide/sphingomyelin gel domains in the presence of an unsaturated phospholipid. A quantitative multiprobe approach. Biophys J 93:1639–1650
Chiantia S, Kahya N, Ries J, Schwille P (2006) Effects of ceramide on liquid-ordered domains investigated by simultaneous AFM and FCS. Biophys J 90:4500–4508
Chiantia S, Kahya N, Schwille P (2007) Raft domain reorganization driven by short- and long-chain ceramide: a combined AFM and FCS study. Langmuir 23:7659–7665
Chiantia S, Ries J, Chwastek G, Carrer D, Li Z, Bittman R, Schwille P (2008) Role of ceramide in membrane protein organization investigated by combined AFM and FCS. Biochim Biophys Acta 1778:1356–1364
Cremesti AE, Goni FM, Kolesnick R (2002) Role of sphingomyelinase and ceramide in modulating rafts: do biophysical properties determine biologic outcome? FEBS Lett 531:47–53
Di Paola M, Cocco T, Lorusso M (2000) Ceramide interaction with the respiratory chain of heart mitochondria. Biochemistry 39:6660–6668
Ghidoni R, Sala G, Giuliani A (1999) Use of sphingolipid analogs: benefits and risks. Biochim Biophys Acta 1439:17–39
Goni FM, Alonso A (2009) Effects of ceramide and other simple sphingolipids on membrane lateral structure. Biochim Biophys Acta 1788:169–177
Grassme H, Jendrossek V, Bock J, Riehle A, Gulbins E (2002) Ceramide-rich membrane rafts mediate CD40 clustering. J Immunol 168:298–307
Grassme H, Cremesti A, Kolesnick R, Gulbins E (2003) Ceramide-mediated clustering is required for CD95-DISC formation. Oncogene 22:5457–5470
Grassme H, Riethmuller J, Gulbins E (2007) Biological aspects of ceramide-enriched membrane domains. Prog Lipid Res 46:161–170
Guarino AJ, Lee SP, Wrenn SP (2005) Interactions between sphingomyelin and cholesterol in low density lipoproteins and model membranes. J Colloid Interface Sci 293:203–212
Hannun YA, Obeid LM (2002) The ceramide-centric universe of lipid-mediated cell regulation: stress encounters of the lipid kind. J Biol Chem 277:25847–25850
Holopainen JM, Lehtonen JY, Kinnunen PK (1997) Lipid microdomains in dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine-ceramide liposomes. Chem Phys Lipids 88:1–13
Holopainen JM, Subramanian M, Kinnunen PK (1998) Sphingomyelinase induces lipid microdomain formation in a fluid phosphatidylcholine/sphingomyelin membrane. Biochemistry 37:17562–17570
Holopainen JM, Angelova MI, Kinnunen PK (2000a) Vectorial budding of vesicles by asymmetrical enzymatic formation of ceramide in giant liposomes. Biophys J 78:830–838
Holopainen JM, Lemmich J, Richter F, Mouritsen OG, Rapp G, Kinnunen PK (2000b) Dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine/C16:0-ceramide binary liposomes studied by differential scanning calorimetry and wide- and small-angle x-ray scattering. Biophys J 78:2459–2469
Holopainen JM, Brockman HL, Brown RE, Kinnunen PK (2001) Interfacial interactions of ceramide with dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine: impact of the N-acyl chain. Biophys J 80:765–775
Huang HW, Goldberg EM, Zidovetzki R (1998) Ceramides perturb the structure of phosphatidylcholine bilayers and modulate the activity of phospholipase A2. Eur Biophys J 27:361–366
Ira, Johnston LJ (2008) Sphingomyelinase generation of ceramide promotes clustering of nanoscale domains in supported bilayer membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1778:185–197
Ira, Zou S, Ramirez DM, Vanderlip S, Ogilvie W, Jakubek ZJ, Johnston LJ (2009) Enzymatic generation of ceramide induces membrane restructuring: correlated AFM and fluorescence imaging of supported bilayers. J Struct Biol 168:78–89
Kolesnick R (2002) The therapeutic potential of modulating the ceramide/sphingomyelin pathway. J Clin Invest 110:3–8
Kolesnick RN, Goni FM, Alonso A (2000) Compartmentalization of ceramide signaling: physical foundations and biological effects. J Cell Physiol 184:285–300
Koumanov K, Wolf C, Bereziat G (1997) Modulation of human type II secretory phospholipase A2 by sphingomyelin and annexin VI. Biochem J 326(Pt 1):227–233
Koumanov KS, Quinn PJ, Bereziat G, Wolf C (1998) Cholesterol relieves the inhibitory effect of sphingomyelin on type II secretory phospholipase A2. Biochem J 336(Pt 3):625–630
Koumanov KS, Momchilova AB, Quinn PJ, Wolf C (2002) Ceramides increase the activity of the secretory phospholipase A2 and alter its fatty acid specificity. Biochem J 363:45–51
Kuikka M, Ramstedt B, Ohvo-Rekilä H, Tuuf J, Slotte JP (2001) Membrane properties of D-erythro-N-acyl sphingomyelins and their corresponding dihydro species. Biophys J 80:2327–2337
Lange Y, Ye J, Steck TL (2005) Activation of membrane cholesterol by displacement from phospholipids. J Biol Chem 280:36126–36131
Laviad EL, Albee L, Pankova-Kholmyansky I, Epstein S, Park H, Merrill AH Jr, Futerman AH (2008) Characterization of ceramide synthase 2: tissue distribution, substrate specificity, and inhibition by sphingosine 1-phosphate. J Biol Chem 283:5677–5684
Massey JB (2001) Interaction of ceramides with phosphatidylcholine, sphingomyelin and sphingomyelin/cholesterol bilayers. Biochim Biophys Acta 1510:167–184
Megha, London E (2004) Ceramide selectively displaces cholesterol from ordered lipid domains (rafts): implications for lipid raft structure and function. J Biol Chem 279:9997–10004
Megha, Sawatzki P, Kolter T, Bittman R, London E (2007) Effect of ceramide N-acyl chain and polar headgroup structure on the properties of ordered lipid domains (lipid rafts). Biochim Biophys Acta 1768:2205–2212
Montes LR, Ruiz-Arguello MB, Goni FM, Alonso A (2002) Membrane restructuring via ceramide results in enhanced solute efflux. J Biol Chem 277:11788–11794
Montes LR, Goni FM, Johnston NC, Goldfine H, Alonso A (2004) Membrane fusion induced by the catalytic activity of a phospholipase C/sphingomyelinase from Listeria monocytogenes. Biochemistry 43:3688–3695
Nybond S, Bjorkqvist YJ, Ramstedt B, Slotte JP (2005) Acyl chain length affects ceramide action on sterol/sphingomyelin-rich domains. Biochim Biophys Acta 1718:61–66
Nyholm TKM, Nylund M, Slotte JP (2003) A calorimetric study of binary mixtures of dihydrosphingomyelin and sterols, sphingomyelin, or phosphatidylcholine. Biophys J 84:3138–3146
Pewzner-Jung Y, Ben-Dor S, Futerman AH (2006) When do Lasses (longevity assurance genes) become CerS (ceramide synthases)?: insights into the regulation of ceramide synthesis. J Biol Chem 281:25001–25005
Pinto SN, Silva LC, de Almeida RF, Prieto M (2008) Membrane domain formation, interdigitation, and morphological alterations induced by the very long chain asymmetric C24:1 ceramide. Biophys J 95:2867–2879
Popov J, Vobornik D, Coban O, Keating E, Miller D, Francis J, Petersen NO, Johnston LJ (2008) Chemical mapping of ceramide distribution in sphingomyelin-rich domains in monolayers. Langmuir 24:13502–13508
Ramstedt B, Slotte JP (1999) Comparison of the biophysical properties of racemic and d-erythro-N-acyl sphingomyelins. Biophys J 77:1498–1506
Ruiz-Arguello MB, Basanez G, Goni FM, Alonso A (1996) Different effects of enzyme-generated ceramides and diacylglycerols in phospholipid membrane fusion and leakage. J Biol Chem 271:26616–26621
Ruiz-Arguello MB, Goni FM, Alonso A (1998) Vesicle membrane fusion induced by the concerted activities of sphingomyelinase and phospholipase C. J Biol Chem 273:22977–22982
Seumois G, Fillet M, Gillet L, Faccinetto C, Desmet C, Francois C, Dewals B, Oury C, Vanderplasschen A, Lekeux P, Bureau F (2007) De novo C16- and C24-ceramide generation contributes to spontaneous neutrophil apoptosis. J Leukoc Biol 81:1477–1486
Shabbits JA, Mayer LD (2003) Intracellular delivery of ceramide lipids via liposomes enhances apoptosis in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta 1612:98–106
Shah J, Atienza JM, Duclos RI Jr, Rawlings AV, Dong Z, Shipley GG (1995) Structural and thermotropic properties of synthetic C16:0 (palmitoyl) ceramide: effect of hydration. J Lipid Res 36:1936–1944
Silva L, de Almeida RF, Fedorov A, Matos AP, Prieto M (2006a) Ceramide-platform formation and -induced biophysical changes in a fluid phospholipid membrane. Mol Membr Biol 23:137–148
Silva LC, de Almeida RF, Castro BM, Fedorov A, Prieto MJ (2006b) Ceramide-domain formation and collapse in lipid rafts: membrane reorganization by an apoptotic lipid. Biophys J 92:502–516
Siskind LJ, Colombini M (2000) The lipids C2- and C16-ceramide form large stable channels. J Biol Chem 275:38640–38644
Sot J, Aranda FJ, Collado MI, Goni FM, Alonso A (2005a) Different effects of long- and short-chain ceramides on the gel-fluid and lamellar-hexagonal transitions of phospholipids. A calorimetric, NMR and X-ray diffraction study. Biophys J 88:3368–3380
Sot J, Goni FM, Alonso A (2005b) Molecular associations and surface-active properties of short- and long-N-acyl chain ceramides. Biochim Biophys Acta 1711:12–19
Sot J, Bagatolli LA, Goni FM, Alonso A (2006) Detergent-resistant, ceramide-enriched domains in sphingomyelin/ceramide bilayers. Biophys J 90:903–914
Staneva G, Chachaty C, Wolf C, Koumanov K, Quinn PJ (2008) The role of sphingomyelin in regulating phase coexistence in complex lipid model membranes: competition between ceramide and cholesterol. Biochim Biophys Acta 1778:2727–2739
Staneva G, Momchilova A, Wolf C, Quinn PJ, Koumanov K (2009) Membrane microdomains: role of ceramides in the maintenance of their structure and functions. Biochim Biophys Acta 1788:666–675
Taha TA, Mullen TD, Obeid LM (2006) A house divided: ceramide, sphingosine, and sphingosine-1-phosphate in programmed cell death. Biochim Biophys Acta 1758:2027–2036
Veiga MP, Arrondo JL, Goni FM, Alonso A (1999) Ceramides in phospholipid membranes: effects on bilayer stability and transition to nonlamellar phases. Biophys J 76:342–350
Wang TY, Silvius JR (2003) Sphingolipid partitioning into ordered domains in cholesterol-free and cholesterol-containing lipid bilayers. Biophys J 84:367–378
Yu C, Alterman M, Dobrowsky RT (2005) Ceramide displaces cholesterol from lipid rafts and decreases the association of the cholesterol binding protein caveolin-1. J Lipid Res 46:1678–1691
Zhang Y, Li X, Becker KA, Gulbins E (2009) Ceramide-enriched membrane domains–structure and function. Biochim Biophys Acta 1788:178–183
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr Thomas Nyholm for constructive comments on the manuscript. This study was supported by the Academy of Finland, the Sigrid Juselius foundation, the Åbo Akademi foundation, the K. Albin Johansson foundation, the Magnus Ehrnrooth foundation, Kommersrådet Otto A. Malms donationsfond and Medicinska Understödsföreningen Liv och Hälsa. The work of Y.J.E. Björkqvist was supported by the National Graduate School in Informational and Structural Biology at Åbo Akademi University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Y. J. E. Isaksson: Née Björkqvist.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Westerlund, B., Grandell, PM., Isaksson, Y.J.E. et al. Ceramide acyl chain length markedly influences miscibility with palmitoyl sphingomyelin in bilayer membranes. Eur Biophys J 39, 1117–1128 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-009-0562-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-009-0562-6