Abstract
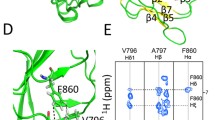
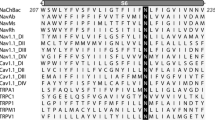
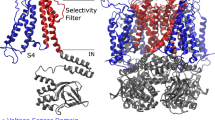
The functional role of the large intracellular regions (which include the cyclic nucleotide binding domain, cNBD, and the Per-Arnt-Sim domain, PAS) in the herg channel is not well understood. We have studied possible interactions of the cNBD with other parts of the channel protein using lysine mutations to disrupt such interactions. Some lysine mutations caused significant right shifts in the voltage dependence of inactivation; almost all the mutants caused speeding up of deactivation time course. In a homology model of the cNBD, lysine mutations that affected both inactivation and deactivation lie in a hydrophobic band on the surface of the structure of this domain. Some known mutations in the Long QT Syndrome type 2, with effects on deactivation, are located at residues close to hydrophobic bands on the cNBD and the PAS domains. Such bands of residues in these intracellular domains may play an important part in channel function.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bracey K, Wray D (2006) Inherited disorders of ion channels. In: Voltage-gated ion channels as drug targets. Wiley, New York, pp 381–427
Morais Cabral JH, Lee A, Cohen SL, Chait BT, Li M, Mackinnon R (1998) Crystal structure and functional analysis of the HERG potassium channel N terminus: a eukaryotic PAS domain. Cell 95:649–655. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81635-9
Chen J, Zou A, Splawski, Keating M, Sanguinetti MC (1999) Long QT syndrome-associated mutations in the Per-Arnt-Sim (PAS) domain of HERG potassium channels accelerate channel deactivation. J Biol Chem 274:10113–10118. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.15.10113
Clayton GM, Silverman WR, Heginbotham L, Morais-Cabral JH (2004) Structural basis of ligand activation in a cyclic nucleotide regulated potassium channel. Cell 119:615–627. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2004.10.030
Ferrer T, Rupp J, Piper DR, Tristani-Firouzi M (2006) The S4-S5 linker directly couples voltage sensor movement to the activation gate in the human ether-a-go-go-related gene (hERG) K+ channel. J Biol Chem 281:12858–12864. doi:10.1074/jbc.M513518200
Finlayson K, Witchel HJ, McCulloch Starkey J (2004) Acquired QT interval prolongation and HERG: implications for drug discovery and development. Eur J Pharmacol 500:129–142. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2004.07.019
Ju M, Wray D (2006) Molecular regions responsible for differences in activation between heag channels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 342:1088–1097. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.02.062
Kobori A, Sarai N, Shimizu W, Nakamura Y, Murakami Y, Makiyama T, Ohno S, Takenaka K, Ninomiya T, Fujiwara Y, Matsuoka S, Takano M, Noma A, Kita T, Horie M (2004) Additional gene variants reduce effectiveness of beta-blockers in the LQT1 form of long QT syndrome. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 15:190–199. doi:10.1046/j.1540-8167.2004.03212.x
Lehmann-Horn F, Jurkat-Rott K (1999) Voltage-gated ion channels and hereditary disease. Physiol Rev 79(4):1317–1372
Li-Smerina Y, Swartza KJ (2001) Helical structure of the COOH terminus of S3 and its contribution to the gating modifier toxin receptor in voltage-gated ion channels. J Gen Physiol 117:205–217. doi:10.1085/jgp.117.3.205
McPate MJ, Duncan RS, Milnes JT, Witchel HJ, Hancox JC (2005) The N588K-HERG K+ channel mutation in the ‘short QT syndrome’: Mechanism of gain-in-function determined at 37°C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 334:441–449. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.06.112
Moss AJ, Zareba W, Kaufman ES, Gartman E, Peterson DR, Benhorin J, Towbin JA, Keating MT, Priori SG, Schwartz PJ, Vincent GM, Robinson JL, Andrews ML, Feng C, Hall WJ, Medina A, Zhang L, Wang Z (2002) Increased risk of arrhythmic events in long-QT syndrome with mutations in the pore region of the human ether-a-go-go–related gene potassium channel. Circulation 105:794–799. doi:10.1161/hc0702.105124
Numaguchi H, Mullins FM, Johnson JP, Johns DC, Po SS, Yang ICH, Tomaselli GF, Balser JR (2000) Probing the interaction between inactivation gating and Dd-sotalol block of HERG. Circ Res 87:1012–1018
Paulussen A, Raes A, Matthijs G, Snyders DJ, Cohen N, Aerssens J (2002) HERG mutation predicts short QT based on channel kinetics but causes long QT by heterotetrameric trafficking deficiency. J Biol Chem 277:48610–48616. doi:10.1074/jbc.M206569200
Piper DR, Varghese A, Sanguinetti MC, Tristani-Firouzi M (2003) Gating currents associated with intramembrane charge displacement in HERG potassium channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:10534–10539. doi:10.1073/pnas.1832721100
Rossenbacker T, Mubagwa K, Jongbloed RJ, Vereecke J, Devriendt K, Gewillig M, Carmeliet E, Collen D, Heidbüchel H, Carmeliet P (2005) Novel mutation in the per-arnt-sim Domain of KCNH2 causes a malignant form of long-QT syndrome. Circulation 111:961–968. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000156327.35255.D8
Sanguinetti MC, Xu QP (1999) Mutations of the S4-S5 linker alter activation properties of HERG potassium channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes. J Physiol 514:667–675. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7793.1999.667ad.x
Sanguinetti MC, Jiang C, Curran ME, Keating MT (1995) A mechanistic link between an inherited and an acquired cardiac arrhythmia. Cell 21 81(2):299–307
Sine SM, Wang HL, Bren N (2002) Lysine scanning mutagenesis delineates structural model of the nicotinic receptor ligand binding domain. J Biol Chem 277:29210–29223. doi:10.1074/jbc.M203396200
Terlau H, Heinemann SH, Stuhmer W, Pongs O, Ludwig J (1997) Amino terminal-dependent gating of the potassium channel rat eag is compensated by a mutation in the S4 segment. J Physiol 502:537–543. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7793.1997.537bj.x
Torres AM, Bansal PS, Sunde M, Clarke CE, Bursill JA, Smith DJ, Bauskin A, Breit SN, Campbell TJ, Alewood PF, Kuchel PW, Vandenberg JI (2003) Structure of the HERG K+ channel S5-P extracellular linker: role of an amphipathic alphahelix in C-type inactivation. J Biol Chem 278:42136–42148. doi:10.1074/jbc.M212824200
Tseng GN (2001) I(Kr): the hERG channel. J Mol Cell Cardiol 33:835–849. doi:10.1006/jmcc.2000.1317
Vandenberg JI, Torres AM, Campbell TJ, Kuchel PW (2004) The hERG K+ channel: progress in understanding the molecular basis of its unusual gating kinetics. Eur Biophys J 33:89–97. doi:10.1007/s00249-004-0419-y
Wang J, Trudeau MC, Zappia AM, Robertson GA (1998) Regulation of deactivation by an amino terminal domain in human ether-à-go-go-related gene potassium channels. J Gen Physiol 112:637–647. doi:10.1085/jgp.112.5.637
Warmke JW, Ganetzky B (1994) A family of potassium channel genes related to eag in Drosophila and mammals. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:3438–3442. doi:10.1073/pnas.91.8.3438
Wray D (2008) Intracellular regions of potassium channels: Kv2.1 and heag. Eur Biophys J. doi:10.1007/s00249-008-0354-4
Wu P, Wang P (2004) Per-Arnt-Sim domain-dependent association of cAMP-phosphodiesterase 8A1 with IκB proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:17634–17639. doi:10.1073/pnas.0407649101
Yang P, Kanki H, Drolet B, Yang T, Wei J, Viswanathan PC, Hohnloser SH, Shimizu W, Schwartz PJ, Stanton M, Murray KT, Norris K, George AL Jr, Roden DM (2002) Allelic variants in long-QT disease genes in patients with drug-associated torsades de pointes. Circulation 105:1943–1948. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000014448.19052.4C
Yusaf SP, Wray D, Sivaprasadarao A (1996) Measurement of the movement of the S4 segment during the activation of a voltage-gated potassium channel. Pflugers Arch 433:91–97. doi:10.1007/s004240050253
Zagotta WN, Olivier NB, Black KD, Young EC, Olson R, Gouaux E (2003) Structural basis for modulation and agonist specificity of HCN pacemaker channels. Nature 425:200–205. doi:10.1038/nature01922
Zhulin IB, Taylor BL, Dixon R (1997) PAS domain S-boxes in archaea, bacteria and sensors for oxygen and redox. Trends Biochem Sci 22:331–333. doi:10.1016/S0968-0004(97)01110-9
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a project grant to DW from the British Heart Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Owais, M., Bracey, K. & Wray, D. Role of intracellular domains in the function of the herg potassium channel. Eur Biophys J 38, 569–576 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-009-0408-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-009-0408-2